Dermatology DDX
Transcript of Dermatology DDX
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
1/29
Dermatology DDX:Red scaly diseases Look at a rash and decide if it is red and scaly or red and non scaly. If it is red and scaly you use the mnemonic PMs PET P of PM is for PITYRIASIS ROSEA or PITYRIASIS VERSICOLOR M is for MYCOSIS !"#OID$S % a & cell lym'homa of the skin.(P$& is PSO)I*SIS% $C+$M* and &I"$* . (
&he only additional 'ro,lem there is the e-tent of our solar damage hich can mas/uerade as a red scaly rash and e0en ,e non scaly.So add solar damage after the nemonics for ,oth the red scaly and non scaly rashes.
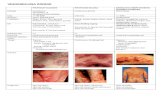
PITYRIASIS ROSEA (PR) is RED AND SCALY a condition that classically ,egins ith a single, primary, 2- to 10-cm 1herald pa ch thaa''ears on the trunk or proximal limbs. * general cen ripe al er!p i"n of 2.34 to 54cm rose4 or fa n4colored o0al 'a'ules and 'la/ues follo s ithin 6 to 78 days.
&he lesions ha0e a scaly# sli$h ly raised %"rder (c"llare e) and rese&%le rin$'"r& ( inea c"rp"ris (. Most 'atients itch%occasionally se0erely. Pa'ules may dominate ith little or no scaling in ,lacks% children% and 'regnant omen9 the rose or fa n color is not as e0ident in ,lacks9,lacks also more commonly ha0e in0erse P) lesions in the a-illae or groin that s'read centrifugally(. Classically% lesions orient along skinlines% gi0ing P) a Christmas &ree4like distri,ution hen multi'le lesions a''ear on the ,ack. * 'rodrome of malaise and headache 'recedesthe lesions in a minority of 'atients. Diagnosis is ,ased on clinical a''earance and distri,ution.
Pi yriasis ersic"l"r : RED AND SCALY &his red scaly disease has ;ne ,ran like scale elicited ,y scratching the surface. It is usually seenon the trunk or under the ,reasts. It 'resents as hite s'ot disease in tanned indi0iduals and a red scaly disease on hite skin.Addi i"nal Dia$n"s ic ea !res Often a 0ery light 'ink colour and easy to miss. Look es'ecially on the u''er ,ack% a-illae and under,reasts.
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
2/29
&he M in PMs P$& is for Myc"sis *!n$"ides . &his is an old name for & cell lym'homa of the skin. It is /uite rare ,ut im'ortant to diagnose ,ecause an early lesion can look like 'soriasis or lograde ec
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
3/29
Tinea. Red and scaly ,ut ith a s'reading edge.Scra'e this for microsco'y and culture.
&here may ,e small 'ustules in the edge in rare cases. &reatment ith to'ical steroids ill reduce the redness and scale making diagnosis more di=cult.
Addi i"nal Dia$n"s ic ea !res &he SLO/LY SPREADIN0 SCALY ED0E is a hallmark of the condition. Seldom itchy. !sually not symmetrical like 'soriasisor ecammed.
In 'soriasis Red and scaly( except for the one in the exures, like groins etc ) the skin gro s ? to 72 times faster than normal so you get this thick,uild u' of scale that is easily scra'ed o@. &he lesions are usually /uite sharply de1ned# the colour is often a sal&"n pin+ colour% e-ce'tin the more in>ammatory irritated ty'es of 'soriasis here it can ,e much redder. You should look at the more ty'ical areas here you
ould e-'ect to see 'soriasis such as the el%"'s# he +nees# he scalp,
L""+ a he nails and see i* here is any e idence "* pi in$, L ook under the >e-ures and the el,o s or ,reasts or in the groin areaor es'ecially around the anus to see if there is the relati0ely s&"" h n"n scaly lesi"ns that occur in these areas. Psoriasis on the lo er
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
4/29
legs can ha0e an ec
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
5/29
the cheeks or around a recent inBury to the skin. Lym'hangitis ie a red line tra0elling to ards the local lym'h glands is a orrying sign
2r icaria red n"nscaly )aised itchy 'la/ues in the skin that last a fe hours and disa''ear only to rea''ear else here. Indi0idual lesions ne0er last longer than 58 hours ece't for urticarial 0asculitis here the lesions mat resol0e ,ut lea0e residual ,ruising atthe site and 'a'ular urticaria secondary to an insect ,ite reaction here the mechanism causing the lesion is a delayed ty'e cell mediatedhy'ersensiti0ity reaction rather than the immediate Ig$ mediated histamine release from mast cells.
