Nutrition Notes Science Form 2
-
Upload
veloo-gunasagaran -
Category
Documents
-
view
598 -
download
56
description
Transcript of Nutrition Notes Science Form 2
2.1Classes of Food
ClassesFunctionsExamples
CarbohydratesSupply main energy to bodysugars: cakes, cholates, fruits
starch: rice, bread, potatoes
cellulose: vegetables, fruit
glycogen (stored in the liver & muscle)
FatsSupply more energy & give heat to bodybutter, cheese, margarine
ProteinsFor growth, repair and replace damaged cellsmeat, fish, milk, eggs, beans,
peas, nuts
VitaminsMaintain good healthvegetables & fruits
MineralsFor proper growth & development of bodymeat, milk, banana, seafood, eggs
FibreTo stimulate peristalsisfruits & vegetables
WaterMedium for chemical reaction in the bodywater
Regulate body temperature
Transport digested food & waste materials
Excess carbohydrates stored as fat in the body.
Vitamins A, D, E, K fats soluble
Vitamins B, C Water soluble Vitamins required in small quantity for bodyVitaminsFunctionsExamplesDeficiency diseases
ATo promote healthy skins & eyescarrot, tomatoes, green vegetablesDry skin , night blindness
BMaintain healthy skin & nervous systemyeast, liver, vegetablesBeri-beri, Pellagra, Anaemia
CTo increase immunity against diseasesguavas, grapes, tomatoes,Scurvy
Maintain healthy skin, teeth, gumscitrus fruit, vegetables
DMaintains healthy & strong teeth & bonesmilk, eggs, fishRickets, softening of bones
Promotes calcium & phosphorus absorption& teeth
EMaintain healthy reproduction systemseeds, nuts, egg yolk, whole grainSterility
KBlood clottingliver, egg yolk, green vegetablesprolong bleeding
MineralsFunctionsExamplesDeficiency diseases
SodiumMaintain body fluid balancecheese, meat, table saltmuscle cramps
PotassiumFor nerve & muscle activitiesbananas, fish, meatparalysis, weak muscles
CalciumMaintain strong & healthy teeth & bonesmilk, eggs, anchovies, Rickets, Osteoporosis,
Helps blood clottinggreen vegetablesprolong bleeding
IronFormation of haemoglobin in red blood cellliver, egg yolk, meatAnaemia
IodineMake the hormones of the thyroid glandseafood, seaweedGoitre
PhosphorusHelp in muscle contraction, make healthy cheese, milk, eggsRickets, tooth decay,
bones, and teethweak muscle
Beri-beri (disease of nervous system)Pellagra (skin disease)
Anaemia (shortage of red blood cell)Scurvy (bleeding gums) Rickets (stunted growth)
Goitre (swollen neck) Kwashiorkor (lack of protein)
Balanced diet Diet which contains all seven types of food classes in the right quantities & proportions.
1. Digestion process of breaking down large food molecules into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by body.2. Physical digestion breaking down food into smaller particles by teeth.3. Chemical digestion breaking down food by enzymes.
4. Peristalsis Contraction & relaxation of digestive tract to channel the food throughout the digestive tract.
1. Absorption of end product take place in small intestine through the diffusion process.2. Length of small intestine 6 metre. Walls of small intestine is folded to increase its surface area.
3. Features of small intestine:
a. Have many finger-like projections known as villi (singular: villus).b. Have many blood capillaries to facilitate absorption.c. Very long about 6 m allows greater absorption.
d. Very thin so that small molecules can enter the blood capillaries.e. Moist lining enables food molecules to dissolve easily.4. Vilus or Villli the surface of small intestine covered with millions of tiny finger-like projections.
5. Functions of vilus Absorb digestion food effectively.
1. Undigested food enters the large intestine.
2. Reabsorption of water & minerals from undigested food (e.g cellulose, fibre) take place. 3. Defecation process where faeces removed from body.4. Faeces is formed and stored in the rectum. Then, removed through anus.
1. Good eating habits Eating nutritious food in right quantities & proportion.2. Healthy eating habits:
a. Eat plenty of vegetables & fruit.
b. Consume less sugar & salt
c. Eat in moderation
d. Drink plenty of water
e. Chew food thoroughly before swallowing
f. Eat nutritious food
g. Avoid junk food
3. Unhealthy eating habits:
a. Consume high sugar lead to diabetes
b. Consume high salt lead to blood pressure
c. Consume too much fat lead to high blood cholesterol and heart diseases4. Constipation difficulty to defecate hard faeces from body.5. Causes of constipation lack of water & roughage in diet. To avoid constipation, must eat food such as fruits, vegetables, and grains.
