Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
-
Upload
shoumi-mahapatra -
Category
Documents
-
view
237 -
download
0
Transcript of Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
1/40
1
CHAPTER: 1
1.1 INTRODUCTION TO FINACIAL MARKETS IN INDIAWITH DEFINITION:
A financial market is a market in which people and entities
can trade financial securities, commodities, and otherfungible items of value
at low transaction costs and at prices that reflect supply and demand.
Securities include stocks and bonds, and commodities include precious
metals or agricultural goods.
There are both general markets (where many commodities are traded) and
specialized markets (where only one commodity is traded). Markets work by
placing many interested buyers and sellers, including households, firms, and
government agencies, in one "place", thus making it easier for them to find
each other. An economy which relies primarily on interactions between
buyers and sellers to allocate resources is known as a market economy in
contrast either to a command economy or to a non-market economy such as
a gift economy.
In finance, financial markets facilitate:
The raising ofcapital (in the capital markets) The transfer ofrisk(in the derivatives markets) Price discovery Global transactions with integration of financial markets The transfer ofliquidity (in the money markets) International trade (in the currency markets)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trade_(financial_instrument)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Securitieshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Commodityhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fungiblehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transaction_costhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supply_and_demandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Market_economyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Command_economyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Market_economicshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gift_economyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Financehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capital_(economics)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capital_markethttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Risk#Risk_in_financehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Derivatives_markethttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liquidityhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Money_markethttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_tradehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Currency_markethttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Currency_markethttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_tradehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Money_markethttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liquidityhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Derivatives_markethttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Risk#Risk_in_financehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capital_markethttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capital_(economics)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Financehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gift_economyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Market_economicshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Command_economyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Market_economyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supply_and_demandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transaction_costhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fungiblehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Commodityhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Securitieshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trade_(financial_instrument) -
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
2/40
2
DEFINITION
In economics, typically, the term market means the aggregate of possible
buyers and sellers of a certain good or service and the transactions betweenthem.
The term "market" is sometimes used for what are more strictly exchanges,
organizations that facilitate the trade in financial securities, e.g., a stock
exchange or commodity exchange. This may be a physical location (like
the NYSE, BSE and NSE) or an electronic system (like NASDAQ). Much
trading of stocks takes place on an exchange; still, corporate actions (merger,
spinoff) are outside an exchange, while any two companies or people, for
whatever reason, may agree to sell stock from the one to the other without
using an exchange.
Trading of currencies and bonds is largely on a bilateral basis, although
some bonds trade on a stock exchange, and people are building electronic
systems for these as well, similar to stock exchanges.
Financial markets can be domestic or they can be international.
Therefore we can conclude saying it is any market place where buyers and
sellers participate in the trade of assets such as equities, bonds, currencies
and derivatives.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
3/40
3
1.2 TYPES OF FINANCIAL MARKETS
Within the financial sector, the term "financial markets" is often used to
refer just to the markets that are used to raise finance: for long term finance,the Capitalmarkets; for short term finance, the Moneymarkets.Money markets and capital markets are parts of financial markets. The
instruments bear differing maturities, currencies, credit risks, and structure.
Therefore they may be used to distribute the exposure.
I. CAPITAL MARKETSA capital market is a market for financial assets which have a long or
indefinite maturity. Generally it deals with long term securities which have a
maturity period of above one year. Capital market may be further divided
into:
(a) Industrial securities market
(b) Govt. securities market and
(c) Long term loans market.
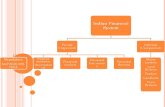
FINANCIAL
MARKETS
Capital
market
Money
market
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
4/40
4
So capital markets are financial markets for the buying and selling of long-
term debt- or equity-backed securities. These markets channel the wealth of
savers to those who can put it to long-term productive use, such as
companies or governments making long-term investments.
Thus capital market generally deals in medium and long-term funds.
Companies and governments use capital markets to raise funds for their
operations; for example, a company may issue an IPO while a government
may issue a bond in order to conduct new or expand
ongoing activities. Investors purchase securities in the capital markets in
order to extract a return and earn profit on the securities.
The market where securities are traded known as Securities market.
It consists of two different segments namely primary and secondary market.
1. Primary market :The primary market deals with new or fresh issue of securities and is,
therefore, also known as new issue market. In primary markets, new stock or
bond issues are sold to investors, often via a mechanism known
as underwriting. The main entities seeking to raise long-term funds on the
primary capital markets are governments (which may be municipal, local or
national) and business enterprises (companies). Governments tend to issue
only bonds, whereas companies often issue either equity or bonds. The main
entities purchasing the bonds or stock include pension funds, hedge
funds, sovereign wealth funds, and less commonly wealthy individuals and
investment banks trading on their own behalf.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
5/40
5
2. Secondary markets :In the secondary markets, existing securities are sold and bought among
investors or traders, usually on an exchange, over-the-counter, or elsewhere.