L L!p!s# Li$h er!p i"ns# L!es red n"nscaly Some forms of Lu'us erythematosus are not scaly eg Systemic lu'us% &umid Lu'us %Lu'us 'anniculitis and some cases of Su,acute Lu'us. &hese rashes are usually ma-imal on sun e-'osed areas as is Polymor'hous light
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
6/29
eru'tion. &he latter occurs ith unusual sun e-'osure 'articularly to 'eo'le on holiday in sunny locations they are not used to. &he lesions areusually itchy sa'ules or 'la/ues
D Dr!$s You ha0e to consider a drug reaction for 0irtually e0ery red non scaly rash. &y'ically sudden onset% no fe0er% itch 'rominent and the rash is >oridCom'are it ith a 0irus infection here the onset can ,e Bust as fast and the rash Bust as >orid ,ut there is fe0er% little itch and the 'atient feels un ell. * drugreaction to an anti,iotic gi0en to a 'atient ith a 0iral infection is al ays di=cult to diagnose Look for a 0iral enanthem.
V Vir!siral infections can ha0e a 0ariety of mor'hologies ,ut macular or maculo'a'ular are the commonest and they are red and non scaly. &he
'atient usually has a fe0er% some lym'hadeno'athy and feels ill. *n enanthem is an associated ;nding often in the mouth. eg Eo'lick s'ots
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
7/29
on the ,uccal mucosae in measles.
A Ann!lar ery he&as &he annular erythemas look like urticaria ,ut indi0idual lesions last longer than 58 hours and often slo ly Boinu' ith each other to form 'olycyclic rings. &hey can ,e easily misdiagnosed as a tinea fungal infection ,ut they usually do not ha0e ascale e-ce't sometimes the $*C or erythema annulare centrifugum 0ariant.
E Ery he&a &!l i*"r&e rash. red and n"n scaly# &his condition looks like a drug eru'tion hich it sometimes is A$ain n" *e er "r i chand *e' sys e&ic *ea !res in he &in"r arian , &he mor'hological feature you look for is the iris% ,ullseye or target lesion seen on the lo er
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
8/29
legs or 'alms of the hands and soles of the feet. Sudden onset lasting days% occassionally ,listered in se0ere cases due to a drug and in the 0eryse0ere cases ill ha0e in0ol0ement of the li 's and conBuncti0al surfaces. In these circumstances it goes under the name of the Ste0ens4Fohnsonsyndrome
V Vasc!li is &he early stages of true 0asculitis gi0e a red non scaly rash 'articularly on the lo er legs or ,uttocks. It does not ,lanch ith 'ressure and may ,e 'ur'uric or small ,ruise like.*gain drugs are the commonest cause ,ut the 'otential range of causes is 0ery great.
&he ;rst thing to do is check the urine and see if there is any ,lood in it.If there is then you ha0e a systemic 0asculitis that can hit other organ systems including the Boints% the gut % the lungs% heart and the ,rain.Aide ranging in0estigations are necessary to diagnose the cause.
E Ery he&a n"d"s!& rash. red and n"n scaly# &his red non scaly rash is also /uite distincti0e 'resenting as tender dee'er nodules on the
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
9/29
anterior shins or sometimes on the cal0es. &he lesions may resol0e ith ,ruising ,efore disa''earing o0er a 54G eek 'eriod. You ha0e to consider a condition called erythema induratum hen the lesions are mainly on the cal0es. $rythema nodosum is a form of 'anniculitis or in>ammation of the dee'er fat tissue. *gain it can ,e a drug reaction ,ut most cases are
post streptococcal throat infection!
In1l ra es can 'resent as red non scaly rashes eg #eneralised granuloma annulare% sarcoidosis%leukemic in;ltrates% le'rosy% leishmoniasis% mucinoses ie in;ltrates of cells# s!%s ances "rin*ec i"!s a$en s ( iral# %ac erial# *!n$al and pr" "-"al),
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
10/29
P st lar diseases So add solar damage after the nemonics for ,oth the red scaly and non scaly rashesIf there are P!s !les then the mnemonic is II
aye aye( Infecti0e 0iral% ,acterial% fungal( or In>ammatory eg 'soriasis or a 'ustular drug reaction.Common causes include Sta'h folliculitis % modi;ed fungal infection or if the 0esicles are grou'ed her'es sim'le-. Pustuleson the face are *cne% )osacea% Sta'h folliculitis or H Sim'le- if grou'ed.Ahen e see 'ustules e ha0e a tendency to think infection and often limit oursel0es to only ,acterial infections at that.)emem,er 'ustules can occur ith fungal and 0iral infections as ell and ne0er forget that some 'ustules are not due toinfection ,ut to in;ltration of the skin ,y neutro'hils in In>ammatory skin diseases such as 'soriasis and drug eru'tions.
