1 Cerebellum NMJ Brachial Plexus, Median, Radial, and Ulnar nerves Radial, and Ulnar nerves.
-
Upload
claire-brooks -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of 1 Cerebellum NMJ Brachial Plexus, Median, Radial, and Ulnar nerves Radial, and Ulnar nerves.
11
CerebellumCerebellum NMJNMJ Brachial Plexus, Median, Brachial Plexus, Median,
Radial, and Ulnar nervesRadial, and Ulnar nerves
22
Cerebellum Cerebellum [17 cm x 120cm][17 cm x 120cm]
AnatomyAnatomy– RelationRelation– 3 Lobes3 Lobes
Functional Functional
– 4 deep nuclei4 deep nuclei fastigialfastigial Interposed x 2Interposed x 2 dentatedentate
– TopographyTopography– Blood supplyBlood supply
33
VermisVermis Ms mvt of the axial body Ms mvt of the axial body The intermediate zoneThe intermediate zone distal distal
portion of the limbs & faceportion of the limbs & face The lateral zoneThe lateral zone [has no topographic [has no topographic
representation]representation]– InputInput motor & premotor areas of the motor & premotor areas of the
frontal cortex & somatosensory & sensory frontal cortex & somatosensory & sensory ass. area of the parietal cortexass. area of the parietal cortex
overall planning & coordination of rapid overall planning & coordination of rapid sequential mvts sequential mvts IncoordinationIncoordination
44
FunctionsFunctions
Timing,Timing, in rapid progression in rapid progression IntensityIntensity of muscle contraction of muscle contraction Continuously updated info. Continuously updated info. Makes corrective adjustments when actual mvt Makes corrective adjustments when actual mvt
unfavorably compares with the intended unfavorably compares with the intended Performs most of the Performs most of the dampingdamping function function Aids the C.Cx in planning next mvt Aids the C.Cx in planning next mvt smooth smooth
progressionprogression Ballistic mvts [typing, guitar] Ballistic mvts [typing, guitar] loss of automaticityloss of automaticity Control the interplay b/n agonist & antagonists, Control the interplay b/n agonist & antagonists, ++
synergists & fixatorssynergists & fixators Extramotor predictive function:- rate of progression of Extramotor predictive function:- rate of progression of
auditory and visual phenomenonauditory and visual phenomenon
55
Afferent pathways Afferent pathways BrainBrain Corticopontocerebellar PathwayCorticopontocerebellar Pathway to lat zone to lat zone Olivocerebellar tractOlivocerebellar tract to all areas to all areas Vestibuloc. fibersVestibuloc. fibers floculonod lobe & Fastigial N. floculonod lobe & Fastigial N. Reticulocerebellr fibersReticulocerebellr fibers vermis vermis
PeripheryPeriphery
Dorsal spinocerebellar tractDorsal spinocerebellar tract vermis & IM zone vermis & IM zone same sidesame side
– From ms spindles and somatic From ms spindles and somatic Ventral spinocerebellar tract Ventral spinocerebellar tract [fastest][fastest]
– SCPSCP Both side Both side– By Motor signals arriving at AHC [“efference copy of the ant By Motor signals arriving at AHC [“efference copy of the ant
horn motor drive]horn motor drive]
66
Major Efferent pathwaysMajor Efferent pathways
MidlineMidline fastigial N. fastigial N. medullary & pontine medullary & pontine fastigiobulbar & C.reticular tracts fastigiobulbar & C.reticular tracts – Equilibrium apparatus & vestibular N. Equilibrium apparatus & vestibular N. Equil. Equil.– Reticular formationReticular formation postural attitude postural attitude
IM zoneIM zone interposed Ninterposed NC. reticular & C. .olivery C. reticular & C. .olivery fs fs – Thalamus Thalamus Cx, Cx, BG, BG, to the red N and RF to the red N and RF– Coordinate reciprocal contraction of limbs msCoordinate reciprocal contraction of limbs ms
Lateral zoneLateral zonedentate N. dentate N. thalamus thalamus Cx Cx Dentatothalamic & Dentatorubral fsDentatothalamic & Dentatorubral fs coordination of sequential motor activitycoordination of sequential motor activity
77
Summary: Summary: It controls motor fIt controls motor fnn at 3 level at 3 level The Vestibulocerebellum [archicerebellum]The Vestibulocerebellum [archicerebellum]
– floculonodular + adjacent vermisfloculonodular + adjacent vermis Equilibrium and postural mvts Equilibrium and postural mvts