The existence of secondary markets increases the willingness of investors in
primary markets, as they know they are likely to be able to swiftly cash out
their investments if the need arises
The secondary market can also be further divided as:
a) Spot market:The spot market where securities are traded for immediate delivery and
payment.
b)Forward market:The forward market is a market where the securities are traded for future
delivery and payment. This forward market is further divided into
Futures and Options Market.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
6/40
6
II. MONEY MARKETSMoney market is a market for dealing with financial assets and securities
which have a maturity period of up to one year. In other words, its a
market for purely short term funds. Generally money market does not
deal in cash or money as such but simply provides a market for credit
instruments such as bills of exchange, promissory notes, commercial
paper, treasury bills, etc. These instruments help the business units, other
organizations and the Government to borrow the funds to meet their
short-term requirement. Most of the money market transactions are taken
place on telephone, fax or Internet. As money became a commodity,
the money market became a component of the financial markets for
assets involved in short-term borrowing, lending, buying and selling with
original maturities of one year or less. Trading in the money markets is
done over the counter and is wholesale.
Various instruments exist, such as Treasury bills, commercial
paper, bankers' acceptances, deposits, certificates of deposit, bills of
exchange, repurchase agreements, federal funds, and short-
lived mortgage-, and asset-backed securities. It provides liquidity funding
for the global financial system.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deposit_(finance)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deposit_(finance) -
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
7/40
7
1.3 DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MONEY MARKET AND
CAPITAL MARKET:
Money market is distinguished from capital market on the basis of thematurity period, credit instruments and the institutions:
1. Maturity Period:
The money market deals in the lending and borrowing of short-term finance
(i.e., for one year or less), while the capital market deals in the lending and
borrowing of long-term finance (i.e., for more than one year).
2. Credit Instruments:
The main credit instruments of the money market are call money, collateral
loans, acceptances, bills of exchange. On the other hand, the main
instruments used in the capital market are stocks, shares, debentures, bonds,
securities of the government.
3. Nature of Credit Instruments:
The credit instruments dealt with in the capital market are more
heterogeneous than those in money market. Some homogeneity of credit
instruments is needed for the operation of financial markets. Too much
diversity creates problems for the investors.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
8/40
8
4. Institutions:
Important institutions operating in the' money market are central banks,
commercial banks, acceptance houses, nonbank financial institutions, bill
brokers, etc. Important institutions of the capital market are stock exchanges,
commercial banks and nonbank institutions, such as insurance companies,
mortgage banks, building societies, etc.
5. Purpose of Loan:
The money market meets the short-term credit needs of business; it provides
working capital to the industrialists. The capital market, on the other hand,
caters the long-term credit needs of the industrialists and provides fixed
capital to buy land, machinery, etc.
6. Risk:
The degree of risk is small in the money market. The risk is much greater in
capital market. The maturity of one year or less gives little time for a default
to occur, so the risk is minimized. Risk varies both in degree and nature
throughout the capital market.
7. Basic Role:
The basic role of money market is that of liquidity adjustment. The basic
role of capital market is that of putting capital to work, preferably to long-
term, secure and productive employment.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
9/40
9
8. Relation with Central Bank:
The money market is closely and directly linked with central bank of the
country. The capital market feels central bank's influence, but mainly
indirectly and through the money market.
9. Market Regulation:
In the money market, commercial banks are closely regulated. In the capital
market, the institutions are not much regulated.
1.4 ROLE OF FINANCIAL MARKETS
One of the important requisite for the accelerated development of an
economy is the existence of a dynamic financial market. A financial market
helps the economy in the following manner.
Saving mobilization:
Obtaining funds from the savers or surplus units such as household
individuals, business firms, public sector units, central government, state
governments etc. is an important role played by financial markets.
Investment:
Financial markets play a crucial role in arranging to invest funds thus
collected in those units which are in need of the same.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
10/40
10
National Growth:
An important role played by financial market is that, they contributed to a
nations growth by ensuring unfettered flow of surplus funds to deficit units.
Flow of funds for productive purposes is also made possible.
Entrepreneurship growth:
Financial market contributes to the development of the entrepreneurial claw
by making available the necessary financial resources.
Industrial development:The different components of financial markets help an accelerated growth
of industrial and economic development of a country, thus contributing to
raising the standard of living and the society of well-being.
1.5 FUNCTIONS OF FINANACIAL MARKETS
Intermediary Functions:The intermediary functions of financial markets include the following:
Transfer of Resources:
Financial markets facilitate the transfer of real economic resources from
lenders to ultimate borrowers.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
11/40
11
Enhancing income:
Financial markets allow lenders to earn interest or dividend on their surplus
invisible funds, thus contributing to the enhancement of the individual and
the national income.
Productive usage:
Financial markets allow for the productive use of the fund borrowed,
enhancing the income and the gross national production.
Capital Formation:Financial markets provide a channel through which new savings flow to aid
capital formation of a country.
Price determination:
Financial markets allow for the determination of price of the traded financial
assets through the interaction of buyers and sellers. They provide a sign for
the allocation of funds in the economy based on the demand and supply
through the mechanism called price discovery process.
