Health Occupations Cardiovascular System. Cardiovascular system Consists of –Heart –Blood...
-
Upload
maximilian-hudson -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
0
Transcript of Health Occupations Cardiovascular System. Cardiovascular system Consists of –Heart –Blood...

Health Occupations
Cardiovascular System

Cardiovascular system
Consists of– Heart– Blood vessels– blood
Transportation system of the body– Transports oxygen & nutrients to cells– Transports carbon dioxide & metabolic
waste away from cells

Heart
Hollow, muscular organ Pump of body – size of closed fist Found in mediastinal cavity
– Between lungs– Behind sternum– Above diaphragm

3 layers of heart tissue Endocardium
– Smooth layer of cells– Lines inside of heart, continuous with inside of blood
vessels– Allows for smooth flow of blood
Myocardium– Thickest layer, muscular, middle layer
Pericardium– Double layered membrane or sac– Covers outside of heart– Pericardial fluid fills the space between 2 layers & prevents
friction & damage to membranes as heart contracts

Heart septum
Muscular wall Separates heart into right & left sides Prevents blood from moving right to left
& vice versa Interatrial septum
– Upper part Interventricular septum
– Lower part

Heart chambers
Divided into 4 parts (chambers) 2 upper – atria 2 lower- ventricles Right atrium
– Receives blood as it returns from the body Right ventricle
– Receives blood from right atrium– Pushes blood into pulmonary artery
• Carries blood to lungs for oxygenation

Heart chambers
Left atrium– Receives blood from lungs (oxygenated)
Left ventricle– Receives blood from left atrium– Pushes blood into aorta so it can be
carried to body cells

Valves One way valves in-between heart chambers keep
blood flowing in right direction Tricuspid valve
– Between right atrium & right ventricle– Closes when right ventricle contracts & pushes blood to
lungs– Prevents blood from flowing back into right atrium
Pulmonary valve– Between right ventricle & pulmonary artery– Closes when right ventricle is finished contracting &
pushing blood into pulmonary artery– Prevents blood from reentering right ventricle

Valves
Bicuspid or Mitral valve– Between left atrium & left ventricle– Closes when left ventricle is contracting & pushing
blood into aorta so it can be carried to the body– Prevents blood from flowing back into left atrium
Aortic valve– Between left ventricle & aorta (largest artery in
body)– Closes when left ventricle is finished contracting &
pushing blood into aorta– Prevents blood from flowing back into left ventricle

Superior vena cavaRight pulmonary artery
Right pulmonary veins
Pulmonary valve
Right atriumTricuspid valve
Right ventricle
Inferior vena cava
Aorta
Left pulmonary arteryLeft pulmonary veins
Left atriumAortic valve
Bicuspid valve
Left ventricleSeptumEndocardium
MyocardiumPericardium
Apex

Cardiac cycle
Right & left sides of the heart work in a cyclic manner, TOGETHER, even though they are separated by the septum
Electrical impulses originating in heart causes myocardium to contract cyclically
Cycle consists of– Diastole
• Period of rest (brief)
– Systole• Period of ventricular contraction

Cardiac cycle
At start of cycle– Right & left atria contract– Blood is pushed into right & left ventricles
through the tricuspid (rt) & bicuspid (lt) valves
– Atria relax & blood reenters them• Right side – from body• Left side – from pulmonary veins (from lung)

Cardiac cycle
While atria are filling, systole begins & ventricles contract
Blood exits ventricle through pulmonary & aortic valves– Right ventricle
• Pushes blood into pulmonary artery & lungs
– Left ventricle• Pushes blood into aorta & body

Cardiac cycle
Blood in right side of heart– Low in oxygen, high in carbon dioxide– Then it goes to lungs via pulmonary artery– When it gets to lungs
• Carbon dioxide released into lungs• Oxygen taken into blood
Blood in left side of heart– Brought there by pulmonary veins– Now blood is high in oxygen, low in carbon dioxide– Ready to go to body

