Lumbosacral plexus and nerves of the lower limb Prof ... · plexus. Again, as with the arteries,...
Transcript of Lumbosacral plexus and nerves of the lower limb Prof ... · plexus. Again, as with the arteries,...

Lumbosacral plexus and nerves of the lower limb
E-mail: [email protected] [email protected]
Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi

The lumbar plexus is a nervous plexus in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the anterior rami of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12). The anterior ramus of the fourth lumbar nerve gives communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh. The plexus is formed lateral to the intervertebral foramina and passes through psoas major. Its smaller motor branches supply the psoas major. The larger branches leave the muscle at various sites (lateral, anterior or medial aspect) to run obliquely down through the pelvis to leave under the inguinal ligament. The obturator nerve leaves the pelvis through the obturator foramen.

Spinal nerve
The anterior rami of the L1-L4 spinal roots, each divides into ventral and dorsal cords. These cords then combine together to form the six major peripheral nerves of the lumbar plexus inside the psoas major muscle

Lumbar plexus

Nerves that run posterior to the psoas major, leave its proximal lateral border and run laterally and obliquely on the anterior side of quadratus lumborum are: 1- Iliohypogastric nerve, 2- Ilioinguinal nerve. Other nerves leave lateral border of Psoas muscle are 3- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh 4- Femoral nerve 1- Iliohypogastric nerve: Roots: L1 + contributions from T12 Pierces the transversus abdominis to run above the iliac crest between that muscle and abdominal internal oblique. It gives off several motor branches to these muscles and a sensory branch to the skin of the lateral hip. Its terminal branch then runs parallel to the inguinal ligament to exit the aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique above the external inguinal ring where it supplies the skin above the inguinal ligament (i.e. the hypogastric region)


2-The ilioinguinal nerve: Roots: L1 closely follows the iliohypogastric nerve on the quadratus lumborum, then perforates the transversus abdominis near the anterior part of the iliac crest, and communicates with the iliohypogastric nerve between the transversus and the internal oblique muscle. It then pierces the internal oblique muscle, giving it some filaments, and then accompanies the spermatic cord (in males) or the round ligament of uterus (in females) through the superficial inguinal ring. it supplies motor branches to the transversus abdominis and internal oblique muscle sensory branches through the external inguinal ring to the skin over the pubic symphysis and the lateral aspect of the Labia majora or scrotum.

3- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh: Roots: L2, L3 pierces psoas major on its lateral side and runs obliquely downward below the iliac fascia. Medial to the anterior superior iliac spine it leaves the pelvic area through the lateral muscular lacuna it enters the thigh by passing behind the lateral end of the inguinal ligament . In the thigh it briefly passes under the fascia lata before it perforate the fascia and supplies the skin of the anterolateral side Of the thigh

4- Femoral nerve: formed by union of dorsal divisions of anterior rami of L2, L3, L4 It leaves psoas major at the lower part of its lateral side. It runs in a groove between psoas major and iliacus passing behind the iliac fascia to the mid-point of the inguinal ligament. It traverses behind the inguinal ligament into the femoral triangle lateral to the femoral vessels. It splits into an anterior and posterior division. It gives off 1- articular branches to the hip and knee joints. 2- It gives motor innervation to iliopsoas, pectineus, sartorius, and quadriceps femoris. 3- It gives sensory branches: It gives the anterior cutaneous branches that arise in the femoral triangle, they supply the skin on the anteromedial thigh.The last cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve is the saphenous nerve which supplies the skin on the medial side of the leg and the foot.

Nerves leaving the anterior surface of the psoas muscle 1- The genitofemoral nerve: Roots: L1, L2 Pierces psoas major anteriorly to immediately split into two branches that run downward on the anterior side of the muscle. a- The lateral branch is the femoral branch, it is purely sensory. It pierces the vascular lacuna near the saphenous hiatus and supplies the skin below the inguinal ligament (i.e. proximal, lateral aspect of femoral triangle). b-The genital branch differs in males and females. In males it runs in the spermatic cord and in females in the inguinal canal together with the round ligament of uterus. It then sends sensory branches to the scrotal skin in males and the labia majora in females. In males it supplies motor innervation to the cremaster muscle.

Nerves descends behind psoas major on it medial side 1- Obturator nerve: formed from ventral divisions of anterior rami of L2, L3, L4 then follows the pelvic brim, which is the edge of the pelvic inlet into the lesser pelvis, and finally leaves the pelvic area through the obturator canal. In the thigh, it sends motor branches to obturator externus before dividing into an anterior and a posterior branches, both of which continues distally. These branches are separated by adductor brevis, they supply all thigh adductors with motor n.(pectineus, adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus, and gracilis). The anterior branch contributes a terminal, sensory branch which supplies the skin on the medial, distal part of the thigh

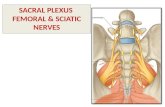
The sacral plexus is formed by: The anterior rami of the S1-S4 spinal roots and the lumbosacral trunk. The lumbosacral trunk is formed by the combination of the 4th and 5th lumbar roots, it descends into the pelvis to meet the sacral roots as they emerge from the spinal cord. The anterior rami of the spinal nerves divide into several cords. These cords then combine together to form the peripheral nerves of the sacral plexus. Nerves of sacral plexus descend down the posterior pelvic wall. They have two main destinations: a- Leave the pelvis via the greater sciatic foramen – these nerves enter the gluteal region of the lower limb, innervating the structures there.