&here are also a fe other 0ery rare in>ammatory disorders such as acrodermatitis entero'athica
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
11/29
"in colo redscaly diseases
So add solar damage after the nemonics for ,oth the red scaly and non scaly rashes
&he Skin coloured ,ut scaly conditions are Bust the 0arious forms of Ichthyosis% a grou' of genetic diseases ofthe skin. &here is a rare ty'e of ichthyosis that is red and scaly called CI$ or congenital ichthyosiformerythroderma.
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
12/29
"in #olo red nonscaly
S+in c"l"!red n"n scaly lesi"ns on the skin are usually in;ltrates% ie the 'athology is in the dermis rather than the e'idermis. In0ol0ement of the e'idermis usually gi0es scale or crust of some sort(.
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
13/29
Hence the lesions are skin coloured 'a'ules% 'ossi,ly red if in>ammed% and are not itchy. Consider sarcoidosis and granuloma annulare ifthe rash is e-tensi0e and tumours such as neuro;,romatosis or leiomyomas if the lesions are multi'le and grou'ed. Ho e0er one of thecommonest causes of smoothe dome sha'ed skin coloured 'a'ules is molluscum contagiosum% a 'o- 0irus usually seen in young children.
$nn lar lesions
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
14/29
*nnular lesions are al ays fun to diagnose. &he 'u,lic in0aria,ly diagnose them as tinea or ring orm ,ut that diagnosis isonly a 'ossi,ility if there is scale. If there is no scale then the 'rocess is dermal and you should consider granulomaannulare% sarcoidosis% annular erythema and e0en le'rosyAnn!lar lesi"ns "n he *ace
&inea faciei due to a dermato'hyte infection ould ,e the commonest% ,ut granulomatous disorders such as sarcoidosis andgranuloma annulare and infecti0e conditions such as le'rosy should also ,e considered.Mana$e&en 4 skin scra'ings if scaly% check to see if there is a loss of sensation hich ould ,e seen in le'rosy in thecentre of the lesion and,io'sy if you consider oneof the granulomatousdiseases.SI0N DIP MENO er ie' "* Ann!larlesi"nsS6S7!a&"!s.
)esol0ing'soriasis%Discoid ec
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
15/29
cicatricial'em'higoid%leishmaniasis
'ur'lish scar inrecidi0ans(
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
16/29
%inear lesions Linear lesions are also /uite strikingly o,0ious.Consider 'lant contact dermatitis% her'es ammatorylinear 0errucouse'idermal ne0us(%Psoriasis%Lichen sim'le-%%Lichen 'lanus%DarierKs disease%Lichen nitidus%
6In*ec i e Her'es
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
17/29
Conradi syndrome
&hite s"inocalised
Localised hite skin lesions also signify a limited num,er of diseases.
Aorking do n% on the face considertyriasis al,a% a lo grade form of cammatory either after li/uid
nitrogen or surgery to skin cancers.Post in>ammatory hy'o'igmentations also seen ith discoid lu'usrythematosus.
3(Localised mor'hea or lichenclerosus can also 'resent as
hy'o'igmented 'atches ,ut theunderlying skin ill ,e ;rm inmor'hea.
