Cell Theory Robert Hooke observed compartments in a thin slice of cork. He named them cells.
Chapter 5 Cell Structure and Function. I. The history of cell study A. Robert Hooke—1665—coined...
-
Upload
stewart-mcdonald -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
2
Transcript of Chapter 5 Cell Structure and Function. I. The history of cell study A. Robert Hooke—1665—coined...

Chapter 5 Chapter 5
Cell Structure Cell Structure and Functionand Function

I. The history of cell studyI. The history of cell study
A. Robert Hooke—1665—coined A. Robert Hooke—1665—coined the word cell, looked at cork the word cell, looked at cork cellscells
B. Robert Brown—1831—B. Robert Brown—1831—discovered the "nucleus"discovered the "nucleus"

I. The history of cell studyI. The history of cell study
C. Theodor Schwann—1838—C. Theodor Schwann—1838—viewed animal cells in cartilageviewed animal cells in cartilage1. Cells are the elementary 1. Cells are the elementary
particles of plants and animalsparticles of plants and animals
D. Mattias Schleiden—Cells are the D. Mattias Schleiden—Cells are the fundamental basis of lifefundamental basis of life
E. Virchow—1858—All cells come E. Virchow—1858—All cells come from cellsfrom cells

I. The history of cell studyI. The history of cell study
F. Cell theoryF. Cell theory1. All living things are composed of 1. All living things are composed of
one or more cellsone or more cells2. Cells are the basic unit of 2. Cells are the basic unit of
structure and functionstructure and function3. All cells come from preexisting 3. All cells come from preexisting
cellscells

II. Attributes of cellsII. Attributes of cells
A. Cell sizeA. Cell size1. 1–100µm1. 1–100µm2. Why is there a limit to cell size?2. Why is there a limit to cell size?
a. Surface-to-volume a. Surface-to-volume ratioratio
b. Distance from b. Distance from surface to centersurface to center

II. Attributes of cellsII. Attributes of cells
B. Cell typesB. Cell types1. Prokaryotic—no nucleus, 1. Prokaryotic—no nucleus,
circular DNA, ribosomescircular DNA, ribosomes2. Eukaryotic—larger, nucleus, 2. Eukaryotic—larger, nucleus,
linear chromosomes, linear chromosomes, membranous organellesmembranous organelles

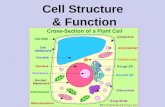
III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
A. All cells possess a plasma A. All cells possess a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, genetic membrane, cytoplasm, genetic materialmaterial1. Plasma membrane has 1. Plasma membrane has
phospholipid bilayer, embedded phospholipid bilayer, embedded glycoproteinsglycoproteins
a. Isolates cytoplasm a. Isolates cytoplasm from environmentfrom environment
b. Regulates molecular b. Regulates molecular movement into and movement into and out of cellout of cell
c. Interacts with other c. Interacts with other cells/environmentcells/environment

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
A. All cells possess a plasma A. All cells possess a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, genetic membrane, cytoplasm, genetic material (cont.)material (cont.)2. Genetic material—DNA, found in 2. Genetic material—DNA, found in
the nucleus (of eukaryotes)the nucleus (of eukaryotes)3. Cytoplasm—water, salts, organic 3. Cytoplasm—water, salts, organic
monomers and polymersmonomers and polymersa. Contains a. Contains
organellesorganelles

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
B. OrganellesB. Organelles1. Endoplasmic reticulum consists of 1. Endoplasmic reticulum consists of
folded membranes attached to the folded membranes attached to the nucleusnucleus
a. Rough ER is site of a. Rough ER is site of protein synthesis and protein synthesis and protein secretionprotein secretion
2. Ribosomes assemble amino acid 2. Ribosomes assemble amino acid monomers into polypeptide chainsmonomers into polypeptide chains
a. Associated with the a. Associated with the ERER
b. Composed of RNA b. Composed of RNA and proteinsand proteins