The Spinocerebellum [paleocerebellum]The Spinocerebellum [paleocerebellum] IM zone IM zone comparison comparison interposed N interposed N corrective signalcorrective signal– Smooth coordinated mvt of agonist and antagonist ms of distal Smooth coordinated mvt of agonist and antagonist ms of distal
limb for acute purposeful patterned mvtlimb for acute purposeful patterned mvt– Damping & ballistic mvt fDamping & ballistic mvt fnn
Cerebrocerebellum [Neocerebellum]Cerebrocerebellum [Neocerebellum] Lateral zone & dentate N Lateral zone & dentate N – Extreme incoordin. of cx purposeful mvts of hands,fingers, & feet Extreme incoordin. of cx purposeful mvts of hands,fingers, & feet
& of speech apparatus& of speech apparatus– Planning & Timing of sequential mvtsPlanning & Timing of sequential mvts– Extramotor predictive functionExtramotor predictive function
88
Clinical AbnormalitiesClinical Abnormalities
Small lesion / Small lesion / !/2 removed !/2 removed Imbalance and Ataxia Imbalance and Ataxia
– Truncal ataxiaTruncal ataxia wide based gait wide based gait– Not lateralized +/- Symmetric nystagmus Not lateralized +/- Symmetric nystagmus toxic, metabolic, toxic, metabolic,
inflammatory or neurodegenerative dis.inflammatory or neurodegenerative dis.– Asymmetric ataxia Asymmetric ataxia structural dis. Ischemia, tumor or mass structural dis. Ischemia, tumor or mass
lesionlesion– Visual cuesVisual cues– C. limb ataxiaC. limb ataxia
Dysmetria Dysmetria DysdiadochokinesiaDysdiadochokinesia TremorTremor Past pointing / reboundPast pointing / rebound
– C. nystagmusC. nystagmus– HypotoniaHypotonia– DysarthriaDysarthria
99
Cerebellar SyndromesCerebellar Syndromes
The Rostral Vermis Sundrome [ant.lobe]The Rostral Vermis Sundrome [ant.lobe]– Wide-based stance and gaitWide-based stance and gait– Ataxia of Gait vs. heel-to shinAtaxia of Gait vs. heel-to shin– Arm coordinationArm coordination Nl/impaired Nl/impaired– Hypotonia/nystagmus/dysarthria Hypotonia/nystagmus/dysarthria infrequent infrequent
Cerebellar cortical degeneration Cerebellar cortical degeneration of Chr. Alcoholicsof Chr. Alcoholics– Ant & sup vermisAnt & sup vermis
1010
Caudal Vermis Synd [Floculonodular & Caudal Vermis Synd [Floculonodular & post lobe]post lobe]– Axial dysequilibirium & staggering gaitAxial dysequilibirium & staggering gait– Little or no limb ataxiaLittle or no limb ataxia– +/- nystagmus &rotated head posture+/- nystagmus &rotated head posture– S/S of Inc ICPS/S of Inc ICP
medulloblastomamedulloblastoma
1111
Cerebellar Hemispheric SyndCerebellar Hemispheric Synd– Mvts requiring fine coord. [ms controlled Mvts requiring fine coord. [ms controlled
by the precentral cx]by the precentral cx]
Infarcts, neoplasm, and abscessesInfarcts, neoplasm, and abscesses Pancerebellar SyndromePancerebellar Syndrome
– Trunk, limbs, cranial msTrunk, limbs, cranial ms– Infectious and parainfectious, Infectious and parainfectious,
Hypoglycemia, hyperthermia, Hypoglycemia, hyperthermia, paraneoplastic d/o, and other toxic-paraneoplastic d/o, and other toxic-metabolic d/osmetabolic d/os
1212
Syndromes of cerebellar infarctionSyndromes of cerebellar infarction
Thrombotic or embolicThrombotic or embolic– Limb & gait ataxia, dysarthria, nyst, & altered mental sttusLimb & gait ataxia, dysarthria, nyst, & altered mental sttus– With/without BS and 4With/without BS and 4thth vent compression vent compression
LargeLarge occiputal headache vetigo, N/V, gait occiputal headache vetigo, N/V, gait unsteadiness and dysarthria, unsteadiness and dysarthria, obst hydrocephalus obst hydrocephalus
neck stiffness,neck stiffness,– HerniationHerniation CR sx VS. MB compression CR sx VS. MB compression PICA, SCA or bothPICA, SCA or both
Border zoneBorder zone not easily localizable not easily localizable
– 47 pts47 pts : cardiac arrest [4%], Atheroma or : cardiac arrest [4%], Atheroma or hypercoagulable state [20%], Large art VB occlusive dis. hypercoagulable state [20%], Large art VB occlusive dis. [34%], Brain embolism [23%], unknown mechanism [19%][34%], Brain embolism [23%], unknown mechanism [19%]
1313
ApproachApproach
Hx Hx Duration, Neurologic Sx, Duration, Neurologic Sx, Alcohol, Nutritional…Alcohol, Nutritional…
Exam –sensory/ motorExam –sensory/ motor Evaluation for Vit. BEvaluation for Vit. B1212 def. def.
