Plasma Membrane
-
Upload
jordan-bowman -
Category
Documents
-
view
42 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Plasma Membrane
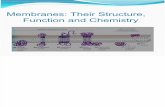
Plasma Membrane (AKA Cell Membrane)
• What is the plasma membrane?
• What does it do?
• What is its composition?
• Plasma membrane = the flexible boundary between the cell and its environment
• Allows:• Things in the cell• Things out of the cell• Maintains BALANCE in the cell
How does the plasma membrane maintain homeostasis?
• Plasma membranes are selectively permeable
• Selective permeability = process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass while keeping others in/out.
Structure is the KEY!
• The specific structure of the plasma membrane allows it to be selectively permeable
Plasma Membrane Structures:
• Thin layer of phosopholipds, proteins, and cholesterol
• Phospholipid = kind of lipid found in the cell membrane– Glycerol, 2 fatty acids,
and phosphate (PO4) – Phospholipids have 2
parts
Each part has a different property in water!
1. Phosphate Head– Hydrophilic – Can dissolve in water
2. Lipid tails (x2)– Hydrophobic– Cannot dissolve in water
What does the polarity mean about the passage of water in/out of the cell?
• Water CAN pass through the polar part, but CANNOT pass through the nonpolar part.
• This allows the cell to prevent water loss and prevent “drowning”
Plasma Membrane
• Made of: phospholipid bilayer– Phosphate head hydrophilic– Lipid tail hydrophobic– Carrier proteins– Cholesterol (good kind)
• Called the fluid mosaic model– Moves fluidly– Mosaic of proteins scattered in membrane– http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qqsf_UJcfBc&featur
e=related
Cell Transport
• Diffusion = movement across a plasma membrane from HI to LO concentration
• Osmosis = diffusion of water across a plasma membrane from HI to LO concentraion
Solution
• Solution = homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances
• Made up of:– Solute = part that gets dissolved– Solvent = part that does the dissolving
• Water is the UNIVERSAL SOLVENT
Types of Cell Transport
• Water can move freely through the plasma memebrane, but can Solute???
• NO!• Water will move to reach equilibrium since the
solute cannot• Which way will the water move?• Depends on the TYPE OF SOLUTION the cell is
in
Types of Solution
• Hypertonic– Solute concentration is higher in solution than cell– Water moves OUT– Cell shrinks
• Hypotonic– Solute concentration is lower in solution than cell– Water moves IN– Cell Swells
• Isotonic– Solute concentration is equal in solution and in cell– Water moves IN and OUT– Cell stays the same
Cell Transport
• Active transport = movement of substances across membrane; requires ATP
• Passive transport = movement of substances across membrane; does NOT require ATP
Active Transport
• Goes against concentration gradient• Exocytosis = move particles OUT of cell• Endocytosis = move particels IN cell– 2 kinds of endocytosis:– Pinocytosis = movement of liquid IN cell– Phagocytosis = movement of solids IN cell– http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4gLtk8Yc1Zc&NR=1
Passive Transport
• Goes with concentration gradient• Osmosis = movement of water across a
membrane with concentration gradient• Facilitated Transport = movement of
substances across a membrane with concentration gradient with the help of a carrier protein
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s0p1ztrbXPY&feature=related
Turgor Pressure and Plasmolysis
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GOxouJUtEhE&feature=related







































![Plasma Membrane [7.2] Goals: Understand the concept of homeostasis in relation to the plasma membrane Demonstrate and understand how the plasma membrane.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5697c01d1a28abf838cd0a9a/plasma-membrane-72-goals-understand-the-concept-of-homeostasis-in-relation.jpg)