Static cone penetration test-basics
-
Upload
discorajan -
Category
Education
-
view
1.074 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Static cone penetration test-basics

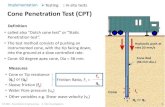
STATIC CONE PENETRATION TEST

INTRODUCTION
Cone
Sleeve
Driving force
Procedure
Interpretation of results

CONE (DUTCH CONE)
Base area = 10 cm2
Apex angle = 600
To measure tip resistance
Related to un-drained shear strength

CONE
Diameter = 35.7 < d < 36 (mm)
Cone height = 31 < hc < 31.3 (mm)
Cylindrical extension = 4.5 < he <
5.5 (mm)

CONE (10 cm2)

CONE (15 cm2)

CYLINDRICAL SLEEVE
Area = 150 cm2
Height ~ 13.4 cm
To measure frictional resistance

PROCEDURE
Cone pushed @ 10
mm/sec (35 mm)(Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engg:
Dr:K R Arora)
Cone withdrawn &
sleeve pushed on to
the cone and driven
together.

CONE PENETROMETER

HAND OPERATED (30kN)

ENGINE OPERATED (200kN)

CPT LOG
hyperlink.pdf

ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES
Speed
Economy
Detailed & precise
data
Soil sample not
obtained
Depth limited
Most useful in
coarser,
permeable soils ie:
sands