Intestinal obstruction
-
Upload
bishal-sapkota -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
160 -
download
0
Transcript of Intestinal obstruction

CASE PRESENTATION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION
INTERN DEEPAK PAUDEL
GMCTH
DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY

68yr/M from Armala ,Ex Army by profession was admitted through GMC ER on 27th of Asad 2073( @ 10:20 PM) with chief complaints of:
• pain abdomen for 3 days• Dyspepsia for 3 days• Abdominal distention for 3 days

HOPI
• Pain - in RIF gradual on onset burning sensation
continuous started in the morning non radiating no known aggravating factor relieved by shifting position

Pain is associated with abdominal distention
water brash nausea burning micturation H/O loss of appetite

• H/O passage of hard stool• No H/O fever ,headache ,trauma• No H/0 cough ,weight loss • No H/0 vomiting.

PAST HISTORY
• H/0 appendectomy 40 yrs ago• From than ,he started to develop abdominal
pain of similar nature .• According to him, he experiences similar
problem once in every year.• Last time on Bhadra 2072 he was admitted to
GMCTH for abdominal pain ,admitted ,treated conservatively and relieved.

FAMILY HISTORY
• No such H/O in the family• no H/O of HTN, DM, TB

PERSONAL HISTORY
• Consumes alcohol occasionally.• Non vegeterian • Doesn’t smoke• But has a habit of chewing tobacco.

ALLERGIC HISTORY
• No known allergic history of any drug

• GENERAL EXAMINATION
Pt .was concious, well oriented to T,P,P lying comfortably in supine position with cannula fitted in the left hand
- Vitals R/R:-25/min
BP:- 110/70 mm of Hg in rt brachial Artery. Pulse-84beats/min Temp 98 F

• Pallor• Icterus • Lymphadenopathy nil• Clubbing• Cyanosis• Oedema nil• Dehydration

GI EXAMINATION
Inspection -umbilicus centrally placed and abdomen is
distended. -visible scar in rt iliac fossa -all quadrants move equally with respiration -no visible pulsation and peristalsis -hernial sites intact -ext. genitilia-normal

Palpation -Abdominal girth :90 cm(01) -86 cm(02) -72 cm
(04/04) -local temprature normal -tenderness on lower abdominal region -no palpable mass -no organomegaly -hernial sites intact and normal ext. genital

Percussion – resonant note - tender RIF -shifting dullness –ve
auscultation – normal bowel sound heard -no vascular bruits heard P/R exm- no mass, no blood, faeces present.

• Respiratory exmn-normal• CVS exmn- normal• CNS exmn –normal

Provisional diagnosis
• Intestinal obstruction: For abdominal pain Constipation Abdominal distention

Differential DiagnosisD/d For AgainstMeckels Diverticulitis
Pain abdomen No antecedent h/o of lower GI bleeding
Rt. Ureteric colic Abdominal PainAggravated on movement
No history of hematuriano radiation to loin

D/D For AgainstPerforated peptic ulcer
Severe pain in RIF history of dyspepsia
pain is not related to food intake.
Crohns diseases Pain abdomen No diarrhoea and wt loss

Investigation
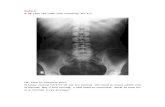
• CBC:-WBC -10,000/mm3• Na+ 141 ,k+ 4.0• USG impression : slightly prominent bowel loop. • Plain abdominal X-ray

Treatment
• Under liquid diet.• IV fluids• Analgesics:inj tramadol ,buscopan,• Antibiotics :levoflox,inj xone • Soap water enema.