Sale Mechanism:
Financial markets provide a mechanism for selling of a financial asset by an
investor so as to offer the benefit of marketability and liquidity of such
assets.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
12/40
12
Information:
The activities of the participants in the financial market results in the
generation and dissemination of information to the various segments of the
market so as to reduce the cost of transaction of financial assets
Financial Functions Providing the borrower with funds so as to enable them to carry
out their investment plans.
Providing the lenders with earning assets so as to enable themto earn wealth by deploying the assets in production debentures.
Providing liquidity in the market so as to facilitate trading offunds.
it provides liquidity to commercial bank it facilitate credit creation it promotes savings it promotes investment it facilitates balance economic growth it improves trading floors
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
13/40
13
CHAPTER: 2
2.1 THE DEPOSITORY ACT
The Depositories Act, 1996, ushered in an era of efficient
capi tal market infrastructure, improved investor protection, reduced risks
and increased transparency of transactions in the securities market. It
also immensely benefited the issuer companies, in terms of reduced
costs and the
effortexpended in manag ing their s harehol der popula ce. Perh
aps, no other single Act other than Depositories Act has had such
profound al l round impact on every s ingle s takeholder in the
Ind ian cap it al mark ets . Thi s legislation envisaged multiple
depositories in India to ensure benefits of competition for the users
of the depository system
2.2 MEANING OF DEPOSITORY PARTICIPANT
In India, a Depository Participant (DP) is described as an agent of the
depository. They are the intermediaries between the depository and the
investors. The relationship between the DPs and the depository is governed
by an agreement made between the two under the Depositories Act. In a
strictly legal sense, a DP is an entity who is registered as such with SEBI
under the sub section 1A of Section 12 of the SEBI Act. As per theprovisions of this Act, a DP can offer depository-related services only after
obtaining a certificate of registration from SEBI.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
14/40
14
SEBI (D&P) Regulations, 1996 prescribe a minimum net worth of Rs. 50
lakh for stockbrokers, R&T agents and non-banking finance companies
(NBFC), for granting them a certificate of registration to act as DPs. If a
stockbroker seeks to act as a DP in more than one depository, he should
comply with the specified net worth criterion separately for each such
depository. No minimum net worth criterion has been prescribed for other
categories of DPs; however, depositories can fix a higher net worth criterion
for their DPs.
2.3 DEPOSITORY SYSTEM
A depository is an organization which holds securities (like shares,
debentures, bonds, government securities, mutual fund units etc.) of
investors in electronic form at the request of the investors through a
registered Depository Participant. It also provides services related to
transactions in securities. At present two Depositories viz. National
Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) and Central Depository Services
(India) Limited (CDSL) are registered with SEBI. The minimum net worth
stipulated by SEBI for a depository is Rs 100 crores.
Depository is an institution or a kind of organization which holds securities
with it, in which trading is done among shares, debentures, mutual funds,
derivatives, F&O and commodities. The intermediaries perform their actions
in variety of securities at Depository on behalf of their clients. Theseintermediaries are known as Depositories Participants. Depository interacts
with its clients / investors through its agents, called Depository Participants
normally known as DPs.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
15/40
15
For any investor / client, to avail the services provided by the Depository,
has to open Depository account, known as Demat A/c, with any of the DPs.
A Depository Participant (DP) is an agent of the depository through which it
interfaces with the investor and provides depository services. Public
financial institutions, scheduled commercial banks, foreign banks operating
in India with the approval of the Reserve Bank of India, state financial
corporations, custodians, stock-brokers, clearing corporations /clearing
houses, NBFCs and Registrar to an Issue or Share Transfer Agent complying
with the requirements prescribed by SEBI can be registered as DP. Banking
services can be availed through a branch whereas depository services can be
availed through a DP.
As per the available statistics at BSE and NSE, 99.9 per cent transactions
take place in dematerialized mode only. Therefore, in view of the
convenience of trading in dematerialized mode, it is advisable to have a
beneficial owner (BO) account for trading at the exchanges.
However to facilitate trading by small investors (Maximum 500 shares,
irrespective of their value) in physical mode the stock exchanges provide an
additional trading window, which gives one time facility for small investors
to sell physical shares which are in compulsory demat list. The buyer
of these shares has to demat such shares before further selling.First an
investor has to approach a DP and fill up an account opening form. Theaccount opening form must be supported by copies of any one of the
approved documents which serve as proof of identity (POI) and proof of
address (POA) as specified by SEBI. Apart from these PAN card has to be
shown in original at the time of account opening.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
16/40
16
2.4 SERVICES PROVIDED BY DEPOSITORY
Dematerialization (usually known as demat) is converting physical
certificates to electronic form Rematerialisation, known as remat, is reverse of demat, i.e. getting physical
certificates from the electronic securities
Transfer of securities, change of beneficial ownership Settlement of trades done on exchange connected to the Depository
2.5 DEPOSITORIES IN INDIA
At present there are two depositories in India, National Securities
Depository Limited (NSDL) and Central Depository Services (CDS).
