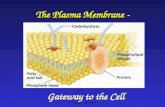
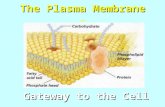
1 The Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell.
Master Basic ConceptsBasic Concepts 6 Plasma Membrane
Transcript of Master Basic ConceptsBasic Concepts 6 Plasma Membrane
UNIT 3 CHAPTER 7 A View of the Cell 61
Name Date ClassC
opyr
ight
© G
lenc
oe/M
cGra
w-H
ill, a
div
isio
n of
The
McG
raw
-Hill
Com
pani
es, I
nc.
Master
6Master
Plasma Membrane Use with Chapter 7, Section 7.2
Basic ConceptsBasic Concepts
Phosphate group
Phospholipidmolecule
Fattyacids
Glycerol backbone
Polarhead
Cholesterol
Membraneprotein
Filaments of cytoskeletonCytoplasm
Membraneprotein
62 CHAPTER 7 A View of the Cell UNIT 3
Name Date Class
Cop
yrig
ht ©
Gle
ncoe
/McG
raw
-Hill
, a d
ivis
ion
of T
he M
cGra
w-H
ill C
ompa
nies
, Inc
.
Worksheet
6Worksheet
Plasma MembraneBasic ConceptsBasic Concepts
Use with Chapter 7, Section 7.2
1. Describe the phospholipid in the upper left part of the transparency.
2. Which end of a phospholipid is attracted to water?
3. How are phospholipids oriented in the plasma membrane?
4. What is the function of membrane proteins?
5. Why is the model of a membrane shown in the transparency referred to as the fluid mosaic model?
6. How would the membrane shown in the transparency behave if its fatty acid tails consisted mostly of unsaturated fatty acids?
7. What is the function of the cholesterol molecules shown in the transparency?
UNIT 3 CHAPTER 7 A View of the Cell 63
Name Date ClassC
opyr
ight
© G
lenc
oe/M
cGra
w-H
ill, a
div
isio
n of
The
McG
raw
-Hill
Com
pani
es, I
nc.
Master
7Master
The Cell Use with Chapter 7, Section 7.3
Basic ConceptsBasic Concepts
Microfilaments
Typical Animal Cell
Typical Plant Cell
Cytoplasm
Chromatin
Nucleolus
Nuclear membrane
Nucleus
Microtubules
Central vacuole
Plasmamembrane
Mitochondria
Golgi apparatus
Cell wall
Nuclear membrane
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Nucleus
Chloroplast
Microfilaments
Microtubules
Cytoplasm
Endoplasmicreticulum withribosomes
Lysosome
64 CHAPTER 7 A View of the Cell UNIT 3
Name Date Class
Cop
yrig
ht ©
Gle
ncoe
/McG
raw
-Hill
, a d
ivis
ion
of T
he M
cGra
w-H
ill C
ompa
nies
, Inc
.
Worksheet
7Worksheet
The CellBasic ConceptsBasic Concepts
Use with Chapter 7, Section 7.3
1. Which cell parts are common to both plant and animal cells?
2. Which organelle aids in digestion of worn-out cell parts?
3. Which organelle is found in plant cells but not in animal cells?
4. What is the function of the central vacuole in plant cells?
5. What would be the likely function of a plant cell that contains many chloroplasts?
6. Which plant cells might not contain any chloroplasts?
7. Which organelles are produced within the nucleolus?
8. Why would a cell that moves by means of cilia or flagella require a relatively large number of mitochondria?
UNIT 3 CHAPTER 7 A View of the Cell 65
Name Date ClassC
opyr
ight
© G
lenc
oe/M
cGra
w-H
ill, a
div
isio
n of
The
McG
raw
-Hill
Com
pani
es, I
nc.
Master
9Master
The Optical Microscope Use with Chapter 7, Section 7.1
Reteaching SkillsReteaching Skills
EyepiecesContain magnifying lenses to look through
Light sourceAllows light to reflectupward through thediaphragm, the specimen,and the lenses
DiaphragmRegulates the amount oflight that passes throughthe specimen
StageSupports the microscopeslide
High-power objectivesContain lenses withgreater powers ofmagnification
Revolving nosepieceHolds and turns theobjectives into viewingposition
Fine adjustmentSharpens the image underhigh and low magnification
Coarse adjustmentFocuses the image under low power
Stage clipsHolds the microscopeslide in place
Low-power objectiveContains the lens with low power magnification
Arm
66 CHAPTER 7 A View of the Cell UNIT 3
Name Date Class
Cop
yrig
ht ©
Gle
ncoe
/McG
raw
-Hill
, a d
ivis
ion
of T
he M
cGra
w-H
ill C
ompa
nies
, Inc
.
Worksheet
9Worksheet
The Optical MicroscopeReteaching SkillsReteaching Skills
Use with Chapter 7, Section 7.1
1. What is the function of the diaphragm?
2. If you want to change the objective lens through which you are viewing a specimen,what must you do?
3. What knob is turned to focus an image under low power?
4. What is the purpose of having a light source on a microscope?
5. Explain the significance of the term compound in describing a modern light microscope.
6. Identify the parts of the microscope that are used for supporting the specimen and holding it in place.
7. If the magnifying power of an eyepiece is 10� and that of an objective is 45�, by howmuch is a specimen magnified through this combination of lenses?
8. What is the fundamental difference between a compound microscope and the simplemicroscope that van Leeuwenhoek used in the 1600s to describe living cells?
9. What major advantage does a transmission electron microscope have over a compoundlight microscope? What is its major disadvantage?