Lungs
Blood to lungs
Blood from lungs
Superior vena cava
Pulmonary valve
Right atrium
Inferior vena cava
Tricuspid valve
Right ventricle
Pericardium
Aorta
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary veins
Left atrium
Bicuspid valve
Aortic valve
Left ventricle
Endocardium
Septum
Apex

Conductive pathway
Electrical impulses originating in the heart cause the cyclic contraction of muscles
Starts in the sinoatrial node (SA node)– Group of nerve cells located in right atrium– Called pacemaker– Sends out an electrical impulse that spreads out
over the muscles in the atria– Atrial muscles then contract & push blood into
ventricles– After electrical impulse passes through atria, it
reaches the atrioventricular node (AV node)

Conductive pathway
Atrioventricular node (AV node)– Groups of nerve cells located between
atria & ventricles– Sends electrical impulse through nerve
fibers in the septum called the Bundle of His
Bundle of His– Nerve fibers in septum– Divides into a right & left bundle branch

Conductive pathway
Right & left bundle branches– Pathways that carry the impulse down through the
ventricles– Bundles continue to subdivide into a network of
nerve fibers throughout the ventricles called Purkinje fibers
Purkinje fibers– Final fibers on conduction pathway– Spread electrical impulse to all of the muscle tissue
in the ventricles– Ventricles then contract

Conductive pathways
Electrical conduction pattern occurs every 0.8 seconds
Movement of the electrical impulse can be recorded on an ECG & used to detect abnormal activity or disease

Sinoatrial node ( SA node)
AtrioventricularNode (AV node)
Bundle of HIS
Left & right bundle branches
Purkinje fibers

Arrhythmias
Interference with normal electrical conduction pattern of heart
Causes abnormal heart rhythms Can be mild to life threatening
– PAC’s (premature atrial contraction)– Atrial fibrillation (A fib)– PVCs (premature ventricular contraction)– Ventricular fibrillation (V fib)- life threatening– Asystole- life threatening

Arrhythmias Cardiac monitors & ECG are used to diagnose Treatment depends on type & severity
– Life threatening – treat with defibrillation• Device that shocks heart with electrical current• Stops uncoordinated contraction• Allows SA node to regain control
– External or internal artificial pacemakers• Small battery powered device with electrodes• Electrodes threaded through vein into right atrium &
ventricle• Fixed pacemakers – predetermined rate• Demand pacemakers – only fire when needed

Normal ECG
Normal sinus rhythm
Premature ventricular contractions
Atrial fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation

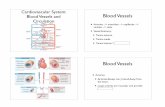
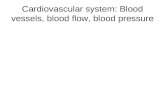
Blood vessels
Blood leaving heart carried via blood vessels– Closed system for flow of blood– 3 main types – arteries, veins, capillaries
Arteries– Carry blood away from heart– Aorta
• Receives blood from left ventricle• Immediately begins branching into smaller arteries
– Arterioles• Smallest branch of arteries• Joins with capillaries

Blood Vessels
Capillaries– Connect arterioles with venules– Thin walled, has only one layer of cells– Allow oxygen & nutrients to enter cells,
CO2 & waste to leave

Blood Vessels Veins
– Blood vessels that carry blood back to heart– Venules
• Smallest branch of veins• Connect with capillaries• Venules join together to become veins
– Superior & inferior vena cava• 2 largest veins• Superior – brings blood from upper part of body• Inferior – brings blood from lower part of body• Both vena cava drain into right atrium
– Much thinner with less muscle than arteries– Most contain valves that keep blood from flowing backwards

Blood Composition
Blood is a tissue 4-6 quarts in average adult Circulates continuously through body Transports many substances
– Oxygen from lungs to cells– Carbon dioxide from cells to lungs– Nutrients from digestive tract to cells– Metabolic wastes from cells to organs of excretion– Heat produced by body parts– Hormones produced by endocrine glands