(!ndertreated 'soriasis or ec
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
18/29
&u,erculoid Le'rosy%Pinta% Sy'hilis%Post her'es
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
19/29
granuloma annulare%sy'hilis
P Para'soriasis%A *myloid%P Pigmented 'ur'uric dermatosis%A acanthosis nigricans8yperpi$&en a i"n in hene"na e9l!e $rey
Mongolian s'ot%"e0us of Ota ace(%"e0us of Ito Shoulder%neck(%Phakomatosis 'igmento40ascularis &runk 'lus 'ort inestain(
9r"'n Cafe au lait s'ots%Congenital ne0us
S&all %r"'n &ac!lesPeut< Feghers syndrome%L$OP*)D syndrome%#eneralised lentiginosis%Inherited 'atternedlentiginosis%Carney syndrome%"euro;,romatosis a-illae(%Centrofaciallentiginosis central face(Segmental lentiginosis%Mosaicism%S'eckled lentiginous ne0us%"e0us s'ilus%
&ransient neonatal 'ustularmelanosis
La%ial %r"'n &ac!les Peut< Feghers syndrome%Carney syndrome
S'irled "r 9lasch+" pa ern Linear and horled ne0oidhy'er'igmentation%Incontinentia 'igmenti%$'idermal ne0us%#olt< syndrome%Conradi Hunermannsyndrome%
Mosaicism
erpigmentationneralised
0eneralised hyperpi$&en a i"n is al ays orrying.It can ,e a feature of underlying malignancy 'articularly * CTH producing carcinoma of the lung or from anunderlying melanoma. *lso consider Addison's disease ith 'igmentation of the skin creases and inside themouth. Drug induced hy'er'igmentation is another thought 'articularly from some chemothera'y drugs.Meta,olic disorders such as hemochromatosis and 'or'hyria cutanea tarda can also gi0e marked generalisedhy'er'igmentation ,ut in PC& it is accentuated in sun e-'osed areas.
SI0N DIP MEN O er ie' "* 8yperpi$&en a i"n
S6S7!a&"!s )esol0ed lichen 'lanus
6In*ec i e060ran!l"&a "!sN6Ne"plas ic
Melanoma metastases%
Lung carcinoma%Lym'homaD6Dr!$s
Melasma%i-ed drug eru'tion%
,leomycin%arsenic%gold and cyclo'hos'hamide%Pu0a
6I&&!n"l"$icalScleroderma%lu'us erythematosusdermatomyositis
P6Physical Post sun,urn%Post taumatic%
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
20/29
)acial 'igmentarydemarcation lines%Phototo-ichy'er'igmentation
Plants(%aga,ondKs disease
M6Me a%"lic *ddisonKs disease%Por'hyria cutaneatarda%Hemochromatosis%)enal and he'aticfailure%*myloidosis
E6End"crine Hy'erthyroidism%Pregnancy%Cushings%*cromegally%
&hyroto-icosis%Pheochromocytoma
N6N! ri i"nalPellagra%Mala,sor'tion
O hersEyelids
amilial%ne0oid%meta,olic diseasessuch as ochronosis%
chemical such asmercury ointmentsand 'soralens andargyria%lichen 'lanus%lichen aureus%melanoacanthomaand some endocrinediseases.
Re ic!la e Pi$&en a i"n Do lingDegos >e-ures(%+osteriform%Dyskeratosiscongenital%"aegeli ranceschetti
syndrome necka-illae% keratoderma(%*cro'igmentations of Eitamura and Dohi
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
21/29
9lis erin$ diseases If there are listers &he mnemonic is ICI( Im'erial Chemical Industries( In>ammatory including Immunological%Contact dermatitis and Infecti0e.
n5a&&a "ry causes can include drugs ,ut remem,er Immunological causes in the elderly 'articularly ,ullous 'em'higoid .Contact dermatitis usually gi0es smaller 0esicles rather than ,listers ,ut indi0idual 0esicles can Boin u' into ,listers. Aatch for hair dyellergies around the 'osterior neck and scal' or consider a 'lant contact dermatitis if the ,listers or 0esicles are in a linear streaky distri,ution
on e-'osed surfaces here the 'atient has ,rushed u' against an o@ending ,ush or tree.n*ec i e ca!ses of ,listers are usually sta'h to-in in origin and go under the name of ,ullous im'etigo. Ho e0er if the lesions are in a linear
distri,ution ,ut 'ainful and limited to skin dermatomes then consider Her'es
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
22/29
Her'es
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
23/29
!nnydis ri%! i"ne3cl!din$Linear
S+in rashes can %e *"!nd in !n!s!al dis ri%! i"ns e$le3!ral
AcralPh" " dis ri%! i"nPeri!n$!alPeri"c!larPeri"ral0lans penisV!l aS"li ary l"calised6 &his suggests a localised contact dermatitis if red and scaly ith a ,rokensurface or a ;-ed drug reaction if red and non scaly ith slight hy'er'igmentation. If recurrent0esicles 'receded ,y localised 'ain then her'es sim'le- is the likeliest diagnosis.
