The Plasma Membrane Honors Anatomy& Physiology. Plasma Membrane boundary between inside & outside of...
-
Upload
tabitha-powell -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
2
Transcript of The Plasma Membrane Honors Anatomy& Physiology. Plasma Membrane boundary between inside & outside of...

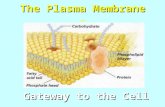
The Plasma MembraneHonors Anatomy& Physiology

Plasma Membraneboundary between inside &
outside of cellflexible structuredynamic role in cellular activities

Plasma MembraneFluid Mosaic Model
resembles an ever-moving sea of fluid lipids that has large proteins bobbing along throughout the lipids

Cell Membrane: Lipid-Bilayer
Fluid Mosaic Model◦phospholipids

Membrane Lipids1. Phospholipids (~70% of
membrane)2. Cholesterol (20%)
◦ changes fluidity of membrane
3. Glycolipids (5%)◦ sugar molecule attached to a
lipid◦ outer membrane only
4. Lipid Rafts◦ control protein-protein
interactions in membrane

Membrane ProteinsIntegral Proteins
◦go all the way thru the membrane
◦channel proteins◦carrier proteins◦receptor proteins◦enzymes
Peripheral Proteins◦on inside or outside of membrane
◦+/- attached to integral proteins

Plasma Membrane

Glycocalyx “sugar-coating” on cell surfaceimportant in cell-cell recognition

Cell Junctions
3 factors binding cells together:1. glycoproteins
◦ sticky
2. membrane contours of 2 cells fit together
3. cell junctions form

Cell Junctions: Tight Jctsintegral
proteins in 2 adjacent cells fuse together◦ impermeable
jct◦ prevent
molecules moving thru ECF between cells

Cell Junctions: Desmosomes
anchoring jcts◦holds cells together in thickening
called a plaque

Cell Junctions: Gap Jctsallows 2 adjacent cells to pass
ions, small molecules important in cardiac muscle
◦allows synchronized contractions

Cell Junctions

Interstitial FluidECF from bloodwater, a.a. sugars, fatty acids,
vitamins, hormones, enzymes, neurotransmitters◦cells must take in what it requires

Membrane Transportplasma membrane is selectively
permeable2 ways substances can pass:
1. Passive Transport2. Active Transport

Passive Transport
1. Diffusion2. Facilitated Diffusion3. Osmosis

Diffusion molecules or ions move from hi
lo concentrations◦due to KE◦Factors that speed up diffusion:1. concentration gradient2. temperature3. size of particles

Diffusion lipid bilayer nonpolar so small
nonpolar molecules allowed to pass◦oxygen molecules◦carbon dioxide◦small, uncharged polar molecules water glycerol


Facilitated Diffusionpolar substances move across
membrane down concentration gradient using a protein
1. carrier-mediated integral proteins carry specific molecules ligand attaches to protein which changes
shape molecule enters cell
2. channel-mediated selective to specific ion or water
(aquaporins) leakage channels always open gated channels controlled by electrical or
chemical signals

Carrier-Mediated Facilitated Diffusion

Leakage Channel

Gated Channel

Osmosis diffusion of water thru selectively
permeable membrane1. simple diffusion thru membranesmall polar molecule that
“wiggles” thru nonpolar bilayer when membrane lipids randomly move
Aquaporins (leakage channels) unsaturated fatty acid tails & cholesterol leave tiny spaces


Isotonic Solutionssame concentration of
nonpenetrating solutes as found inside cells◦0.9% saline◦5% glucose◦body fluids

Hypertonic Solutionshigher concentration of
nonpenetrating solutes than inside cells
cells crenate (shrink)used for extreme edema (excess
water in extracellular spaces)

Hypotonic Solutionsmore dilute than inside cellscells take in water burst =
cytolysis◦(hemolysis if RBC)◦used in extremely dehydrated
patients

Active Transportrequires proteins that combine
specifically and reversibly w/transported substance
solutes move against their concentration gradient◦so cell must expend nrg

Active Transport ProcessesPumps
◦Primary Active Transport◦Secondary Active Transport
Vesicular Transport◦Endocytosis
Phagocytosis Pinocytosis
◦Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis◦Exocytosis

Primary Active Transporthydrolysis of ATP provides nrg by:
1. transferring its 3rd phosphate group to the protein pump
2. pump changes configuration (shape)
3. causing ligand to move across membrane
4. are specific (no pump in particular cell no transport)


Na+K+Pump[K+] inside cell 10x > outside cell[Na+] outside cell 10x > inside cellconcentration gradient necessary for
all cells to maintain normal fluid vol.◦leakage channels in membrane allow
both to diffuse slowly but continuously ◦diffuse according to electrochemical
gradientsantiporter: moves 2 substances in
opposite directions



http://www.siskiyous.edu/class/bio12b/SodPotassXchngPmp.swf
http://brookscole.cengage.com/chemistry_d/templates/student_resources/shared_resources/animations/ion_pump/ionpump.html

2◦ Active Transport1◦ pump indirectly drives 2◦
pump moving other solutesnrg stored in the electrochemical
gradient created from 1◦ pump used to drive 2◦ pump◦Na+ moves back into cell (leakage
channels) as symporter◦sugars


Vesicular Transportmove fluids made of large
particles & macromolecules ◦Endocytosis◦Exocytosis◦Transcytosis substances move across cell
organelle organelle

Phagocytosis: Cell Eating

Pinocytosis: Cell Drinking

Endocytosis: Receptor-Mediated

Exocytosis ejects substances out of cellstimulated by:
◦hormone binding to receptor◦change in membrane voltage
release of:◦hormones◦neurotransmitters◦mucus◦cell waste



Resting Membrane Potential
consequence of pumps, especially Na+/K+ pump, a difference in charge exists across membrane = voltage
in resting state all plasma membranes have resting membrane potential of
-50 to -100mV(-) sign indicates inside of cell (-) compared to outside
so we say all cells are polarized

Resting Membrane Potential
exists only at the membrane◦overall inside and outside neutral

Cell-EnvironmentInteractions
always involves plasma membrane
glycocalyx is key

![Plasma Membrane [7.2] Goals: Understand the concept of homeostasis in relation to the plasma membrane Demonstrate and understand how the plasma membrane.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5697c01d1a28abf838cd0a9a/plasma-membrane-72-goals-understand-the-concept-of-homeostasis-in-relation.jpg)