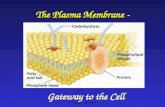
Plasma Membrane
description
Transcript of Plasma Membrane

Plasma Membrane

Plasma Membrane• Separates intracellular (within the cell) fluids from
extracellular (outside the cell) fluids
• Made up of lipids, proteins and carbs (on outer surface)
• Plays a dynamic role in cellular activity & homeostasis– Controls and regulates what enters and leaves the cell

Lipids in the Membrane• Glycolipids are found only in the outer membrane
surface
• 20% of all membrane lipid is cholesterol– Maintain mobility of phospholipids in membrane
• Lipid Rafts:– Make up 20% of the outer membrane surface
– Composed of sphingolipids and cholesterol
– Are concentrating platforms for cell-signaling molecules


Glycocalyx• a fuzzy, sticky carb.-rich area (“sugar-coating”)
• Made up of glycoprotein on the surface of the cell
• Acts as highly specific biological markers by which cells recognize one another
– Examples: • sperm recognize ovum by its glycocalyx
• immune cells recognize bacteria by their glycocalyx.

Cell Membrane Proteins
• Proteins play a major role in membrane functions
– 2 main types:• Peripheral-on outside or inside of membrane
• Integral- are imbedded into membrane– Some go through entire membrane, others do not

Functions of Membrane Proteins
• Transport-spans the membrane and is selective for a particular solute– Some use ATP to actively pump across
membrane
• Enzymatic activity- some membrane proteins may be enzymes
• Receptors for signal transduction-have a specific binding site on outside of cell, once stimulated may initiate a chain reaction in the cell.
Figure 3.4.1

Functions of Membrane Proteins
• Intercellular adhesion-adjacent cells can hook together
• Cell-cell recognition- glycoproteins (proteins bonded to short sugar chains) act as an ID tag to other cells
• Attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix- anchor cell, help maintain cell shape and/or maintain location.– Some play role in cell movement or binding to
adjacent cells
Figure 3.4.2

Microvilli
• “little shaggy hairs”
• Minute, fingerlike extensions that project from an exposed cell surface
• Increase plasma membrane surface area greatly– Found typically on surface of absorption cells

Membrane Junctions• Most cells are bound to other cells
• 3 factors typically act to bind cells together:1. Glycproteins act as an adhesive
2. Wavy contours of membranes on adjacent cells fit together in a zipper fashion
3. Special membrane junctions are formed- 3 types:

1. Tight Junction
Figure 3.5a
Examples: between epithelial cells in digestive tract keep unwanted material from seeping into blood stream
• impermeable junction that encircles the cell

2. Desmosome
Figure 3.5b
Examples: Skin and heart muscle
• anchoring junction scattered along the sides of some cells
• Keeps cells from being pulled apart during mechanical stress

3. Gap Junction
Figure 3.5c
Example: electrically excitable tissues like heart and smooth muscle
• a nexus that allows chemical substances to pass between cells








![Plasma Membrane [7.2] Goals: Understand the concept of homeostasis in relation to the plasma membrane Demonstrate and understand how the plasma membrane.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5697c01d1a28abf838cd0a9a/plasma-membrane-72-goals-understand-the-concept-of-homeostasis-in-relation.jpg)