THE THREE TYPES OF ROCKS (Lets Rock N Roll)
-
Upload
cyra-mae-soreda -
Category
Education
-
view
176 -
download
0
Transcript of THE THREE TYPES OF ROCKS (Lets Rock N Roll)

Specific Learning OutcomesAt the end of the lesson, I will be able to:
a. I can identify and describe the three basic rock types;b. I can describe how and define what type of environment
each of these rock types are formed;c. I can describe how rocks are transformed from one rock
type to another through the rock cycle;d. I can identify and describe the different geologic
processes that operate within the rock cycle.

8 ELEMENTS comprising almost 99% of the minerals making up the Earth’s crust.

■ Approximately 85% of the Earth's crust is composed of oxygen and silicon. Together they form the silicon oxygen tetrahedron, which is the basic building block of silicate minerals.
■ Silicates are also termed as (common) rock forming minerals.
- ROCKS are an aggregate of minerals. A rock can be composed of a single mineral (e.g. Quartzite is a metamorphic rock composed predominantly of Quartz) or more commonly composed of an aggregate of two or more minerals.
Can a name of a mineral be also used as a rock name?

Show a video of the different rock types.3 Types of Rocks.mp4
How can we classify rocks? Would it be by color, hardness, texture, density or other physical properties? Is it by chemical composition?

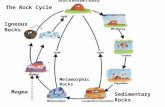
1. IGNEOUS ROCKS• these are rocks that are derived from the cooling
and solidification of magma or lava• from solidified molten rock materials, usually
hard and crystalline• rate of cooling as one of the most important
factors that control crystal size• solidification can occur along the surface of the
earth or beneath the surface of the earth

MAGMA VS LAVA• Magma is a molten rock material beneath the surface of the earth.• Lava is molten rock material extruded to the surface of the earth through a central vent (volcano) or as fissure eruption.

1. Plutonic or Intrusive Rocks from solidified magma underneath the earth gradual lowering of temperature is indicated
by the movement of magma from depth to surface
causing slow cooling /crystallization Phaneritic textures
Forms large interlocking crystals from cooling Examples: granite, diorite, gabbro
2 TYPES OF IGNEOUS ROCKS

2. Volcanic or Extrusive Rocks from solidified lava at or near the surface of the earth fast rate of cooling/crystallization due to huge variance
in the temperature between Earth’s surface and underneath
common textures: aphanitic, porphyritic (define groundmass vs phenocrysts), vesicular Porphyritic texture: formed through two stages of
crystallization where in magma partly cooled below the surface of the earth providing time for the large crystals to grow (phenocrysts) before it is extruded to the surface forming the fine-grained matrix (groundmass).
Aphanitic texture: fine-grained texture; minerals not visible to the naked eye; relatively fast rates of cooling/ solidification prevent the formation of large crystals.
Vesicular texture: voids created by rapid cooling which causes air bubbles to be trapped inside.

examples: rhyolite, andesite, basalt
pyroclastic rocks: fragmental rocks usually associated with violent or explosive type of eruption.
Examples tuff and pyroclastic flow deposits (ignimbrite)

Common intrusive rocks with their extrusive counterparts
GRANITE RHYOLITE

DIORITE ANDESITE

GABBRO BASALT



Igneous rocks are also classified according to silica content and relative amounts of K, Na, Fe, Mg and Ca. They can be classified as felsic, intermediate, mafic and ultramafic, practically based on presence of light and dark colored minerals. The relatively dark minerals are olivine, pyroxene, hornblende and biotite. The relatively light colored minerals are plagioclases, K-feldspars, quartz and muscovite.