NSDL is the first Indian depository; it was inaugurated in November 1996.
NSDL was set up with an initial capital of US$28mn, promoted by Industrial
Development Bank of India (IDBI), Unit Trust of India (UTI) and National
Stock Exchange of India Ltd. (NSE). Later, State Bank of India (SBI) also
became a shareholder.
The other depository is Central Depository Services (CDS). It is still in the
process of linking with the stock exchanges. It has registered around 20 DPs
and has signed up with 40 companies. It had received a certificate of
commencement of business from Sebi on February 8, 1999.
These depositories have appointed different Depository Participants (DP) for
them. An investor can open an account with any of the depositories DP. But
transfers arising out of trades on the stock exchanges can take place only
amongst account-holders with NSDLs DPs. This is because only NSDL is
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
17/40
17
linked to the stock exchanges (nine of them including the main ones-
National Stock Exchange and Bombay Stock Exchange).
In order to facilitate transfers between investors having accounts in the two
existing depositories in the country the Securities and Exchange Board of
India has asked all stock exchanges to link up with the depositories. Sebi has
also directed the companies registrar and transfer agents to effect change of
registered ownership in its books within two hours of receiving a transfer
request from the depositories. Once connected to both the depositories the
stock exchanges have also to ensure that inter-depository transfers take place
smoothly. It also involves the two depositories connecting with each other.
The NSDL and CDSL have signed an agreement for inter-depository
connectivity.
1 NATIONAL SECURITIES DEPOSITORY LIMITED
NATIONAL SECURITIES DEPOSITORY LIMITED [NSDL] is
a depository promoted by National Stock Exchange of India Limited,
IDBI, UTI, SBI and other financial institutions. NSDL commenced
operation in November 1996.
2 CENTRAL DEPOSITORY SERVICE [INDIA] LIMITED
CENTRAL DEPOSITORY SERVICE (INDIA) LIMITED
[CDSL] is a depository promoted by The Stock Exchange, Mumbai
jointly with SBI, Bank Of India, HDFC Bank and other financial
institutions. CDSL commenced its operations in July 15
th
1999.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
18/40
18
CHAPTER: 3
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO CENTRAL DEPOSITORY
SERVICE (INDIA) LIMITED [CDSL]
Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL) is the second Indian central
securities depository based in Mumbai. Its main function is the holding
securities either in certificated or uncertificated (dematerialized) form, to
enable book entry transfer of securities. CDSL is promoted by Bombay
Stock Exchange Limited (BSE) jointly with State Bank of India, Bank of
India, Bank of Baroda, HDFC Bank, Standard Chartered Bank and Union
Bank of India and CenturionBank.
A Depository facilitates holding of securities in the electronic form and
enables securities transactions to be processed by book entry. The
Depository Participant (DP), who as an agent of the depository, offers
depository services to investors. According to SEBI guidelines, financial
institutions, banks, custodians, stockbrokers, etc. are eligible to act as DPs.
The investor who is known as beneficial owner (BO) has to open a demat
account through any DP for dematerialisation of his holdings and
transferring securities.
The balances in the investors account recorded and maintained with CDSL
can be obtained through the DP. The DP is required to provide the investor,
at regular intervals, a statement of account which gives the details of the
securities holdings and transactions. The depository system has effectively
eliminated paper-based certificates which were prone to be fake, forged,
counterfeit resulting in bad deliveries. CDSL offers an efficient and
instantaneous transfer of securities.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
19/40
19
CDSL was promoted by BSE Ltd. jointly with leading banks such as State
Bank of India, Bank of India, Bank of Baroda, HDFC Bank, Standard
Chartered Bank and Union Bank of India.
CDSL was set up with the objective of providing convenient, dependable
and secure depository services at affordable cost to all market participants.
Some of the important milestones of CDSL system are:
CDSL received the certificate of commencement of business from SEBIin February, 1999.
Honorable Union Finance Minister, Shri Yashwant Sinha flagged offthe operations of CDSL on July 15, 1999.
Settlement of trades in the demat mode through BOI ShareholdingLimited, the clearing house of BSE Ltd., started in July 1999.
All leading stock exchanges like the National Stock Exchange, CalcuttaStock Exchange, Delhi Stock Exchange, The Stock Exchange,
Ahmadabad, etc have established connectivity with CDSL.
As at the end of Jan 2012, Over 10,000 issuers have admitted theirsecurities (equities, bonds, debentures, and commercial papers), units of
mutual funds, certificate of deposits etc. into the CDSL system.
A Depository facilitates holding of securities in the electronic form
ande n a b l e s s e c u r i t i e s t r a n s a c t i o n s t o b e p r o c e s s e d b y b
o o k e n t r y b y a Depository Participant (DP), who as an agent of
the depository offers depository services to investors. According to SEBI
guidelines, financial institutions, banks, custodians, stockbrokers, etc.
are eligible to act as DPs. The investor who is known as beneficial
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
20/40
20
owner (BO) has to open a demat account through any DP for
dematerialisation of his holdings and transferring securities.