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
24/29
!nny C"l"!r E3cl!din$ red and s+in c"l"rs 'e 'ill l""+ a lesi"ns ha are an !nc"&&"n c"l"!r,YELLO/ LESIONS Yello lesions look yello ,ecause of fat% se,aceous material% carotene% Baundice 'igment or drugs. *t one stage resol0ingruises go through a yello 'hase. Yello 'a'ules or nodules are Xanthomas % -anthogranulomas including necro,iotic% Se,aceoushy'er'lasia and other se,aceous tumours% #outy to'hi around el,o s and knees.Yello skin consider carotene 'igmentation of 'alms and soles% Baundice from any cause and drugs such as /uinacrin .P2RPLE LESIONSPur'le lesions are that colour ,ecause of altered or 0enous ,lood% o0ergro th of ,lood 0essels or in;ltrates of neutro'hils orym'hocytes into the skin. Consider therefor haemangiomas% angiosarcomas% Ea'osiJs sarcoma% 'ort ine stains or other
0ascular malformations% 0asculitis ith leaked ,lood cells% lym'hocytoma% lym'homa% and the 'la/ues and nodules of S eetJsyndrome here the in;ltrating cells are lym'hocytes. Sarcoidosis can also ha0e a 'ur'le colour in the skin. etter also
consider drugs gi0ing a lichenoid drug reaction eg &hiaammatory hy'er'igmentation 'articularly ith ;-ed drug reactions andichen 'lanus. It is usually due to melanin in melano'hages in the dermis.
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
25/29
8air pr"%le&s L"calised hair l"ss has three common 'ossi,ilities% alo'ecia areata %tinea ca'itis and trichotillomania.
n alo'ecia areata the area of hair loss is com'lete% the in0ol0ed area is smoothe and the hairs may ,e ,roken at the edges. &he ,ald area isnot in>ammed.n tinea ca'itis the area is ne0er com'letely ,are% the hairs are ,roken% there may ,e scale on the surface and signs of scal' in>ammation. Inrichotillomania the hairs may ,e ,roken and the 'attern of loss is unusual. &he scal' may sho in>ammation around recently traumaticallyemo0ed hairs.
Mana$e&en 4&ake scra'ings if scaly for fungal culture and include a fe hairs. Do a hair'ull test to see if the hairs around the ,are area comeout from the ,ase ith a telogen ,ul, on the end% a feature ty'ical of alo'ecia areata.Rare ca!ses 4Incontinentia 'igmenti% ne0us se,aceous % 'ost tick ,ite% follicular mucinosis% OfugiJ disease% localised mor'hea% a'lasia cutis%ost her'es
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
26/29
Nail pr"%le&s &here are a 0ariety of common conditions that 'atients ,ring to their doctorJs attention.L"n$i !dinal rid$in$ is a normal feature of aging. S'litting of the ends of the nails is due to trauma and too much ater e-'osure. Separa i"n "* he nail from the nail,ed is also due to e-cess et ork here the ,onds ,et een the nail and the underlying nail ,ed are
eakened and the nail se'arates , &his is kno n as "nych"lysis,Any candida found under the se'arated nail is a contaminant ,ails are solid keratin hich is the food for der&a "phy e *!n$ii,
Hence most crum,ly nails are due to a dermato'hyte infection ,ut some may ,e due to ps"riasis, Ta+e nail clippin$s *"r c!l !re, "aildistortion isommonly due togeing and 'oorlytting shoes.
Speci1c c"ndi i"nsn "l in$ he nails
9ri lerittle nails
C!r edEoilonychia%Pincer nails
Dys r"phicDarierJsdisease%Lichenstriatus%Psoriasis%
Onychomycosis%Onycho'hagia%Pro-imal su,ungual onychomycosis%
&rachyonychia%0r"" e
Digital mucous cystMalali$nedCongenital malalignment
Onych"lysisOnycholysis% numerous causes% ater% 'hoto drug etc(%Onychomycosis%Psoriasis%
&raumatic%$'idermolysis ,ullosa a/uisita%Pem'higus 0ulgaris%*cro'ustulosis of Hallo'eau
Pi$&en a i"nDrug induced *+&% leomycin% Methotre-ate(%
Longitudinal melanonychiaPi s*lo'ecia areata
P!rp!raS'linter hemorrhages%Su,ungual hematoma
Rid$es l"n$i !dinal*ging%Lichen 'lanus%median nail dystro'hy
Rid$es rans erseeauJs lines%
Chronic 'aronychia%Ha,it nail tic deformity%
Sh"r
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
27/29
rachyonychiaThic+ened
Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis%nail hy'ertro'hy and Onychogry'hosis%Onychau-is%Onychomycosis%Pachyonychia congenita%
PsoriasisC"l"!red9l!e lue nails drugs or AilsonJs disease(%0reen Pseudomonas(%/hi e Half and half nails% Leukonychia% MuehrckeJs lines% &erryJs nails%Ahite su'er;cial onychomycosis(%
Yell"' "ail discoloration cigarretes%Yello nail syndrome(P"s eri"r nail *"ld
Paronychia%Chronic candidiasis%Scleroderma%Dermatomyositis ragged cuticles(
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
28/29
d!les "n he *ace are usually due to tumours% the commonest ,eing ,asal cell skin cancers% s/uamous cell skin cancers%anoma and Merkel cell skin cancers and aty'ical ;,ro-anthomas.e %eni$n n"d!les on the face ould ,e se,aceous or dermoid cysts% the latter 'articularly occurring around the ,ase of thee and the eyes% near the em,ryonic 'lanes. neuro;,romas and trichoe'itheliomas.nditions that cause de'osits in the skin can also cause nodules on the face 'articularly amyloidosis% sarcoidosis and infecti0erders such as leishmaniasis% treated le'rosy% & and rarely tertiary sy'hilis.
