Cellular Structure and Function 7.1 Cell Discovery and Theory 7.2 The Plasma Membrane.
Plasma Membrane Structure and Role in Cellular Transport.
-
Upload
marcia-reeves -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
0
Transcript of Plasma Membrane Structure and Role in Cellular Transport.

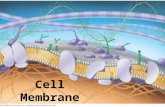
Plasma Membrane
Structure and Role in Cellular Transport

Membrane Structure
• Phospholipid bilayer• Protein• Fluid Mosaic Model• Hydrophobic• Hydrophylic

Membrane Proteins
• Transport• Enzyme• Signal transduction• Cell recognition• Cell joining• Attachment to
cytoskeleton and ECM

External to Plasma Membrane
• Prokaryote– Cell wall– Peptidoglycan
• Plant Cell– Cell wall– Cellulose
• Animal Cell– Extra Cellular Matrix

Extracellular Matrix
• Integrin• Fibronectin• Collagen• Proteoglycan• Microfilaments

Cell Junctions
• Tight Junction– Seal– actin
• Adherens junction– Cytoskeleton to ECM– Actin– integrin
• Desmosome– Rivet like– keratin

Transport
• Passive– Diffusion– Osmosis– Facilitated diffusion
• Active– Pump
• Bulk– Endocytosis– exocytosis

Diffusion
• Solute moves• Net movement down
a concentration gradient
• Endpoint equilibrium• Oxygen• Carbon dioxide

Osmosis
• Solvent moves• Requires a semi
permeable membrane• Concentration
gradient driven• Endpoint equilibrium

Facilitated Diffusion
• Protein required• Concentration
gradient driven• Net movement down
the concentration gradient
• Endpoint equilibrium

Active Transport
• Requires membrane protein
• Requires ATP• Pump• Moves substances
against a concentration gradient
• Ions

Bulk Transport
• Very large substances
• Requires use of vesicles
• Fusion with plasma membrane
• Endocytosis• Exocytosis• Phagocytosis• pinocytosis

Videos
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ULR79TiUj80
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4gLtk8Yc1Zc&feature=related
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W6rnhiMxtKU