Intestinal obstruction

Definition:
• Intestinal Obstruction(IO) is a condition in which there is a sudden stoppage of the onward passage of intestinal contents-i.e. Gas, digestive juices and food

Intestine

CLASSIFICATIONAccording to: Aetiopathology
Onset Level Nature

Peristalsis is working against a mechanical obstruction
DYNAMIC(MECHANICAL)
Result from atony of the intestine with loss of normal peristalsis, in the absence of a mechanical cause.
or it may be present in a non-propulsive form (e.g. mesenteric vascular occlusion or pseudo-obstruction)
ADYNAMIC(FUNCTIONAL)

Small or Large bowel
High (Proximal) or Low (Distal) small bowel
According to LEVEL

High IO- near the ampulla- jejunum and proximal ileum.
Low IO- distal to the ampulla- distal ileum and colon.


According to nature of Obstruction:
1. Simple Obstruction- the bowel lumen is occluded ,blood supply remains intact. The source of obstruction is usually intra-abdominal. ( Eg. Intra-abdominal adhesions, very rarely gallstones, ball of worms, bezoars).
2. Strangulation- the bowel lumen together with its blood supply is cut-off. Eg. Strangulated inguinal hernias. Pure strangulation without bowel luminal narrowing is usually due to mesenteric embolism/thrombosis.

3. Closed loop obstruction- The bowel is obstructed both proximally and distally. Here the blood supply may be impaired.A classic example is seen in an obstruction of the colon with a competent ileo-caecal valve.NB: All the 3 types spoken about can occur at the same time for example in a strangulated inguinal hernia.

Closed loop obstruction

According to onset:
-Chronic Obstruction-Usually seen in large bowel obstruction. The symptoms may arise from the cause and the subsequent obstruction.-Acute on Chronic Obstruction- sudden obstruction in a previously incomplete obstruction.Sub-acute Obstruction- There is a partial obstruction.

Causes Dynamic obstructrion
Intraluminal• Impaction• Foreign bodies• Bezoars• Gallstone
Intramural• Congenital atresia• Stricture• Malignancy(15%)
Extramural• Bands/
adhesion(40%)• Hernia (12%)• Volvulus• Intussusception• Tumor-benign/
malignant

BANDS

Ball of Ascaris worms

Adynamic cause of Obstruction
• Paralytic ileus• Electrolyte imbalance• Spinal injury• Diabetis mellitus• Renal surgeries• Mesenteric ischemia

PathophysiologyProximal
bowel dilated
& develops altered motility dilate
reduce
peristaltic
strength
flaccidity &
paralysis (prev.
vascular damage due to
inc. intralum
inal pressure
Distal to obs. Bowel
exhibits normal peristal
sis & absorbtion becom
e empty
contrac
t & becom
e immobi
le
Distention is by gas & fluid-Gas:
aerobic &
anaerobic
growth-Fluid:
Digestive juices
& retarde
d absorp
tion
Dehydration &
electrolytes loss: Reduced
oral intake,
defective
intestinal
absorption, loses
from vomiting
& sequestration in
bowel of lumen.

Clinical presentation
The clinical presentation varies according to;- The location of the obstruction- The age of the obstruction- Underlying pathology- Presence or absence of intestinal ischaemia.

Clinical features• Abdominal pain• Vomiting• Distension• Constipation• Dehydration• Feature of toxemia and septicemia• Feature of strangulation• Temperature• Bowel sound• Per rectal examination

Small vs large bowel obstruction

Investigation
• CBC• Electrolyte Na/K• Plan X-ray abdomen erect and supine• CT scan

A. Investigations(i) Supportive- FBC, BU+Cr. Other investigations may be requested on the basis of clinical suspicion. (ii)Diagnostic -Plain abdominal x-rays Erect and supine -CXR-Enema-Endoscopic techniques

ManagmenetI.V fluids and electrolytes rescusitation N.G tube if repeated vomitingAntibiotics Exploratory laparatomyHernia operationAdhesions AdhesiolysisObstruction removeVolvulus derotate and or operateMesenteric ischemia operateAbscess or peritonitis drain and treatIntussusception pneumatic or barium reduction or
operate

• SRB’s Manual of surgery, 4E• Bailey & Love’s Short practice of surgery, 25th
Edition• Principles of surgery • Internet
REFRENCES: