Unit 5 Ancient Greece. Ch. 25 The Geography and Settlement of Greece.
-
Upload
cornelius-carroll -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Unit 5 Ancient Greece. Ch. 25 The Geography and Settlement of Greece.

Unit 5
Ancient Greece

Ch. 25 The Geography and Settlement of Greece

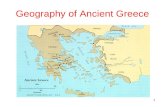
25.1 Introduction1. What are the mountains
in Greece like?
• Steep and rocky
2. Why was the sea important?
• Trade• Establish colonies

25.2 Isolated Communities and the Difficulties of Travel
1. Why were ancient Greek communities isolated from one another?
• Mountains made travel and communication difficult
2. What were some of the dangers of travel?
• Land - bandits & broken wheels• Sea – pirates & storms

25.3 Farming 1. Crops and animals they raised.
• Wheat, barley, grapes, olives, vegetables, fruit, nuts
• Sheep, goats, pigs, chickens, bees, ox, mules/donkeys
2. Why did settlements fight?
• Shortage of land

25.4 Starting Colonies 1. Why did they start colonies?• Needed more farmland (to grow
more food…to feed the increasingpopulation).
2. Steps to start a new colony.• Oracle (holy person believed to communicate
with the gods)• Food and supplies• Sacred flame• Sea voyage• Found good farmland and harbors• Established

25.5 Trading 1. Why did some settlements trade?
• To get needed goods
2. What products from the Greek mainland were traded?
• Olive oil, pottery, wine What did they get in exchange?
• Grain, timber, metal