Coarctation of aorta
-
Upload
amrutha-ramakrishnan-nair -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
830 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Coarctation of aorta

AMRUTHA R1st yr MSc nursing
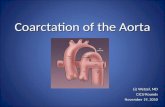
COARCTATION OF AORTA

MORGAGNI in 176040 – 80 % patients have a bicuspid aortic valve.

There is localised narrowing of the aortic arch, just distal or proximal to the ductus or ligamentum arteriosus

CAUSE
DUCTUS TISSUE THEORY
HEMODYNAMIC THEORY

EPIDEMIOLOGY
6-8% OF ALL CHD Male:female is 2:5

Associations
Turners syndromeBicuspid aortiv valve 30-40%VSDPDAAortic stenosisMitral stenosis Intra cerebral associations

EMBRYOLOGY




EMBRYOLOGY

EMBRYOLOGY
6—8 th week of gest 4th and 6th aortic arches4th arch Connect dorsal to ventral aorta Form aortic arch6th arch Develop distally to DA


RT COMMON CAROTID
RT SUB CLAVIAN
BRACHIO CEPHALIC
LT SUB CLAVIAN
LEFT COMMON CAROTID

DUCTAL
PREDUCTAL
POSTDUCTAL
TYPES

PREDUCTAL


DEVELOPMENTAL PATTERNS
LOCALISED LESION

HYPOPLASTIC SEGMENT

SIMPLE

COMPLEX

GENETIC DISORDERS

PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
EARLY DAYS
PDA
ACYNOTIC

Post ductal
POSTDUCTAL


Perfusion of lower body depends upon rt ventricular output
Right to left shunting
Upper extrimities pink and lower blue
Severe pulmonary HTN
LT ventricular hypertrophyHEART FAILURE

CARDINAL FEATURES
HTN – Upper body
Palpable collaterals
Thrill
Heave


CLINICAL FEATURES
PULSES
BP
MURMUR

INFANT
DEPENDS ON PATENCY OF PDA ShocK and HF METABOLIC DISTURBANCES Hypothermia Hypoglycemia Hypo perfusion Renal failure

Child
Upper extrimity HTN
Widened pulse pressure
Varibility in rt and lt arm pressures
Murmurs

. Grade 1 refers to a murmur so faint that it
can be heard only with special effort. A grade 2 murmur is faint, but is
immediately audible. Grade 3 refers to a murmur that is
moderately loud, and grade 4 to a murmur that is very
loud

. A grade 5 murmur is extremely loud and is
audible with one edge of the stethoscope touching the chest wall.
A grade 6 murmur is so loud that it is audible with the stethoscope just removed from contact with the chest wall. In general, murmurs with an intensity of grade 4 or higher are accompanied by a palpable thrill.

Others
Intermittent claudication (due to a temporary inadequate supply of oxygen to the muscles of the leg)
Pain and weakness of legs and
Dyspnea on running

Investigations
ANTENATAL Fetal echo 16-18 weeks of gestation Helpful identifiers:
Long segment Small LV Dilated RV
Flow through ductus difficult to detect coarctation

cardiomegaly
Rib notching
3 sign
X RAY

RIB NOTCHING


ECHO
High parasternal, suprasternal long axis
Shelf within lumen of thoracic aorta
Color and pulse wave doppler to locate area
Continuous wave doppler to detect maximum flow velocity

ECG MRI BARIUM SWALLOW CARDIAC CATHETERISATION

MANAGEMENT
MEDICAL Initial stabilisation Ionotropic drugs Prostaglandin E 1 IV .01mcg/kg/mt

SURGICAL
REPAIR

END TO END ANASTAMOSISEXCISION OF COA INTERRUPTED
SUTURING

LEFT SUB CLAVIAN FLAP
LIGATE LT SUB CLAVIAN ARTERY
CLOSE SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY FLAP OVER THE COA AND SUTURE IN PLACE

PROSTHETIC PATCH AORTOPLASTY
LONGITUDINAL INCISION MADE ACROSS COA
AREA ENLARGED WITH PATCH

BYPASS GRAFT
A TUBE IS SEWN BETWEEN ASCENDING AND DESCENDING AORTA

BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY

STENT IMPLANTATION

COMPLICATIONS
Residual COA Recurrent COA Systemic arterial HTN CAD PROGRESSIVE VALVE DISEASE Bicuspid stenosis Bicuspid regurgitation Aortic aneurysm Bact endocarditis