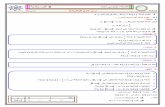
CONTINUITY Mrs. Erickson Continuity lim f(x) = f(c) at every point c in its domain. To be...
-
Upload
lynn-cummings -
Category
Documents
-
view
240 -
download
1
Transcript of CONTINUITY Mrs. Erickson Continuity lim f(x) = f(c) at every point c in its domain. To be...
- Slide 1
Slide 2 CONTINUITY Mrs. Erickson Slide 3 Continuity lim f(x) = f(c) at every point c in its domain. To be continuous, lim f(x) = lim f(x) = lim f(c) x c+x c+ x c-x c- Slide 4 Continuity ContinuousRemovable Discontinuities because you can remove the fact that this function is discontinuous. Fill the hole and it becomes continuous. Slide 5 Continuity Jump DiscontinuityInfinite DiscontinuityOscillating Discontinuity Slide 6 Continuity Polynomial functions Rational functions Absolute value function Exponential Function Natural log function Trig functions Radical functions Continuous at every point in the domain. Zeros in denominator are points of discontinuity, however they are not in the domain. f(x) = a n x n + a n-1 x n-1 + + a 1 x + a 0 f(x) =, q(x) 0 p(x) q(x) y = |x| y = e x y = ln(x) y = sin(x), y = cos(x), y = tan(x), y = x Slide 7 The Intermediate Value Theorem f(x) is a continuous function on [a,b]. f(x) takes on every value between f(a) and f(b). There exists a value c, where a



![Residykalkyl - Chalmersfy.chalmers.se/~tfkhj/MatFysResidy2018.pdf · 2018-11-06 · f : [a, b] ⌅ R ⌥ b a f(x)dx ⇤ lim n⇥⌅ ⌃n k=0 f(x k1)(x k x k1) ⌥ b a f(x)dx ⇤ lim](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5e2c705fc817e801e672ecbe/residykalkyl-tfkhjmatfysresidy2018pdf-2018-11-06-f-a-b-aoe-r-aoe-b.jpg)





![nenomatica · 2018. 8. 15. · v) lim f(x) lim f(x) —2 limf(x)] 1 = 2 l, liml:rl lim xl=O lim I ae IR (u ( —21 = —4 — a L. Jlþy=x a lim x—sa www_ n . lim f (x) = — lim](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/60da74b2850abc389e16bf7e/nenomatica-2018-8-15-v-lim-fx-lim-fx-a2-limfx-1-2-l-limlrl-lim.jpg)