Imaging studiesImaging studies
1414
Neuromuscular Junction Dis.Neuromuscular Junction Dis.
Fatigable/ ptosis, diplopia or bulbar Fatigable/ ptosis, diplopia or bulbar weaknessweakness
Proximal weaknessProximal weakness Normal mental fNormal mental fnn, , FluctuatingFluctuating Ms tone/Reflexes/AtrophyMs tone/Reflexes/Atrophy Most often gradualMost often gradual
1515
Major causes of intermittent generalized Major causes of intermittent generalized weakness are:weakness are:– Electrolyte disturbancesElectrolyte disturbances– Ms disorders [channelopathies, metabolic defects]Ms disorders [channelopathies, metabolic defects]– NMJ disorders [MG, LEMS]NMJ disorders [MG, LEMS]
Myopathic Myopathic proximal and are rarely limited to proximal and are rarely limited to the limbsthe limbs
Proximal weakness of 2/4 limbsProximal weakness of 2/4 limbs ms, less ms, less commonly, NMJ or AHCcommonly, NMJ or AHC– MyopathyMyopathy pelvic or shoulder girdle ms pelvic or shoulder girdle ms– NM disorders such as MG NM disorders such as MG Proximal weakness ass Proximal weakness ass
with ptosis,diplopia or bulbar weakness & fluctuating with ptosis,diplopia or bulbar weakness & fluctuating in severity during the dayin severity during the day
– The proximal weakness of AHC disThe proximal weakness of AHC dis asymmetric asymmetric Numbness is absent in allNumbness is absent in all sensation is intactsensation is intact
1616
Myasthenia GravisMyasthenia Gravis
AutoantibodyAutoantibody anti AchR anti AchR The most common [1 in 7500]]The most common [1 in 7500]] Fatigable weaknessFatigable weakness The cranial msThe cranial ms Early Early
– Diplopia, ptosis, Chewing, speech, Diplopia, ptosis, Chewing, speech, regurgitation, aspirationregurgitation, aspiration
– 85% 85% generalized generalized– DTR & sensationDTR & sensation preserved preserved– Response to Tx, RNSResponse to Tx, RNS
1717
DDXDDX
Neurasthenia Neurasthenia nonorganic nonorganic Drug induced myastheniaDrug induced myasthenia LEMSLEMS presynaptic/ auto Ab against Ca presynaptic/ auto Ab against Ca++++
channels[85%]channels[85%]– Often ass with malignancyOften ass with malignancy
Hyper-/hypothyroidismHyper-/hypothyroidism inc. myasthenic weakness inc. myasthenic weakness Grave’s disease VS. ocular MGGrave’s disease VS. ocular MG BotulismBotulism pupil and Incremental RNS pupil and Incremental RNS Intracranial mass lesion Intracranial mass lesion Congenital myasthenic syndromeCongenital myasthenic syndrome
1818
The Brachial PlexusThe Brachial Plexus
CC55-T-T11 to the entire UL + to the entire UL + shoulder and neck msshoulder and neck ms
root, trunk, division, cords root, trunk, division, cords and branches.and branches.
