Plasma membrane
-
Upload
bella-chan -
Category
Education
-
view
182 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Plasma membrane

Plasma Membrane
1 PPISMP SAINS 2014
By:o Sabila


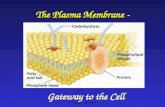
Plasma Membrane• Biological membrane that encloses the
cytoplasm/protoplasm of the cell.• Separate the interior and external of the cell.• Provides shape & protection.• Semipermeable or selectively permeable.• Made of a phospholipid bilayer ;- Hydrophilic [water liking] face ouside.- Hydrophobic [water dreading] face inside.


Structure of Plasma Membrane
DANIELLI-DAVSON MODEL• Proposed by Danielli & Davson in 1953.• Made of phospholipid bilayer where;- the hydrophilic [polar] heads facing outside &
coated with protein.- Hydrophobic [non-polar] tails facing inwards,
sandwiched between two bilayer.- Structure is stable, static & rigid.


FLUID MOSAIC MODEL• Also known as Singer Model.• Proposed by S.Jonathan Singer & Garth Nicolson in
1972 based on their study by using freeze-fracture technique.
• In this model, membrane is a fluid system with proteins embedded in phospholipid bilayer.
• Composed of : - 2 type of protein [ Integral & peripheral ]
- Phospholipid - Cholesterol - 2 type carbohydrates [ glycoprotein & glycolipid ]


• The membrane is a dynamic fluid system with globular proteins embedded in the phospholipid bilayer mosaic structure.
• Phospholipid move through the membrane and flip flopping across it fluidity
• Protein do not coat the membrane surface.• Thickness of PM: 7.5 nm.• Phospholipid is the main component of PM.

• Composed of 2 protein ; Integral & peripheral proteins.
- Integral proteins > interspersed between phospholipids.> act as enzymes, pumps, carriers, channels & receptors.- Peripheral proteins > attached to the inner or
outer surface of the membrane.

• Composed of carbohydrates [glycoproteins & glycolipid]
- Glycoproteins ; formed when oligosaccharides attached to globular proteins.
- Glycolipid ; formed when oligosaccharides attached to phospholipids.
• Both act as – chemical receptors - cell recognition
that enable the cells to : (i) recognise each other.(ii) differentiate themselves from foreign cells.

• Composed of cholesterol – reduce the membrane flexibility & permeability to the substances.
- Increasing the fluidity.• PM are semi permeable.• Small uncharged polar molecules are able to
cross the PM freely.• Ions & large uncharged polar molecules such
as glucose are not allowed.


Functions of Plasma Membrane• Controls the inflow & out flow of materials to
maintain the internal environment of the cell.• Separate the cytoplasm from its external
environment.• Act as cell identity marker provided by
glycoprotein & glycolipids.• Act as receptor for chemicals.• Helps transporting ions and large, polar substances
into & out of the cell.• Act as attachment site for cytoskeleton that
maintain the cell shape.• Play a role in cell adhesion.










![Plasma Membrane [7.2] Goals: Understand the concept of homeostasis in relation to the plasma membrane Demonstrate and understand how the plasma membrane.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5697c01d1a28abf838cd0a9a/plasma-membrane-72-goals-understand-the-concept-of-homeostasis-in-relation.jpg)