Intestinal Obstruction
-
Upload
hidayat-shariff -
Category
Documents
-
view
705 -
download
8
Transcript of Intestinal Obstruction

INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTIONPrepared by : Maziyana MusaWong Soo Ching
Supervised by :Dr.Koh Cher Hui

OUTLINE Definition Causes & Classification Sign and Symptoms Investigation Management Take home messagers

Definition : impairment or arrest of the passage of contents through the intestine.
Involve either small or large bowel.
It can be partial or complete obstruction.

CLASSIFICATION
Nature Site of obstruction Blood supply Rate Small bowel or large bowel

Nature Dynamic
mechanical obstruction Adynamic
no structural obstructionie: paralytic ileus – absence of normal peristalsis contraction. Causes :1. post-abdominal surgery 2. electrolyte imbalance
ie hypokalaemia 3. intra or retroperitoneal inflammation ie appendicitis, diverticulitis 4. reduce blood supply to abdomen
ie mesentric artery ischaemia

Location Intraluminal
- colorectal carcinoma- constipation (faecal impaction)- foreign body
Intramural- strictures
ie Crohns, Diverticular Disease, due to radiation
- acute pseudo-obstructionie Olgivie Syndrome

Extramural- adhesion
- hernia
- volvulus-bowel twisted on its mesentry which
cause rapid, severe strangulated obstruction
-common site : sigmoid- intussusception
bowel telescoped into its distal segment
Peritonitis
Previous abdominal surgery
Congenital adhesion band
obstructedstrangulate
d

Blood supply Simple obstruction
- without vascular compromise- ingested fluids, foods, gas and digestive secretion accumulate above obstruction.- proximal bowel distended- bowel wall become edematous as reduce secretion and absorption function of mucosa
Strangulated obstruction- compromise blood flow- usually associated with hernia, volvulus and intussusception - can progress to infarction and gangrenous
bowel in 6hours

Closed loop obstruction- 2 points along the course of bowel are
obstructed at a single location, thus forming closed loop obstruction
- ie : recto sigmoid tumour which caused intestinal obstruction.
- Proximal bowel distends and decompression into small bowel depends on competency of
ileo caecal valve. - Competent ileo caecal valve prevent decompression and lead to distension of large bowel particularly caecum. - Increase intraluminal pressure of caecum
impedes blood flow which then can results in caecum perforation.

Rate Acute
sudden onset, rapidly progressive abdominal pain, vomiting, constipation and abdominal distension.
Chronicsign and symptoms of intestinal
obstruction slowly develop over time.

Small bowel obstruction- sudden onset- abdominal pain - vomiting- constipation- AXR : central, valvulae conniventes
Large bowel obstruction- mild symptoms that develop gradually- constipation- abdominal distension- crampy abdominal pain- vomiting - AXR : peripheral, haustra

4 Cardinal features of IO Abdominal pain Vomiting Constipation Abdominal distension

How To Approach Intestinal Obstruction?
Visible scar -band-adhesion
Palpation•hernial orifices
•large, slightly tender, mobile•mass changes its position with colicky pain•tender indurated mass•hard impacted masses
-incarcerated -strangulated hernia+torsion+intussusception-mass of Ascaris worms
+intraperitoneal abscess-fecaloma
GENERAL EXAMINATION:

Percussion - tympanic soundAuscultation -runs of borborygmi
-tinkling high pitched musical sounds
Rectal examination•fresh blood and mucus
•hard mass of faeces•hard mass in the rectovesical pouch
-strangulating lesion-carcinoma of large gut-intussusception+constipation-extraintestinal tumour

How To Initiate Investigation?Lab investigation:•FBC
•BUSE•Clotting profile•Arterial blood gasses• Optional (ESR, CRP,
Hepatitis profile, tumour markers)
-high Hb and hematocrit-leukocytosis-anaemia+electrolytes depletion
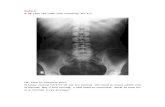
Radiological:•X-RAYS -Gas pattern
-Fluid level-Masses shadow-Fecal pattern

• USE -free fluid-masses-mucosal folds-pattern of paristalsis
• CT, MRI, Contrast studies -level of obstruction-partial or complete-cause of the obstruction
• Optional (colonoscopy, endoscopy, laparoscopy)

Large Bowel: Small Bowel:•Peripheral•Diameter ~8 cm•Presence of haustration
•Central•Diameter ~5 cm•Vulvulae coniventae•Ileum: may appear tubeless

Multiple air fluid levels located centrally-small bowel obstruction
Small bowel volvulus-coffee bean appearance.

Air fluid level centrally-small bowel obstruction
Small intestinal invagination

How to manage intestinal obstruction? Conservative Operative
Conservative treatment Nasogastric tube
to help decompress the dilated bowel aspirate it with a 20 or 50 ml syringe half- hourly
CBD To monitor urine output

IV Fluids Normal saline or lactated ringer’s solution for
intravascular volume depletion Electrolytes correction
Guided by test results Analgesic
Opioid pain relievers may be used for patients with severe pain
Antibiotics If bowel ischemia or infarction is suspected

Operative repair of hernias removal of foreign bodies lysis of the offending adhesions Resection colostomy.

Indication For Surgery: Immediate intervention:
Evidence of strangulation (hernia….etc) Signs of peritonitis resulting from perforation or
ischemia
In the next 24-48 hours Clear indication of no resolution of obstruction
( Clinical, radiological). Diagnosis is unclear in a virgin abdomen
Intermediate stage The cause has been diagnosed and the patient is
stabalised

Take Home Messages: The 4 main Cardical signs of intestinal obstruction
are Abdominal pain, Abdominal distention, Vomiting and Constipation.
Always examine for hernia orifice. Follow-up lab results and correction of electrolyte
imbalance. Always request for Supine, Erect and CXR. Always provide adequate resusitation to the patient. Always be attentive of signs of peritonitis resulting
from perforation or ischemia of bowel.

References :- Manipal manual of surgery by K Rajgopal Shenoy- Life in the fast lane journal- Surgery International Journal- www.meb.uni-bonn.de- www.merckmanuals.com- www.radiologyassistant- emedicine.medscape.com