5 major nerves: Axillary, 5 major nerves: Axillary, Radial [posterior], Radial [posterior], Musculocutaneous Musculocutaneous [Lateral], Ulnar [medial] [Lateral], Ulnar [medial] and Median [lateral + and Median [lateral + Medial]Medial]
PlexopathyPlexopathy Diffuse Diffuse focused study of PNsfocused study of PNs
RadiculopthyRadiculopthy sensation sensation is sparedis spared
Most B.P Most B.P regional regional involvement involvement localizing to localizing to the specific region in the the specific region in the B.P B.P 11stst step step then easy then easy
1919
General rulesGeneral rules– Weakness in a “myotomal” patternWeakness in a “myotomal” patternC8 to T1 msC8 to T1 mslower trunk/medial cord lower trunk/medial cord C5 and C6 ms C5 and C6 ms upper trunk/lateral cord upper trunk/lateral cordisolated to a single nr is unlikely to be of plexus isolated to a single nr is unlikely to be of plexus
origin, origin, Inv’t of ms innervated by Radial & axill nrInv’t of ms innervated by Radial & axill nrPost Post
cordcordIsolated middle trunkIsolated middle trunkunheardunheard C7 radiculopathy C7 radiculopathyFixed sensory loss extending into the medial Fixed sensory loss extending into the medial
forearm forearm lower trunk/medial cord plexopathy; lower trunk/medial cord plexopathy; sensory loss extending into the lat forearm sensory loss extending into the lat forearm upper trunk/lateral cord plexopathy upper trunk/lateral cord plexopathy
2121
Weakness of the serratus Weakness of the serratus anterioranterior radiculopathy or a radiculopathy or a componentcomponent
Specific disorders of the brachial Specific disorders of the brachial plexus plexus
– Downward movement of the Downward movement of the shoulder results in an upper shoulder results in an upper trunk disorder (Erb's palsy)trunk disorder (Erb's palsy)
– hyperabduction hyperabduction causes a lower trunk causes a lower trunk injury (Klumpke's injury (Klumpke's palsy).palsy).
– Lower trunk Lower trunk plexopathyplexopathy by by compression compression TOS TOS
2222
Upper trunk plexopathies Upper trunk plexopathies may ff surgical may ff surgical intervention in the region of the neck.intervention in the region of the neck.
Lower trunk plexopathies also can occur Lower trunk plexopathies also can occur after chest-splitting cardiothoracic surgery. after chest-splitting cardiothoracic surgery.
Compression by tumors/masses Compression by tumors/masses lower lower trunk plexopathies from “trunk plexopathies from “Pancoast tumors”Pancoast tumors”
Backpack palsyBackpack palsy —patients often present —patients often present with arm/shoulder weakness after wearing a with arm/shoulder weakness after wearing a backpack for a prolonged period of time, backpack for a prolonged period of time, suggestive of a predominantly upper trunk suggestive of a predominantly upper trunk lesion. Some sensory loss is also present. lesion. Some sensory loss is also present.
2323
RADICULOPATHYRADICULOPATHY Structural spine disease of the cervical spine Structural spine disease of the cervical spine
remains one of the most frequent problems remains one of the most frequent problems affecting the upper extremities. affecting the upper extremities. – In the young individual with an acute herniated disc, In the young individual with an acute herniated disc,
severe radiating pain, sensory loss, and weakness in severe radiating pain, sensory loss, and weakness in muscles of the myotome of the affected nerve root can muscles of the myotome of the affected nerve root can be present. be present.
– In the elderly- acute herniation of discs is uncommon;In the elderly- acute herniation of discs is uncommon; cervical spondylosis 2cervical spondylosis 2oo to disc degeneration, to disc degeneration, calcification,…calcification,… more frequent --.they often present more frequent --.they often present present with more diffuse pain, sensory loss, and present with more diffuse pain, sensory loss, and weakness. weakness. involvement of multiple myotomes involvement of multiple myotomes
– Head turning, coughing, or sneezing may exacerbate Head turning, coughing, or sneezing may exacerbate symptoms, regardless of age. symptoms, regardless of age.
C7 radiculopathies C7 radiculopathies 70%. C6 n 19 to 25 %; C8 in 70%. C6 n 19 to 25 %; C8 in 4 to 10 %; and C5 in 2 %. 4 to 10 %; and C5 in 2 %.