The balances in the investors account recorded and maintained with CDSL
can be obtained through the DP. The DP is required to provide the
investor , a t regular in tervals , a s ta tement of account which g
ives thedetails of the securities holdings and transactions. The depository
system has effectively eliminated paper-based certificates which were prone
to be fake, forged, counterfe i t resul t ing in bad del iver ie s.
CDSL offe rs an efficient and instantaneous transfer of securities.
CDSL was promoted by Bombay Stock Exchange Limited
(BSE) joint l y with leading b anks such as State Bank of In dia,
Bank of India, Bank of Baroda, HDFC Bank, Standard Chartered
Bank, Union Bank of India and Centurion Bank.
CDSL Ventures Limited (CVL)
CDSL Ventures Limited is a subsidiary of Central Depository Services
(India) Limited. It was set with the motive to provide convenient,
dependable services at affordable prices. CDSL Ventures Limited (CVL) is
a wholly owned subsidiary of CentralDepository Services (India) Limited
(CDSL), a leading securities depository in the country. CVL derives its
confidence from its team, which has a 'Securities Market Domain
Expertise'. CVL has in place a stringent policy and systems to ensure
confidentiality of data. Strong electronic and physical security measures
ensure security of confidential data.
CSDL ventures limited (CVL) is owned subsidiary of central depository
services India limited it is one of the leading depository in the country.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
21/40
21
CSDL is promoted by Bombay stock exchange in association with most of
the leading banks such as bank of India, bank of Baroda, state bank of India,
HDFC. CDSL was set with the motive to provide convenient, dependable
services at affordable prices to all the market participants. According to
SEBI norms any one can act as depository participant (DP) which includes
banks, financial institutes, or even a stock broker and many more. Person
who wants to invest in this field is popularly known by the name beneficial
owner has to open a DMAT account through any of the depository
participant for holding and transferring securities.
3.2 WHY A DEMAT ACCOUNT WITH CDSL
WHY DEMAT
ACCOUNT WITH
CDSL
CONVINIENCE DEPEDABILITY SECURITY
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
22/40
22
WHY A DEMAT ACCOUNT WITH CDSL
CONVENIENCE:
WIDE DP NETWORK:CDSL has over 300 DPs spread around cities/towns across the country,
o f f e r i n g c o n v e n i e n c e f o r a n i n v e s t o r t o s e l e c t a D P
b a s e d o n h i s location.
ON-LINE DP SERVICES:The DPs and i t s branches can a lso be d i rec t ly connected to
CDSL thereby providing on-line and efficient depository service to
investors.
WIDE SPECTRUM OF SECURITIES AVAILABLE FOR DEMAT:Over-5000 users have admitted their securities in CDSL consisting of debt
instruments viz. bonds, debentures, commercial paper, government
securities, certificate of deposits, etc. Thus an investor can hold almost all
his securities in one account with CDSL.
COMPETITIVE FEES STRUCTURE:C D S L h a s k e p t i t s t a r i f f s v e r y c o m p e t i t i v e t o p r o v i d e
a f f o r d a b l e depository services to investors.
INTERNET ACCESS:A DP of CDSL can provide to its BOs their demat account
statement along with a valuation of their holding as per the last
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
23/40
23
traded price on BS E an d a su m m a r y o f t h e i r t r an sa c t i o n s
f o r a l l a c c o u n t h o l d e r s through CDSLs internet facility easi. The
BOs can also avail of the facility of execution of all types of
transactions viz, on market, off-market and inter-depository, through
CDSLs internet facility easiest.
DEPENDABILITY:
ON-LINE INFORMATION TO USERS: CDSL's system is built on a centralized database architecture and
thusenab les DPs t o pr ovid e on -
li ne de po si to ry se rv ic es wi th th e la te st status of the investor's
account.
C O N V E N I E N T T O D P S :In case any system related problem develops at the DPs end, it
doesn o t a f f e c t t h e B O s i n t e r e s t i n a n y w a y a s t h e C D S L
d a t a b a s e i s maintained centrally.
CONTINGENCY ARRANGEMENTS:CDSL has made provisions for contingency terminals, which enables aDP
to update transactions, in case of any system related problems at the
DP's office.
MEETING USER'S REQUIREMENTS: C o n t i n u o u s u p d a t i o n o f p r o c e d u r e s a n d p r o c e s s e s i n t u
n e w i t h evolving market practices is another hallmark of CDSL's system.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
24/40
24
AUDIT AND INSPECTION:C D S L c o n d u c t s r e g u l a r a u d i t o f i t s D P s t o e n s u r e c o m p
l i a n c e o f stringent operational and regulatory requirements.
SECURITY:
COMPUTER SYSTEMS:CDSL has state-of-the-art computer systems, data storage methods and
communication networks which ensure the security and integrity of all data
uninterruptedly. All data at CDSL and is automatically mirrored
and t ransmi t ted to a Disas ter Recovery s i te , which i s located
away from the main site.
UNIQUE BO ACCOUNT NUMBER:Each BO in CDSL is allotted a unique account number. This
preventsw r o n g t r a n s f e r o f s e c u r i t i e s i n t h e e v e n t t h e t r a n
s f e r e e s a c c o u n t number is keyed in wrongly.
SYSTEM ACCESS:Only a person at the DPs end who has been pre authorized by
CDSL can access the CDSL system.
INSURANCE COVER:CDSL has obta ined adequate insurance cover for any
unl ikely loss occurring to a BO due to the negligence of CDSL
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
25/40
25
3.3 BENEFITS OF CDSL:
Dematerialization of securities with CDSL offers numerous benefits to
the issuer of securities. Some of the benefits are:
In the demat form transfer of securities takes place at CDSL and if theentire issue of a security is held in demat form, the issuer can
save considerable t ime and money being incur red on i t s
share department.
Demat ted secur i t ies are not subjec t to loss , thef t , mut i lat ion o r misuse by faking or forging certificates, thereby saving
companies from lengthy correspondence, litigation and complaint
handling. It will therefore eliminate instances of bad delivery.
All noncash corpora te ac t ions such as r ights , bonus, merg er s, consolidations, subdivision of holdings, conversion ofsecurities, issuing securities on mergers/amalgamations and in
initial public offerings (IPO) can be handled in demat form
without any hassles in the shortest possible time and at very low
cost.
With the CDSL's centralized database, the issuer can get upto-the-moment informat ion on any ch anges in i ts holding
pat te rn of a securi ty.
Thus, the company ef fec t ive ly moni tors the change in
holding and is alert to any undue threat.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
26/40
26
CHAPTER: 4
4.1 SERVICES OFFERED BY CDSL
The Depository Participant (DP) is the link between the investor, the
company and CDSL and provides the following services:
Account OpeningTo utilize the services offered by a depository, any person having investment
in any security or intending to invest in securities needs to have a demat
account with a CDSL-DP. The holder of such demat account is called
as "Beneficial Owner (BO)". A BO can maintain a demat account with
zero balance in such account. A BO can open more than one account with
the same or multiple DPs, in the same name/s and order, if he/she desires so.
The investor can approach any DP/s of his/her choice to open a demat
account.
DematerializationDematerialization is a process by which physical certificates (of shares /
debentures / other securities) are converted into electronic balances. A BO
has to submit the request for dematerialization by submitting the demat
request form (DRF) duly completed along with the concerned physical
certificates, to his/her DP.
Processing Delivery & Receipt InstructionsTo settle trades done on a stock exchange (on-market trades) and trades,
which are directly settled between two BOs (off-market trades), BOs submit
duly completed delivery instructions in the prescribed form to DP. For
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
27/40
27
receipt of securities into his/her account, a BO can give one time "standing
instruction" to DP. Once such a standing instruction is given to the DP, there
is no need to submit separate instructions for receipt every time the investor
buys securities.
Account StatementGenerally a DP sends to the BO, a statement of his account, monthly, if there
is any transaction in the account or every quarter if the account is not
operated during that period. The balances and transactions can also be
viewed by the BOs through CDSL web based facility 'easi'
RematerialisationRematerialisation is the process by which the electronic balances held in the
demat account can be converted back into physical certificates
PledgingIf the BO decides to pledge any securities in his BO account, he can avail of
the same by submitting the pledge creation form duly completed, to his DP.
NominationIndividual BOs have a facility for nomination in favor of an individual. If
the sole or all the joint holders are deceased, the shares of different
companies held in the demat account will be transmitted easily to the demat
account of the nominee on submission of the death certificate and
transmission form. It may be noted that in the event of the death of one of
the joint holders, the securities will be transmitted in the demat account of
the surviving holders.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
28/40
28
Transmission of securitiesCDSL offers a facility for transmission of balances held in BO
account/s (to other BO account/s) if so required due to death, lunacy,
bankruptcy, insolvency or required due to operation of any law.
Change in AddressA BO who wishes to register his change in address submits his/her
request in writing to his/her DP. The changes entered by the DP in the
CDSL system will be automatically downloaded to all the companies
in which the BO is holding securities. This facility offered by CDSL
saves money, time and effort for the BO.
Bank Account DetailsSEBI has made it mandatory for companies to print details of bank
account of the BO on dividend/interest warrants etc. to prevent
possibilities of misuse of the warrants. All BOs should submit a
request in writing to the DP if they wish to record / change their bank
account details.
SMSCDSL sends SMS regarding transactions and modifications in account
details to the mobile number registered in the account.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
29/40
29
4.2 FEATURES OF CDSL
Convenience: Wide DP Network:
CDSL has a wide network of DPs, operating from over 10,000 sites, across
the country, offering convenience for an investor to select a DP based on his
location.
On-line DP Services:The DPs are directly connected to CDSL thereby providing on-line and
efficient depository service to investors.