6. Over weight/ Obesity Excess body fat which can cause health problem such as diabetes, hypertension, heart diseases, cancer, & failure in respiratory and excretory systems.7. Causes of obesity Genetic, lack of exercise, unbalanced nutrition8. Saturated fat is bad for body because fat will accumulate in the blood stream and cause blockage of blood vessels and lead to heart attack and stroke.CHAPTER 2: NUTRITION
Classes of Food
Carbohydrates
Fats
Proteins
Fibre
Minerals
Vitamins
Water
INCLUDEPICTURE "http://www.blatner.com/adam/consctransf/historyofmedicine/5-deficiencydiseases/pellagrskin.JPG" \* MERGEFORMATINET
INCLUDEPICTURE "http://www.howtogetrid.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/beriberi.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET
INCLUDEPICTURE "https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5z50c578/2.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET
INCLUDEPICTURE "https://escholarship.org/uc/item/0vq0t201/1b.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET
INCLUDEPICTURE "http://cdn.natural-homeremedies.org/buzz/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/deficiency-of-vitamin-C.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET
INCLUDEPICTURE "http://news.bbcimg.co.uk/media/images/64747000/jpg/_64747000_rickets.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET
INCLUDEPICTURE "http://www.natural-health-news.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/Rickets.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET
INCLUDEPICTURE "http://diseasespictures.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/Goiter.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET
INCLUDEPICTURE "http://simple-health-secrets.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/Goiter-2.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET
INCLUDEPICTURE "http://discoveringreligion.net/wp-content/uploads/2011/07/Kwashiorkor1.png" \* MERGEFORMATINET
INCLUDEPICTURE "https://mchinmedicaljournal.files.wordpress.com/2012/04/kwashiorkor-8416_3.gif" \* MERGEFORMATINET
Food Test
ClassesType of testReagentResultStarchIodin testIodinebrown colour Iodine change into blue blackGlucoseBenedict's test / Fehling's testBenedict's solutionbrick-red precipitate formedProteinsMillon's testMillon's reagentwhite precipitate - red colourFatsEmulsion testEtanolmilky solution or white emulsion formedFilter paperA translucent spot formed
Factors affecting balanced diet
FactorsExplanationReasonAgebabies, children, & teenagers need more Babies, children, and teenagers energy than adultsmore active & life process fasterGenderMen need more energy than woman Men are more active than womanof the same age & body sizeBody sizeBig size individuals need more energy Big size individual need morethan small size individual energy for life processHealthPatients needs more energy than Patients need more energy to conditionsomeone who is healthyrecover from diseases.Type ofHeavy work need more energy Heavy work need more jobthan light workenergy to performClimateIndividual live in cold weather need more More energy required in cold weatherenergy than individual live in warm weatherto maintain body temperature
Calorific value of food
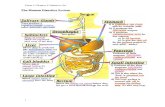
Human digestive system
Mouth
Oesophagus
Stomach
Duodenum
Anus
Rectum
Large intestine
Small intestine
OrgansFunctionsMouth Cut & chews the food into smaller moleculesOesophagus Channels food (bolus) to stomach through peristalsis actionStomach Begins the digestion of proteinDuodenum Secret pancreatic juices to digest protein, carbohydrate, & fatsSmall intestine Complete the food digestion and absorb end product of digestionLarge intestine Reabsorb water & minerals from indigested foodRectum Store the faecesAnus Removes faeces from bodySalivary glands Produce saliva which contain amylase enzymeLiver Secrets bile to emulsify fatsGall bladder Store bile which is secreted by liverPancreas Produce digestive enzymes (amylase, protease, lipase)
INCLUDEPICTURE "http://3.bp.blogspot.com/-znmfrPKjRLw/T72NUUyII7I/AAAAAAAAAIQ/quX_xVxeUtY/s1600/gr294.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET
OrgansJuicesEnzymeFunctionsMouthSaliva (alkaline)AmylaseStarch - MaltoseStomachGastric juiceProteaseProtein - Polypeptide or Peptone(acidic)Casein/RenninLiquid milk protein - Solid formHydrochloric acidKills bacteria in the foodDuodenumPancreatic juiceAmylaseStarch - Maltose(secreted by pancrease)ProteaseProtein - Polypeptide or Peptone(Alkaline)LipaseFat - Fatty acid + GlycerolBile (alkaline greenish fluid secreted by liver)Emulsify fats & oils into globulesSmall intestine
Intestinal juiceMaltaseMaltose - GlucoseProteasePeptone - Amino acidLipaseFat - fatty acid + Glycerol
Water, minerals, vitamins are need not to be digested because these food are very small and simple molecules that can be absorbed into body.
Food classEnd productCarbohydrateGlucoseProteinAmino acidFatGlycerol + fatty acid
Absorption of digested food
Reabsorption of water & defecation
Good eating habits
6