b- Remain in the pelvis – these nerves innervate the pelvic muscles, organs and perineum Sacral plexus and the lumbar plexus are considered to be one large nerve plexus, called the lumbosacral plexus. The lumbosacral trunk connects the two plexuses.
Lumbosacral trunk


Nerves leaving the pelvis 1- Superior Gluteal Nerve: Roots: L4, L5, S1. The superior gluteal nerve leaves the pelvis via the greater sciatic foramen, entering the gluteal region superiorly to the piriformis muscle. Motor Functions: Innervates the gluteus minimus, gluteus medius and tensor fascia lata. Sensory Functions: None.

2- Inferior Gluteal Nerve: Roots: L5, S1, S2. The inferior gluteal nerve leaves the pelvis via the greater sciatic foramen, entering the gluteal region inferiorly to the piriformis muscle. Motor Functions: Innervates gluteus maximus. Sensory Functions: None

3- Sciatic nerve: Roots: L4, L5, S1, S2, S3 The sciatic nerve is derived from the lumbosacral plexus. After its formation, it leaves the pelvis and enters the gluteal region via greater sciatic foramen. It emerges inferiorly to the piriformis muscle and descends in an inferolateral direction. As the nerve moves through the gluteal region, it crosses the posterior surface of the superior gemellus, obturator internus, inferior gemellus and quadratus femoris muscles. It then enters the posterior thigh by passing deep to the long head of the biceps femoris. Within the posterior thigh, the nerve gives rise to branches to the hamstring muscles and adductor magnus. When the sciatic nerve reaches the apex of the popliteal fossa, it terminates by bifurcating into the tibial and common peroneal (fibular) nerves

Sciatic nerve

Motor Functions of sciatic nerve Tibial Portion – Innervates all of the muscles in the posterior compartment of the thigh, including the hamstring portion of adductor magnus, (apart from the short head of the biceps femoris Which is supplied by common peroneal nerve). All muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg. All muscles in the sole of the foot. Common peroneal Portion (Fibular) Short head of biceps femoris, all muscles in the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg and extensor digitorum brevis.

Sensory Functions: Tibial Portion: Innervates the skin on the posterolateral and medial surfaces of the foot as well as the sole of the foot. Common peroneal Portion: Innervates the skin on the anterolateral surface of the leg and the dorsal aspect of the foot

The course of the common peroneal nerve It is the dorsal branches of the L4, L5. S1, S2. It descends obliquely along the lateral side of the popliteal fossa to the head of the fibula, close to the medial margin of the biceps femoris muscle. It lies between the tendon of the biceps femoris and lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle, winds around the neck of the fibula, between the peroneus longus and the bone, and divides beneath the muscle into the superficial peroneal nerve and deep peroneal nerve.

The tibial nerve: L4,L5,S1,S2,S3.is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus. Below the soleus muscle the nerve lies close to the tibia and supplies the tibialis posterior, the flexor digitorum longus and the flexor hallucis longus. The nerve passes into the foot running posterior to the medial malleolus. Here it is bound down by the flexor retinaculum in company with the posterior tibial artery. In the foot, the nerve divides into medial and lateral plantar branches

4- Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh:Roots: S1, S2, S3 The posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh leaves the pelvis via the greater sciatic foramen, entering the gluteal region inferiorly to the piriformis muscle. It descends deep to the gluteus maximus and runs down the back of the thigh to the knee. Motor Functions: None Sensory Functions: Innervates the skin on the posterior surface of the thigh and leg. Also innervates the skin of the perineum

5- Pudendal Nerve: Roots: S2, S3, S4.This nerve leaves the pelvis via the greater sciatic foramen, then re-enters via the lesser sciatic foramen. It moves anterosuperiorly along the lateral wall of the ischiorectal fossa, and terminates by dividing into several branches. Motor Functions: Innervates the skeletal muscles in the perineum, the external urethral sphincter, the external anal sphincter, levator ani. Sensory Functions: Innervates the penis and the clitoris and most of the skin of the perineum

Other Branches of sacral plexus leaving the pelvis below the piriformis muscle are 6- Nerve to obturator internus & superior gemellus muscles 7- Nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles

1.The nerves of the gluteal region are branches of the lumbosacral plexus. Again, as with the arteries, the nerves arise in the pelvis and pass through the greater sciatic foramen to reach the gluteal region.
The piriformis muscle separates the greater sciatic foramen into superior and inferior parts. The branches either come through the
superior part or the inferior part. The nerves are: 1-superior gluteal (the only branch that comes through the superior part). The longest branch of this nerve supplies the tensor fasciae lata muscle. 2-inferior gluteal 3-sciatic 4-posterior femoral cutaneous 5-pudendal 6-nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles 7-nerve to obturator internus and superior gemellus muscles
Nerves of the Gluteal Region

Thank You