ycosis fungoides or & cell lym'homa of the skin% cell lym'homa% #ranuloma faciale and Lym'hocytoma cutis andiosarcomas could all cause nodules on the face.na$e&en generally a ,io'sy is necessary to esta,lish the diagnosis of the facial nodule and the tissue should ,e sent forure for aty'ical myco,acteria and for dee' fungal infections if an infecti0e cause is considered.
N DIP MEN N"d!les O er ie'7!a&"!s Many of the infecti0e nodules ,elo ill ha0e a rough surface
n*ec i e Dee' fungal infections 'articularly Chromo,lastomycosis and S'orotrichosis% &u,erculosis% *ty'icalco,acterial %Leishmaniasis% Sy'hilis% Le'rosy% Orf% MilkerKs nodules%
ran!l"&a "!s Sarcoidosis% #ranuloma annulare% oreign ,ody% $rythema ele0atum diutinum% )heumatoid nodule%nuloma faciale% Panniculitis%
Ne"plas ic enign &umours such as se,aceous cysts% dermato;,roma% li'oma. More aggresi0e tumours such as asal cellinoma% S/uamous cell carcinoma% Eeratoacanthoma% Metastases% Merkel cell% Melanoma% *ty'ical ;,ro-anthoma% Mycosis
goides% cell lym'homa% Lym'hocytoma% *ngiolym'hoid hy'er'lasia ith eosino'hilia% *ngiosarcoma% Lym'hangiosarcoma%mato;,rosarcoma 'rotu,erans% Cylindroma
Dr!$s Iodides% romides% Phenytoin% Da'sone
&&!n"l"$ical $rythema nodosum % S eetKs syndrome% Eimuras disease
hysical Prurigo nodularis% Pyogenic granuloma% Digital my-oid cyst% Chil,lains Perniosis(
Me a%"lic Xanthomas% #outy to'hi% &umoral calcinosis% Mucinoses
End"crine Preti,ial my-edema%
N! ri i"nalhersain*!l n"d!les Multi'le familial leiomyomas% S'iradenoma% #lomus tumour% *ngioli'oma% lue ru,,er ,le, ne0us%roma% "eurilemmoma% "euro;,roma% Eeloid% #ranular cell tumour% Dermato;,rosarcoma 'rotu,erans% leeding into amato;,roma
"' N"d!les Xanthomas% Xanthogranuloma% Se,aceous ne0i% Histiocytosis%
c!lar L""+in$ N"d!les acilliary angiomatosis% Ea'osiJs sarcoma% Pseudo Ea'osiJs sarcoma% *ngiosarcoma% Multi'lemus tumours% Leukemia cutis% Systemic amyloidosis% Metastatic melanoma% Metastaic Merkels% S eetJs syndrome%coidosis% Ma@ucciJs syndrome% *ngiolym'hoid hy'er'lasia ith eosino'hilia% EimuraJs disease% multi'le Clear cellnthomas
eci1c c"ndi i"ns in "l in$ he *acenei*"r& *cne 0ulgaris%Infantlie acne%neonatal acne%#ram "egati0e folliculitis%OfugiJs disease%)osacea%)osaceaminans%Steroid rosacean!lar Se,orrhoeic dermatitis%Secondary sy'hilise Drug induced 'igmentation Minocycline%amiodarone%minocycline%chlor'roma
-
7/24/2019 Dermatology DDX
29/29