Blood composition
Plasma– Fluid or liquid portion of blood– 90% water– Many substances dissolved or suspended
• Blood proteins- fibrinogen & prothrombin for clotting• Nutrients – vitamins, CHO, proteins• Mineral salts or electrolytes• Gases – CO2 & O2• Metabolic & waste products• Hormones• enzymes

Blood Cells
Solid elements of blood 3 main types 1. Erythrocytes – red blood cells
– Produced in red marrow at rate of 1,000,000 per minute
– Live about 120 days, broken down by liver & spleen– 4 ½ - 5 ½ million per cubic millimeter of blood (25
trillion)– Mature form circulating in blood has NO nucleus &
is shaped like a disc with a thinner central area

Erythrocytes
Contain complex protein – HGB– Composed of protein molecule (globin) &
iron compound (heme)– Carries both (O2 & CO2)– When HGB carries O2, it gives blood its
red color– When there is decreased O2, the blood is
darker red

2. Leukocytes White blood cells Not as numerous Formed in bone marrow & lymph Live 3 – 9 days 5 – 10,000 per cubic millimeter Can pass through capillary walls & enter body
tissue Main function – fight infection Phagocytosis – process by which some WBCs
engulf, ingest, & destroy pathogens

Leukocytes 5 types
– Neutrophils• Phagocytize bacteria, secrete lysosomes
– Eosinophils• Remove toxins, defend from allergic reactions• Make antihistamines
– Basophils• Inflammatory response• Produce histamine (vasodilator) & heparin (anticoagulant)
– Monocytes• Phagocytize bacteria & foreign bodies
– Lymphocytes• Immunity by making antibodies, protect against cancer formation

3. Thrombocytes
Platelets Fragments or pieces of cells No nucleus, vary in size & shape Formed in bone marrow Live 5 – 9 days 250,000 – 400,000 per cubic millimeter

Thrombocytes – clotting process Blood vessel torn, thrombocytes collect to form sticky plug Secrete serotonin, causes blood vessel spasm & decreased
blood flow Release thromboplastin, acts with calcium to form thrombin Thrombin acts with fibrinogen to make fibrin – gel like net of
fine fibers that trap RBCs, plts, & plasma to form clot Effective with small vessel bleeding If large vessel is torn, rapid blood flow interferes with fibrin
formation Dr. may insert sutures to close opening & control bleeding

Blood typing
O+ 38% O- 7% A+ 34% A- 6% B+ 9% B- 2% AB+ 3% AB- 1%

Abnormal conditions
Anemia – inadequate number of erythrocytes, HGB, or both
5 types– 1. Acute blood loss anemia
• Caused by hemorrhage or rapid blood loss• TX with transfusion
– 2. Iron deficiency anemia• Inadequate amount of iron to form HGB in RBCs• TX with increased iron intake from green leafy
vegetables, red or organ meats, meds

Types of anemias
3. Aplastic anemia– Results from injury or destruction of bone marrow– Causes poor or no formation of RBCs– Caused by chemo, radiation, chemicals, viruses– TX – eliminate cause, blood transfusions, bone
marrow transplants 4. Pernicious anemia
– Lack of intrinsic factor, results in poor absorption of Vitamin B12
– Results in formation of large inadequate RBCs– Tx – replace intrinsic factor, give Vit B12 shots

Types of anemias
5. Sickle cell anemia– Chronic & inherited– Results in production of abnormally
crescent shaped RBCs that carry less oxygen, break easily, & block blood vessels
– Racially exclusive – black– Tx – transfusions & supportive therapy,
need genetic counseling to prevent

Aneurysm
Ballooning out or saclike formation on artery wall
Causes – disease, congenital, injuries leading to weakening of arterial wall
Sx – some cause pain/pressure & others have no sx
Common sites – cerebrum, aorta, abd If rupture – hemorrhage, can cause death TX – surgical removal of damaged area &
replacement with plastic graft or other vessel