FELSIC: granitic: >65% silica, generally light-colored
INTERMEDIATE: andesitic: 55-65% silica, generally medium colored (medium gray)
MAFIC: basaltic: 45-55% silica, usually dark colored
ULTRAMAFIC: <45% silica, generally very dark colored


2. SEDIMENTARY ROCKS• these are rocks that are formed at or near the surface of the Earth• sedimentary processes include:
1. weathering of rocks2. erosion3. deposition 4. compaction 5. Cementation
• Sediment are fragments of rock that have been broken down as a result of weathering



COMMON SEDIMENTARY FEATURES
1. fossil assemblages remains and traces of plants and animals that are preserved in
rocks
2. Stratification stratification or layering (strata which is >1cm is called bedding
and < 1cm is called lamination): layering is the result of a change in grain size and composition;
each layer represents a distinct period of deposition

Photo of the Kapurpurawan Formation located at the coastal town of Burgos, Ilocos Norte, courtesy of riderako.com. Shows series of sedimentary strata





TWO TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY
ROCKS

1. Clastic sedimentary rocks■Inorganic land derived sedimentary rocks■Clastic sedimentary rocks form by
weathering processes which break down rocks into pebble, sand, or clay particles by exposure to wind, ice, and water.
■Compacted and cemented sediments■Clastic sedimentary rocks are named
according to the grain size of the sediment particles








2. Non-clastic sedimentary rocks■Organic or crystalline■Nonclastic sedimentary rocks form from
chemical reactions, chiefly in the ocean.■Nonclastic sedimentary rocks are named
according to the mineral present.■classified as evaporites (halite, gypsum and
dolostone), precipitates (limestone) and bioclastics (coal, coquina)

– Evaporites: rocks formed from the evaporation of water leaving the dissolved minerals to crystallize
– Precipitates: rocks formed when minerals from a mineral supersaturated waters start to crystallize at the bottom of the solution
– Bioclastic: rock formed from compacted organic matter





Bioclastic: rock formed from compacted organic matter



Sedimentary rocks are the only type of rocks that may contain fossils, or evidence
of past life.


METAMORPHIC ROCKS• formed below the surface of the earth through the process of metamorphism with the recrystallization of minerals in rocks due to changes in pressure and temperature conditions• contact and regional metamorphism

1. CONTACT METAMORPHISM■HEAT AND REACTIVE FLUIDS as main factors:
occurs when a pre-existing rock gets in contact with magma which is the source of heat and magmatic fluids where metamorphic transformations occur around the contact / metamorphic aureole of the intruding magma and the rock layers.
■The aureole occurs on different scales depending on the sizes of the intruding magma and the amount of water in the intruded rocks and the reactive fluids coming from the magma.
■creates non-foliated metamorphic rocks■example: hornfels



2. REGIONAL METAMORPHISM■PRESSURE as main factor: occurs in areas that
have undergone considerable amount of mechanical deformation and chemical recrystallization
■occurs in a regional/large scale ■creates foliated metamorphic rocks■examples: schist, gneiss■non-foliated rocks like marble also form through
regional metamorphism, where pressure is not intense, far from the main geologic event


Common Metamorphic Rocks.

THANK YOU FOR
LISTENING!

Concept Mapping – Types of RocksEach group will fill up the chart which correspond to the list of words provided to choose from. When done, the group leaders will present their work to class.



VIDEO SUMMARY
■Igneous Rocks.mp4■Sedimentary Rocks.mp4■Metamorphic Rocks.mp4

Evaluation (20 mins)
1 whole sheet of paper

1. How does a vesicular texture in a volcanic rock develop?2. How do clastic rocks differ from non-clastic rocks in terms of process
of formation?3. Explain how the physical features of sediments change during
transport.4. Differentiate between a foliated and non-foliated rock.5. What do butterflies and metamorphic rocks have in common?6. Heat is a major agent in metamorphism and igneous rock formation,
but not in sedimentary rocks. Why?7. Does every rock go through the complete rock cycle, i.e. changing
from igneous to sedimentary rock to metamorphic then back to igneous rocks? Explain.

Homework to be submitted on next meeting on a 1 whole sheet of paper. Each student will research on 3 rocks (one for each rock type). Include in the discussion the following:1. common environment of formation2. common textures3. common use of the rock










![How to be a rock star CMO? Adding rocks to the roll [sic] of the CMO](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/55c3a30abb61eb3d338b45fd/how-to-be-a-rock-star-cmo-adding-rocks-to-the-roll-sic-of-the-cmo.jpg)