Wide Spectrum of Securities Available for Demat:The equity shares of almost all A, B1 & B2 group companies are available
for dematerialisation on CDSL, consisting of Public (listed & unlisted)
Limited and Private Limited companies. These securities include equities,
bonds, units of mutual funds, Govt. securities, Commercial papers,
Certificate of deposits; etc. Thus, an investor can hold almost all his
securities in one account with CDSL. A BO can also hold warehouse
receipts pertaining to commodities, in a demat account. However, a separate
account should be opened for holding warehouse receipts.
Competitive Fees Structure:CDSL has kept its tariffs very competitive to provide affordable depository
services to investors.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
30/40
30
Internet Access:
A DP, which registers itself with CDSL for Internet access, can in turn
provide demat account holders with access to their account on the Internet.
Dependability: On-line Information to Users:
CDSL's system is built on centralized database architecture and thus enables
DPs to provide on-line depository services with the latest status of the
investor's account.
Convenient to DPs: The entire database of investors is stored centrally atCDSL. If there is any system-related issues at DPs end, the investor is not
affected, as the entire data is available at CDSL.
Contingency Arrangements:CDSL has made provisions for contingency terminals, which enables a DP
to update transactions, in case of any system related problems at the DP's
office.
Meeting User's Requirements:Continuous updating of procedures and processes in tune with evolving
market practices is another hallmark of CDSL's services.
Audit and Inspection:CDSL conducts regular audit of its DPs to ensure compliance of operational
and regulatory requirements.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
31/40
31
Dormant Account Monitoring:CDSL has in place a mechanism for monitoring dormant accounts.
Helpdesk:DPs and investors can obtain clarifications and guidance from CDSL's
prompt and courteous helpline facility.
Security: Computer Systems:
All data held at CDSL is automatically mirrored at the Disaster Recovery
site and is also backed up and stored in fireproof cabinets at the main and
disaster recovery site.
Unique BO Account Number:Every BO in CDSL is allotted a unique account number, which prevents any
erroneous entry or transfer of securities. If the transferor's account number is
wrongly entered, the transaction will not go through the CDSL system,
unless corrected.
Data Security:All data and communications between CDSL and its users are encrypted to
ensure its security and integrity.
Claims on DP:
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
32/40
32
If any DP of CDSL goes into liquidation, the creditors of the DP will have
no access to the holdings of the BO.
Insurance Cover:CDSL has an insurance cover in the unlikely event of loss to a BO due to the
negligence of CDSL or its DPs.
4.3 TECHNOGOLIES USED IN CDSL
Software:The software is developed and supported by CMC Ltd., who have also
developed the BOLT system for BSE and Indian Railway Reservation
System. The software is a modified version of the banking software-TC4
developed by a subsidiary of CMC Ltd. (in USA), which is currently being
used by several banks worldwide. The software has been customised to suit
the requirement of CDSL.
HardwareThe server infra structure is procured from Hewlett Packard Company. The
hardware systems at CDSL is powered by mission critical HP UNIX
operating system, which is proven for Reliability, Scalability and High
Availability These systems are highly scalable and provide main frame class
Reliability and Robustness.
This system is connected to one of the most robust and secure storage
systems in the world from EMC, the world leader in products, services, and
solutions for information storage and management. CDSL has invested in an
end-to-end fiber architecture storage system, which combines Fiber Channel
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
33/40
33
connectivity, non-disruptive capacity and performance scalability, multiple
processors, resulting in faster performance, continuous data availability and
data integrity. The EMC systems also provide the most advanced software
capabilities, including full and incremental replication and anytime/any
distance mirroring for business continuity protection.
Database ArchitectureCDSL has gone in for a centralised database system. This centralised
architecture provides distinct advantages to the users. The initial set-up cost
for Issuer Companies/their RTAs and Depository Participants is low.
Information on investor's holdings is available to the Depository Participantand the Issuer or its RTA instantly.
Disaster Recovery Site (DRS)From the business continuity angle, CDSL has in place, a robust system with
multiple back-up levels including a redundant fail-over cluster and a DRS,
Located at a different seismic zone over 1000 kms from the main site.
Consequently, in the event of a disaster at the main site, users connected to
the CDSL connectivity network viz. Depository Participants (DPs), Clearing
Corporations and Registrar & Transfer Agents (RTAs) can electronically
connect to the DRS for seamlessly carrying on day-to-day operations.
Information SecurityCDSL has committed itself to highest level of information security practices
and is committed to maintain the Confidently, Integrity and Availability of
all its information, in any from whatsoever. Towards, this end CDSL has
complied with ISO 27001 Standards and has been awarded the coveted ISO
27001 certificate by leading certification body.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
34/40
34
Business ContinuityCDSL is one of the few depository institutions in the world to be awarded
ISO22301:2012 certification for it Business continuity Management Systems
in June 2013. It is a step to assure all its stakeholders across the world for
uninterrupted operations of CDSL depository services.
