Intestinal obstruction neo
-
Upload
nawin-kumar -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
281 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Intestinal obstruction neo

Intestinal obstruction
Dr nawin kumar

1. Dynamic- mechanical
obstruction
2. Adynamic- – Peristalsis –absent – Peristalsis -non-
propulsive form


Pathology
Proximal to obstruction– Altered mobility
– Distension
Distal to obstruction
– Normal peristalsis
– Absorption

Pathology
Proximal to obstruction – Altered mobility
– Distension
– Dilates
– flaccid
– Paralysis
• Exhaustion
• to prevent Viability

Distension
Gas– Swallowed air– Diffusion from blood– Products of digestion and bacterial activity– O2 & CO2 reabsorbed– Nitrogen 90% and H2S
Fluid– Digestive juice
– No absorption of food

• Electrolyte imbalance– Reduced intake– Defective intestinal absorption– Vomitintg– sequestration

• Distal to obstruction
– Normal peristalsis
– Absorption
– Empty and contracted
– immobile

• Veins compressed first - Edema
and hemorrhages
• Arterial compression –
Haemorrhagic infarction
• Translocation of bacteria, toxins
and systemic absorption

Strangulation External Internal
• Smaller absorptive surface
• Short segment – Less blood and fluid loss
• Larger absorptive surface
• Large segment – More blood and fluid loss - shock

Closed loop obstruction
• Obstruction both at proximal
and distal point
– Strangulated loops
– Colonic obstruction with a
competent ileocecal valve

Special types
• Internal hernia
• Entric stricture
• Bolus obstruction
• Adhesion and bands
• Intussusception
• volvulus

Clinical features
• Classical qurtet
1. Pain
2. Vomiting
3. Distension
4. Constipation

pain
• Colicky
• Mild constant diffuse
• severe

vomiting
• Proximal- more vomiting
• With time– Undigested food to faeculant

distension
• More distal- more distension

constipation
• Absolute
• Relative
• Absent in– Richter’s hernia– Gall stone obstruction– Mesentric vascular obstruction– obstruction with pelvic abscess– Partial obstruction- faecolith, neoplasm

Levels
• Small bowel obstruction– High– low
• Large bowel obstruction

Levels
• Small bowel obstruction- High– Early vomiting– Rapid dehydration– Minimal distension– X ray -fluid level ?

Levels
• Small bowel obstruction- low– Pain- prominent– Late vomiting– Central distension– X ray -fluid level - multiple

Levels
• Large bowel obstruction– Early distension, severe– Late vomiting, dehydration– Pain mild– X ray –caecum , ascending colon distended

Nature of presentation
• Acute- SB, sudden onset of pain• Chronic- LB, constipation,
distension• Acute on Chronic- recurrant• Subacute- constipation?

Other features
• Dehydration
• Hypokalemia
• Pyrexia –
Ischemia/perforation/Inflammatory obs.
• Hypothermia
• Abdominal tenderness

Type of presentation
• Simple – Intact blood supply
• Strangulated – Compromised blood supply


Signs of strangulation
• Continous pain
• Localised tenderness, rigidity,
rebound tenderness
• Shock
• Does not respond to conservative
management

Radiology
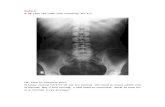
• X – ray abdomen ErectAir fluid levels
• X – ray abdomen SupineDistended bowel


Small bowel
• Central and transverse lie
• Jejunum – Valvulae conniventes
(concertina / Stack of coins)
• Ileum – Characterless
• Colon – Haustral folds

Treatment
• Gastrointestinal drainage
• Fluid and electrolyte replacement
• Relief of obstruction

Timing of surgery• Emergent
Obstructed/strangulated Ext hernia
Internal intestinal strangulation
Acute obstruction
• Other cases
Atleast within 24 hrs
• Adhesions
upto 72hrs

Principles of Surgical intervention
• Mt. of the segment at the site of
obstruction
• The distended proximal bowel
• Underlying cause of obstruction

assessment
• Site of obstruction
• Nature of obstruction
• Viability of gut

Site of obstruction
Caecum
Dilated Not dilated
Large bowel Small bowel
Trace distally Trace proximally

Nature of obstruction

Viability of bowelViable
Dark color – Light Dark persists
Mesentery bleeds on pricking
No bleeding
Peritoneum – Shiny Dull & Lustreless
Int Musc – Firm, Peristalsis seen
Flabby, thin, friable
Non viable
Mesenteric pulsation + Absent

