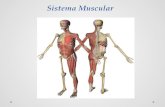
The Muscular System Week 6 Seminar Presented by Dr. Carlene Graham.
-
Upload
stephen-washington -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of The Muscular System Week 6 Seminar Presented by Dr. Carlene Graham.

The Muscular System
Week 6 Seminar
Presented by
Dr. Carlene Graham

SKELETAL MUSCLE GROUPS
2Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscles of the Head and Neck
Provide facial expressions• Raising the eyebrows
• Closing an eye
• Puckering the lips
Assisting with chewing movement
Flex, extend, and rotate head and shoulders
3Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

04/21/23 Dr. C. Graham 4
Facial MusclesSee page 169

Muscle groups upper bodyAnterior
Pectoralis major
Deltoid
Bicep brachii
5Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscle groups upper bodyPosterior
Latissimus brachii
Triceps brachii
6Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscles of the trunk
External oblique Rectus abdominis Internal oblique Serratus Transverse abdominis
7Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscles of the lower extremitiesAnterior Posterior Vastus lateralis Fibularus longus & brevis Vastus medialis Pectineus Rectus femoris Tibialis anterior Lliopsoas Adductor longus Sartorius
Gluteus maximus Semimembranosus Gracillis Semitendinous Adductor magnus Gastrocnemius Bicep femoris Soleus
8Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

04/21/23 Dr. C. Graham 9

Muscle Names - Size
Vastus — means huge (vast) Maximus – means large
(maximum) Minimus – means small (minimum
Can you name any muscle group with these names?
10Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Vastus,Maximus & Minimus
The Vastus lateralis is the largest part of the Quadriceps femoris. (page 166)
Gluteus maximus larges tof the gluteal muscles
The gluteus minimus, the smallest of the three gluteal muscles, is situated immediately beneath the gluteus medius.
04/21/23 Dr. C. Graham 11

VASTUS MUSCLES
04/21/23 Dr. C. Graham 12

Muscle Names – Shape
Deltoid – means Triangular (see page 167, shoulder muscle)
Latissimus – means wide (see page 167)
13Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscle Name–Direction of fibers
Rectus – means straight (rectus abdominis, “6-pack” in the abdomen – page 166).
Transverse – means across – (sternocleidomastoid – page 169)
Oblique – means diagonal (external abdominal oblique, page 167).
Circularis – means circular (orbicularis occuli and orbicularis oris, page 169).
14Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscle name - Location
Pectoralis – means chestPectoralis major
Gluteus – means buttockGluteus maximus
Brachii – means armBiceps brachii & Triceps brachii
See pages 166 & 167
15Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscle name – Number of origin
Biceps (bi means 2) anchored to 2 sites.
Tricep (tri means 3) anchored to 3 sites.
Quadriceps (quad means 4) anchored to 4 sites
16Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscle name - Action
Abductor – moves away from the midline
The abductor pollicis
brevis is a muscle in
the hand that functions
as an abductor of
the thumb.
17Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscle name - Action
Adductor – moves toward midline
18Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscle name - Action
Flexor –means muscle
flexes a limb.
Example:
Opening and closing
the fist.
19Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscle name - Action
Extensor –means muscle extends a limb.
Example: Extending your arms over your head.
20Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Muscle name - Action
Elevator – means muscle lifts a limb.
For example:The Mandibular elevator muscle of the jaw that facilitates chewing.
ACTIVITY: Pinch your upper lip (just below your nose) and pull upward.
That was another elevator muscle!
21Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES
22Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

MOVEMENT
Skeletal movement is produced by muscular contraction and is voluntary, involving:
The prime mover that is responsible for producing a particular movement.
In synergy (combination with) with the prime mover to produce movement.
As an antagonist working in opposition with the prime mover and synergist.
23Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

POSTURE/MUSCLE TONE
It is normal for the muscles to retain a partial state of contraction.
This enables the body part to remain in the position that favors proper function.
24Dr. C. Graham04/21/23

Maintenance of body Temperature
Most of the heat necessary to maintain the body temperature comes from the heat produced when the muscle fiber contracts.
25Dr. C. Graham04/21/23