Plasma Membrane & Cellular Transport
description
Transcript of Plasma Membrane & Cellular Transport

Plasma Membrane & Cellular Transport
http://www.i-sup2008.org/images/venue_transport.jpg

Cell Transport
A cell has to move food and wastes into and out of the cell. Materials must move through the plasma membrane which maintains homeostasis in the cell.
food
waste
food
foodfood
waste
waste
waste

Cell Transport
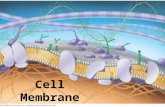
The Plasma Membrane surrounds the cell. How does it work?

Plasma Membrane
Boundary between the cell and its environment1. Allows nutrients into the cell2. Removes wastes and excess materials3. Maintains homeostasis: a stable internal
environment

Plasma MembraneHow does it work?1. Selectively permeable: only allows some
molecules in the cell, keeps others out
http://media3.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/photo/2006/10/15/PH2006101500491.jpg

Plasma Membrane2. Fluid Mosaic Model: membrane is flexible,
made of many pieces working together
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qqsf_UJcfBc
Molecules are able to move around within each layer of the membrane.
FluidMolecules moving around on surface create different patterns.
Mosaic

Plasma Membrane3. Phospholipid Bilayer: membrane is 2 layers,
made of phospholipids with proteins mixed in
http://www.utm.utoronto.ca/~w3bio315/lecture2.htm

Plasma Membrane PartsPhosphate heads – hydrophilic (like water), outside and
inside membraneFatty Acid Tails – hydrophobic (fear water), inside
membrane, like OREO creamCholesterol – prevents fats from sticking together,
stabilize membraneTransport proteins – move molecules into and out of
cellIdentification proteins – outside cell, “nametag”Support proteins – inside cell for framework, “skeleton”Carbohydrates – serve as markers or “nametags”

1. Diffusion - molecules move from an area of high concentration to low concentration
http://iweb.tntech.edu/mcaprio/diffusion-animated.gif
NO ENERGY required, moves molecules from high concentration to low concentration
Passive Transport

http://schools.moe.edu.sg/chijsjc/Biology/Diffusion&osmosis/osmosis.gif
2. Osmosis – diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane
Passive Transport – no energy required

Solutions
Isotonic solution – equal concentrations of solute (salt) inside and outside cell
http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/isotonic.gif

Solutions
Hypotonic solution – less solute in solution, more solute in cell, WATER FOLLOWS SALT, cells swell
http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/hypotonic.gif

Solutions
Hypertonic solution – more solute in solution, less solute in cell, WATER FOLLOWS SALT, cells shrink
http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/hypertonic.gif

Osmosis in blood cells
http://aryatiabdul.files.wordpress.com/2008/07/osmosis2.gif

Solutions – how transport affects animals and plants
http://kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.ca/cm1504/Image130.gif

Transport in PlantsHealthy plant cells are crisp due to TURGOR PRESSURE
Wilted plant cells are flaccid due to lack of water

Passive Transport – no energy required
3. Facilitated Diffusion – movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration with help of membrane transport proteins
http://www.biology.arizona.edu/CELL_BIO/problem_sets/membranes/graphics/CHANNEL.GIF
High concentration
Low concentration

Active Transport
Requires energyMoves molecules against concentration gradientMoves molecules from area of low concentration
to area of high concentrationExamples:
gated channels, sodium/potassium pumps, endocytosis, exocytosis

Active TransportEndocytosis and Exocytosis
http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/38/8038-004-A29C9C02.jpg