4.4 CDSL LATEST NEWS:
CDSL has s igned a Memorandum of Unders tanding (MOU)
with The Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation [DTCC] of New York,
designed to build a cooperative relationship. Under the terms of
the MOU, DTCC and CDSL will establ ish a mechanism whereby
board members, senior management and s taff of both s ides
co ul d me et on a reg ula r ba si s t o i n c r e a s e m u t u a l
u n d e r s t a n d i n g
a n d e x c h a n g e m a r k e t u p d a t e i mp ro v em e nt o p p o rt u n
i t i e s a n d i n f o r m a t i o n o n b u s i n e s s o p e r a t i n g models.
CDSL AND DTCC (U.S.A.) SIGN INFORMATION
SHARING AND COLLABORATION PACT
The MOU noted that the parties anticipate developing a closer
working re la t ionship in the fu ture and wish to mainta in chan
nels of communicat ion for exchange of informat ion and to
promote v is i t s for reasons of friendship and other businesspurposes.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
35/40
35
India is one of the fastest growing areas of the world and CDSL is a major
part of the securities infrastructure in the country, said Donald F Donahue
DTCC Chai rman e lec t and Chief Execut ive Off icer . This
agreement with CDSL will give us a structure to exchange ideas,
share market insights and develop coordinated ways of working with each
otherin what is rapidly becoming a global trading environment.
The MOU with DTCC is an extension of the good relations that
CDSL shares with them. I see it as an initial formal handshake, the
beginning of a long and mutual ly benefi cial
business re la t ionship , sa id Vi jay V. Raut , CDSL Managing
Director & CEO. We are sure that th is event wi l l resul t
insignificant, tangible benefits, not just to both organizations but also to
ours takeholders and to the secur i t ies markets a t large . He
fur ther added, Although DTCC and CDSL have different
legislative frameworks and settlement systems; it would be
beneficial for both depositor ies to share their experiences to reduce
risks and to enhance the efficiency of systems. We look forward to sharing
our experience and tapping DTCC's expertise on global market practices.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
36/40
36
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
An Individual who wants to keep his / her cash safe in a bank has to open
an account wi th a bank as a f i r s t s tep and mainta ins cash in
book entry form. Similar ly, an investor has to open a demat
account with any DP of CD SL as a f i r s t s t ep to ho ld
s e c u r i t i e s i n d e m a t f o r m i n t h e d ep os it or y s ys te m. T he
investor can op en an account with a ny DP of CDSL. CDSL
system facilitates opening of demat account for different categories
of investors. De mat ac cou nt ope ned wi th CD SL are re fer red as
B enef ici al Owner Accountsor BO Account.When securities are held in physical form name of the investor i s
recorded in the books of the company as R e g i s t e r e d
O w n e r . W h e n t h e s a m e s e c u r i t i e s a r e c o n v e r t e d i n t o e l e
c t r o n i c f o r m a n d h e l d i n d e m a t a c c o u n t , t h e d e p o s i t o r y
b e c o m e s r e g i s t e r e d o w n e r o f t h e s e c u r i t i e s
S i n c e d e p o s i t o r y i s a c t i n g a s a c us to di an o f t he
secur i t ies , or ig inal investor i s legal ly ent i t led for a l l r ights
and l iabi l i t ies a t tached wi th the secur i t ies and i t i s ca l led as
Be ne fi ci al Owne r. All accounts opened on CDSL system are
beneficial accounts irrespective of the type of accounts. A Demat account
may be opened and maintained in the name(s) of one person or more than
one person. All he joint holders have to sign the application form
and the agreement. The supporting documents and p ho to gr ap h
should a lso be provided for a l l jo in t holders . Though
the beneficial ownership of jointly held securities vests equally in
all joint holders, communications about depository account are
provided only to the first holder.
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
37/40
37
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Books:
Financial markets and services Gordon and Natarajan
NSEs Certification in FinancialMarkets
Website:
www.cdslindia.com
www.cdsl.net.in
www.cvlindia.com
www.cdsl.co.in
http://www.cdsl.net.in/http://www.cdsl.net.in/ -
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
38/40
38
ANNEXURE
What is a depository?
Who is a Depository Participant?
What are the services provided by a DP?
What are the benefits of opening a CDSL demat account?
Can a demat account be opened directly with CDSL?
What are the benefits of opening a demat account?
What should an investor do to open a demat account?
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
39/40
39
Is it necessary for a BO to open a demat account with the same DP asthat of the broker for settling trades done through him?
How does a BO get information that the account has been updatedafter each transaction?
Is it mandatory to submit PAN card details?
Is dematerialisation of securities compulsory?
Can a sole holder of the share certificate, add/ delete any name as ajoint holder, at the time of dematerialising the share certificate?
What is the procedure for delivery of securities demats form in caseof sale of securities?
-
7/29/2019 Introduction to Finacial Markets Final with refence to cdsl
40/40
What is the procedure for delivery of securities demats form in caseof sale of securities?
What is transmission of dematerialised securities?
What are differed services provided by CDSL?