Arteriosclerosis
Hardening or thickening of arterial walls Causes loss of elasticity & contractility Occurs as result of aging Causes HTN & can lead to aneurysm or
cerebral hemorrhage

Atherosclerosis
Fatty plaques, frequently cholesterol on walls of arteries
Causes narrowing of opening, decreasing or eliminating blood flow
If plaques break loose, become emboli TX – low cholesterol diet, meds to lower
cholesterol, exercise Surgery – balloon angioplasty, coronary
atherectomy, coronary stent, bypass surgery

Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
Heart muscle doesn’t beat adequately to supply blood needs of the body
Involves right or left sides of heart Symptoms
– Edema– Dyspnea– Pallor & cyanosis– Neck vein distension– Weak & rapid pulse– Productive cough with pink frothy sputum

Congestive Heart Failure
Treatment– Cardiac drugs– Diuretics– TED hose– Oxygen– Bedrest– Low sodium diet

Embolus
Foreign substance circulating in blood stream– Air– Fat– Blood clot– Bacterial clumps
Blockage of vessel occurs when embolus enters an artery or capillary too small for passage

Hemophilia
Inherited disease occurring almost exclusively in males, but carried by females
Blood is unable to clot due to lack of plasma protein
Minor cut can lead to prolonged bleeding Bump can lead to internal bleeding Treatment
– Transfusions– Administration of missing protein factor

HTN - hypertension
Systolic >140 mm Hg Diastolic > 100 mm Hg Risk factors
– Family history– Obesity– Race– Stress– Smoking– Age– Diet high in saturated fat

HTN Treatment
– No cure– Antihypertensives– Diuretics– Decreased stress– No tobacco– Low sodium & low fat diet
If untreated, causes permanent damage– Heart– Blood vessels– Kidneys– eyes

Leukemia Malignant disease of bone marrow or lymph tissue
resulting in large numbers of immature WBCs Can be acute or chronic Symptoms
– Fever– Pallor– Swelling of lymph tissues– Fatigue– Anemia– Bleeding gums– Excessive bruising– Joint pain

Leukemia
Treatment– Varies with type– Chemotherapy– Radiation– Bone marrow transplant

Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Blockage in coronary arteries cuts off supply of blood to heart
Affected heart tissue dies (infarcts) Death can occur immediately if a large
area infarcts Also called heart attack Angina pectoris can be a precursor

MI
Symptoms– Severe crushing pain radiating to arm,
neck or jaw– Pressure in chest– Diaphoresis – Cool, clammy skin– Dyspnea– BP & pulse changes

MI
Treatment– CPR if cardiac arrest– Thrombolytic clot busters (Streptokinase or TPA)
to restore blood flow within the first several hours – can’t use if bleeding present
– Complete BR– Pain meds– Anticoagulants– Oxygen– Treatment of arrhythmias

MI
Long term care– BP control– Diet low in cholesterol & saturated fats– No tobacco– No stress– Regular exercise– Weight control

Phlebitis
Inflammation of vein Frequently in leg Called thrombophlebitis if clot forms Symptoms
– Pain– Edema– Redness– Discoloration at site

Phlebitis
Treatment– Anticoagulants– Pain meds– Elevate area– TED hose– Surgery

Varicose veins Dilated & swollen veins that have lost elasticity &
cause a stasis or decreased blood flow Occurs frequently in legs Results from pregnancy, prolonged sitting or
standing, heredity Treatment
– Exercise– Avoid prolonged sitting/standing– TED hose– No tight-fitting clothing– Surgery to remove vein in severe cases


Erythroblastosis fetalis
Condition in unborn baby where mom forms antibodies against the antigens in the baby’s blood
RH+ child (after 1st pregnancy) born to RH- mother
May cause brain damage in baby Treatment
– Monitor bilirubin levels during pregnancy– Intrauterine transfusions if needed– May need exchange transfusions at birth