Doubtful – Resected ends as stomas
No resection / Multiple ischaemic areas (Mesenteric Vasc Occlusion)
2nd look laparotomy after 24-48hrs

Surgical procedure
• Adhesiolysis
• Excision / Resection
• Bypass / Proximal decompression

Operative decompression
• Compromise of Exposure / Viability / Closure
• Septic complications of spillage
• Savage’s decompressor / NG tube
• Replace fluid

Large bowel obstruction
Caecum to Prox trans colon
– Rt. Hemicolectomy, if resectable
– Ileotransverse bypass if not
resectable
Splenic flexure
– Extended Rt.Hemicolectomy

Left colon / Rectosigmoid
• Decompression proximal colostomy
• Resection with – Anastamosis with covering colostomy– Paul Mikulicz procedure– Hartmann’s procedure

Thank youThank you

SPECIAL TYPES
• internal hernia• Enteric Stricture• Bolus obstruction
– Gallstone – Food– Bezoars
• Adhesion and bands• Intussusception• volvulus

INTERNAL HERNIA
• Internal hernia– Retroperitoneal fossa
• Duodenal fossa-– Left– right
• Caecal/appendicaeal fossa– Superior– Inferior– retrocaecal
• Intersigmoid fossa
– Congenital peritoneal defect• Foramen of winslow• Hole in mesentry, mesocolon, broad ligament
– Diaphragmatic hernia

• Duodenal fossa-
– Left– right

• Caecal/appendicaeal fossa
– Superior

• Caecal/appendicaeal fossa
– Inferior

• Retrocaecal fossa

intersigmoid

Foramen of winslow

• Release the constriction agent by division
• Donot-• Duodenal fossa-
• Foramen of winslow
• Hole in mesentry, mesocolon, broad ligament
• Decompress and reduce

Enteric Stricture
• Benign– TB– Chrohn’s
• Malignant– Lymphoma– Ca – sar

Enteric Stricture
• t/t– RA– stricturoplasty

bolus
• Gall stone
• Food
• Bezoars
• Stercolith
• worms

Gall stone
• Fistula
• 60 cm proximal to IC
• Ball valve effect
• t/t– Crush– Milk– Enterotomy– Faceted stone

food
• Post gastrectomy
• t/t– same

bezoars
• Trychobezoars
• Phytobezoars

stercolith
• Diverticula
• Stricture

worms
• Ascariasis
• Follow anti helminthic therapy
• perforation
• X ray- medusa head
• t/t

Adhesions
• Most common cause
• Difficult to differentiate from paralytic ileus

Causes• Ischaemic areas
• Foreign material
– Talc
– Starch
– gauze
– silk
• Infection – Peritonotis
– TB
• Inflammatory conditions-
• Radiation enteritis
• Drugs – Practolol

Peritoneal irritation
Local fibrin production
Adhesion between apposed surfaces
Early fibrinous adhesions Late fibrous adhesions

Prevention
• Good Surgical technique
• Peritoneal wash
• Minimizing contact with gauze
• Covering anastamosis & raw
peritoneal surfaces

Classification
• Early / Flimsy
• Late/ Dense

Bands
• Congenital
• Acquired
– Peritonitis
– Greater omentum adherent to
parietes

Treatment
• Conservative
– NPO
– RT aspiration
– IV fluids
– Vital signs & Abd. girth monitoring
– Signs of strangulation
– Maximum 72hrs

Surgery
• Adhesiolysis
– Only those causing obstruction
– Covering with omental grafts
– Constriction sites

Recurrent adhesive obstruction
• Repeat Adhesiolysis
• Noble’s plication procedure
• Charles phillip Transmesenteric plication
• Intestinal intubation

intussusception
• Telescoping
• Proximal to distal
• Children- 5-10 yr
• follow URTI
• weaning

Lead point
Inner tubeMiddleouter

types

• Strangulating
• t/t
• Radiological reduction
• Sx

volvulus
• Primary– Volvulus neonatorum– Sigmoid– Caecal– Gastric– midgut
• Secondary

Sigmoid volvulus
• Anticlockwise
• BONE

• X-ray
• Inner tube
• Cofee bean
• t/t
• Endoscopic reduction
• Sx

Caecal volvulus
• mobile

Compound volvulus
• Ileosigmoid knotting