2424
C5 radiculopathyC5 radiculopathy — Sry loss — Sry lossproximal lat arm. proximal lat arm. Weakness Weakness shoulder muscles including deltoid shoulder muscles including deltoid and biceps brachii . Biceps reflex- lostand biceps brachii . Biceps reflex- lost
C6 radiculopathyC6 radiculopathy — Sry loss — Sry loss lat forearm and lat forearm and digit 1 of the hand. Weaknessdigit 1 of the hand. Weaknessbiceps and biceps and brachioradialis, deltoid, pronator teres, and triceps brachioradialis, deltoid, pronator teres, and triceps minimally. Biceps and brachioradialis reflexminimally. Biceps and brachioradialis reflex lost lost
C7 radiculopathyC7 radiculopathy — Sry loss — Sry loss digits 2 to 4, with digits 2 to 4, with digit 3 most affected. Weaknessdigit 3 most affected. Weakness triceps , wrist triceps , wrist flexors, pronator teres, and wrist extensors. flexors, pronator teres, and wrist extensors. Triceps reflex Triceps reflex lost.lost.
C8 radiculopathyC8 radiculopathy — Sry loss — Sry loss digit 5, medial digit 5, medial hand, and medial forearm. Weaknesshand, and medial forearm. Weakness finger finger flexors, thumb abduction, interossei, and finger flexors, thumb abduction, interossei, and finger extensors. extensors.
2525
MEDIAN NERVE SYNDROMES MEDIAN NERVE SYNDROMES Pronator teres syndromePronator teres syndrome [rare] [rare]
– Entrapment Entrapment in the proximal in the proximal forearm forearm physically active . physically active .
– Forearm pain and sry loss over Forearm pain and sry loss over entire lateral palm. Sry loss over entire lateral palm. Sry loss over the thenar eminencethe thenar eminence typical, typical, Vs. from carpal tunnel Vs. from carpal tunnel syndrome syndrome
Anterior interosseous Anterior interosseous neuropathyneuropathy br around the br around the elbow. elbow. innervates the flexor innervates the flexor pollicis longus, the deep flexors pollicis longus, the deep flexors of digits 2 and 3, and pronator of digits 2 and 3, and pronator quadratus.quadratus. not sry; O/E: not sry; O/E: cannot make a standard "O"cannot make a standard "O"
2626
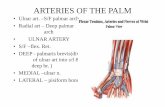
ULNAR NERVE SYNDROMES ULNAR NERVE SYNDROMES – At the elbow — Ulnar neuropathy is At the elbow — Ulnar neuropathy is
the 2the 2ndnd most common compression most common compression neuropathy.neuropathy. sry loss and sry loss and paresthesias over digits 4 and 5. & paresthesias over digits 4 and 5. & worsened grip and clumsiness. plus worsened grip and clumsiness. plus weakness in finger and wrist flexion. A weakness in finger and wrist flexion. A prominent prominent Tinel's signTinel's sign Epicondylar grooveEpicondylar groovethe Tardy ulnar palsythe Tardy ulnar palsy Entrapment as it enters the cubital tunnelEntrapment as it enters the cubital tunnel
– At the wristAt the wrist same finding – finger same finding – finger flexersflexers
2727
RADIAL NERVE SYNDROMES RADIAL NERVE SYNDROMES – At the spiral grooveAt the spiral groove ffs ffs
prolonged pressure . "prolonged pressure . "Saturday Saturday night palsynight palsy" " O/EO/E the triceps is OK the wrist, finger the triceps is OK the wrist, finger
extensors, and brachioradialis are weak. extensors, and brachioradialis are weak. Sry loss over the dorsum of the hand, Sry loss over the dorsum of the hand, possibly extending up the posterior possibly extending up the posterior forearm. Thumb abduction is affected forearm. Thumb abduction is affected as abductor pollicis longus is a radial-as abductor pollicis longus is a radial-innervated muscle. innervated muscle.
– Posterior interosseous neuropathy — Posterior interosseous neuropathy — nerve branches off just proximal to nerve branches off just proximal to the elbow and innervates the the elbow and innervates the extensor muscles of the forearmextensor muscles of the forearm O/E medial deviation of the wristO/E medial deviation of the wrist




























![The Elbo · Ulnar nerve dislocation & injury 3]. proximal ulna fracture 4]. fracture of ulnar component 5]. impingement of the radial head 6]. hardware failure 7]. Loosening 8]. Wound](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/601baef6c039f322a241fc86/the-ulnar-nerve-dislocation-injury-3-proximal-ulna-fracture-4-fracture.jpg)