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
B. Organelles (cont.)B. Organelles (cont.)3. Golgi apparatus (dictyosomes) are 3. Golgi apparatus (dictyosomes) are
membranous sacs associated membranous sacs associated with ERwith ER
a. Processing and a. Processing and transport of transport of proteins, lipidsproteins, lipids
b. Synthesis and b. Synthesis and transport of transport of polysaccharidespolysaccharides
4. Lysosomes are Golgi-derived 4. Lysosomes are Golgi-derived vesicles containing digestive vesicles containing digestive enzymesenzymes

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
B. Organelles (cont.)B. Organelles (cont.)5. Mitochondria provide energy for 5. Mitochondria provide energy for
cellular functions (respiration)cellular functions (respiration)a. Membrane bound, a. Membrane bound,
numerousnumerousb. Matrix/ cristaeb. Matrix/ cristaec. Have their own c. Have their own
DNA and DNA and ribosomes; self-ribosomes; self-replicatereplicate

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
B. Organelles (cont.)B. Organelles (cont.)6. Plastids6. Plastids
a. Chloroplasts—function a. Chloroplasts—function in photosynthesisin photosynthesis
1) Green—contain 1) Green—contain chlorophyll pigmentchlorophyll pigment2) Stroma/grana 2) Stroma/grana
(thylakoid stacks)(thylakoid stacks)3) Have their own DNA 3) Have their own DNA
and ribosomes; self-and ribosomes; self-replicatereplicate4) Up to 100 per cell4) Up to 100 per cell
b. Mitochondria, plastids, b. Mitochondria, plastids, and the endosymbiont and the endosymbiont hypothesishypothesis

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
B. Organelles (cont.)B. Organelles (cont.)7. Vacuoles7. Vacuoles
a. Large, water-filled a. Large, water-filled spaces (cell sap)spaces (cell sap)
b. Can take up over b. Can take up over 90% of cell 90% of cell volumevolume
c. Surrounded by c. Surrounded by tonoplast (a tonoplast (a single membrane)single membrane)

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
B. Organelles (cont.)B. Organelles (cont.)7. Vacuoles (cont.)7. Vacuoles (cont.)
d. Functions:d. Functions:1) Storage of 1) Storage of
red/blue red/blue anthocyanins, anthocyanins, acids, salts, acids, salts, wasteswastes2) Maintain cell 2) Maintain cell
pressure (turgor pressure (turgor pressure)—pressure)—wiltingwilting

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
B. Organelles (cont.)B. Organelles (cont.)8. Nucleus is control center of the 8. Nucleus is control center of the
cellcella. Membrane bound a. Membrane bound
(nuclear (nuclear envelope)envelope)
b. Contains nucleoli; b. Contains nucleoli; synthesizes synthesizes ribosomal RNAribosomal RNA
c. DNA in c. DNA in chromosomes chromosomes (DNA and (DNA and proteins)proteins)

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
C. Cell walls in plant cells, C. Cell walls in plant cells, prokaryotic cells, fungiprokaryotic cells, fungi1. Polysaccharide composition1. Polysaccharide composition2. Function: support, protection2. Function: support, protection

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
D. Cytoskeleton of protein fibers D. Cytoskeleton of protein fibers (microfilaments, microtubules)(microfilaments, microtubules)1. Cell shape1. Cell shape2. Cell movement2. Cell movement3. Organelle movement3. Organelle movement4. Cell division4. Cell division

III. Cell structureIII. Cell structure
E. Cilia and flagella are protein E. Cilia and flagella are protein microtubule extensions of the microtubule extensions of the plasma membraneplasma membrane1. Aid in movement of simple 1. Aid in movement of simple
organismsorganisms

IV. Cell functionIV. Cell function
A. Protein assemblyA. Protein assemblyB. MetabolismB. Metabolism






































![[PPT]The Cell · Web viewThe Cell The basic unit of life Cell History The study of cells is called cytology. Robert Hooke was the first scientist to use the word cell. Robert Brown](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5af624ee7f8b9a154c90b720/pptthe-viewthe-cell-the-basic-unit-of-life-cell-history-the-study-of-cells-is.jpg)






![CELL THEORY A Brief History. Robert Hooke named the cell [1665] based on observations of the cell walls of cork tissue.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/56649f265503460f94c3dff5/cell-theory-a-brief-history-robert-hooke-named-the-cell-1665-based-on-observations.jpg)









