Upper limb
description
Transcript of Upper limb

UPPER LIMB POSITIONING
By: Dr Kushagra V
Garg

Clavicle

Scapula


Scapula

Scapula

Humerus

Sternoclavicular Joint (SC)

Acromioclavicular Joint (AC)

Glenohumeral Joint (GH)

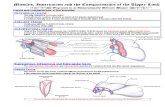
Upper extremity consists of:
Phalanges Metacarpals Carpals Radius Ulna Humerus

View for clavicle
PA AP Inferosuperior

Postero-anterior – erect (basic)
Prone or upright Ant aspect towards the
cassette Arm should be in neutral
position Perpendicular to midclavicle According to the size of the
patient tailor-made angulation can be given



Antero-posterior – supine


Infero-superior forward-angulation of the
cassette of 15 degrees towards the shoulder
Unaffected side is slightly raised CR is given 30 degree
angulation to throw the clavicle away from the bony thorax
Clavicle should be horizontal


Infero-superior – supine
Patient is supine A NRO sponge supports the
arm under investigation The cassette is given 20-25
degree angulation and tube is given 45 degree of cranial angulation
Centering is at the mid of clavicle


Sternoclavicular jointsPostero-anterior oblique (basic)

Postero-anterior
Both SC jts are included

Semi-prone

Cross Table Lateral

Scapula(AP)
Supine or erect Affected scapula towards
the IR Forearm semi flexed IR should be 5 cms above
the shoulder CR centered at the mid of
the film with centering at the head of humerus


Scapula Y view
supine or upright Post surface of the body towards plate Affected arm in neutral position Turn the patient 30 degree away Central rays perpendicular to gh Possible dislocation of head of humerus



AC joint AP
Upright with arms on the sides
B/L image with and without stress
Central ray perpendicular to midpoint B/W the two ac joints
Rotation should be checked by sc joints
To demonstrate dislocations and subluxation



Shoulder AP(NR)
supine or upright Post surface of the body
towards plate Affected arm on patients
side CR perpendicular to
coracoid process #,dis.,tendon and lig
dam.,cyst and tumors


Shoulder AP (ER)
supine or upright Post surface of the body
towards plate Affected arm on patients
side IC line Parallel to image
receptor CR perpendicular to
coracoid process greater tubercle on the
lateral aspect


Shoulder joint ap(ir)
supine or upright Post surface of the body towards plate Affected arm on patients side IC line Perpendicular to image receptor CR perpendicular to coracoid process Lesser tubercle on the medial aspect


Shoulder inferosuperior(lawrence method) Supine IR Perpendicular to table Abduct the affected arm by
90 Neck away Non opaque sponge under
the shoulder CR horizontal towards the
axilla exit at AC joint LT superiorly GH should be clear


Shoulder inferosuperior(WEST Point method)
Supine IR Perpendicular to table Abduct the affected arm by
90 Neck away Non opaque sponge under
the shoulder CR 25 degree up and medial
to horizontal towards the axilla exit at AC joint
LT superiorly Coracoid process should not
be over the humeral head GH should be clearly
demonstrated


Clements modification

Shoulder joint AP axial Coracoid process
Supine or upright Affected arm resting on the
side Hand supinated CR 30 degree cephalad and
directed towards coracoid process
coracoid process elongated and superimposed on clavicle slightly


Shoulder glenoid cavity(grashey method)
Supine or upright Forearm resting on the chest 35 to 45 degree turn on the
affected side Scapula parallel to IR LPO for left side and vice a
versa CR perpendicular to gh Dislocation of head of
humerus Superimposition of humeral
head should not be there


Humerus(AP)
Supine or upright Fully extend the elbow Hand rest on the side IC line should be parallel to
the IR


supine or upright Flex the elbow and medially
rotate the arm IC perpendicular to IR Include both shoulder and
elbow joint CR perpendicular to
midshaft of humerus Epicondyles should be
overlapping each other LT on the medial aspect


Humerus transthoracic lat position(lawrence method)
Upright and affected Affected arm in neutral
position IR should be above the
shoulder CR horizontal and
perpendicular to the midshaft of affected humerus
NOTE :patient should breath normally
Proximal 2/3rd of humerus and GH should be demonstrated


References
Clarks radiographic positioning Radiographic positioning by greathouse Radiopedia Learning radiology Valuable inputs by my seniors and
professors

On public demand torticollisThank You