CHAPTER 4 ANATOMY of PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC CELLS SUFFOLK COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Dr. Reitano.
-
Upload
shanon-lloyd -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
3
Transcript of CHAPTER 4 ANATOMY of PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC CELLS SUFFOLK COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Dr. Reitano.

CHAPTER 4
ANATOMY ofPROKARYOTIC
and EUKARYOTIC CELLS
SUFFOLK COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE
Dr. Reitano

BASIC STRUCTURE OF ___KARYOTIC CELL

Basic Bacterial Shapes
BASIC SHAPES:
1. __________ rod-shaped
2. Coccus __________
3. Spiral

PROKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURES
• ______________– Cytoplasm– Nucleoid Region
• _____– Double-stranded– circular
– _____________– Inclusions/granules– Endospores
• ___________– Glycocalyx
• ________• Slime layer
– Appendages• Flagella• Pili• Fimbriae• Axial Filaments
CELL __________
(Outer Membrane)Cell Wall
Cell Membrane

______________• DESCRIPTION
– Sticky, gel-like– made of polysaccharides,
polypeptides, or both– surrounds cell
• TYPES– ______ – organized, firmly attached to cell wall;
ex. S. mutans – Slime layer – unorganized, _______ attached to cell wall, ex. S. __________, B. _________
• FUNCTION– __________ protect against phagocytosis– Protection against dehydration– ________ – play role in attachment and production
of biofilms

________________• Microbes ______ to solid surfaces and
grow into _____________• Masses will grow on rocks, pipes, teeth,
and medical implants

____KARYOTIC FLAGELLADescription
long, whip-like appendagesLocation
external to cell Structure
______ -outermost hook-widest
basal body-anchors Function
_____________Runs, tumbles, swarmsChemotaxis - response to chemical signals

AXIAL FILAMENTS in ___KARYOTESa.k.a. endoflagella
• Description– Bundles of filaments
• Location– Anchored at 1 end of
spirochete cells– Wrap around the length of
the spirochetes, ex. T. pallidum, B. burgdorferi
• Function– Spiral, corkscrew
___________

PROKARYOTIC __________• Description
– hair-like appendages
• Location– Surrounds entire cell or at poles of cell
• Function– __________ (_______________) – Ex. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
• Structure– Protein (pilin)

PROKARYOTIC _________• Structure
–Long, rigid, tubular structures–1 or 2 per cell
• Function–Conjugation –
transfer of _________ from 1 bacterial cell to another

BACTERIAL CELL __________:determine ________
provide structural __________

COMPARISON of GRAM POSITIVE and GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIAL CELL WALLS

PEPTIDOGLYCAN• Polymer of a _______________
N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) & N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM)
• Linked by polypeptides
Figure 4.13a

Figure 4.13b, c
BACTERIAL CELL ____ STRUCTURE
____________________________________________________

GRAM-_____________ CELL WALLS• PG -thick• __________ acids: Alcohol + phosphate
• Lipoteichoic acid links to plasma membrane• Wall teichoic acid links to peptidoglycan
– May regulate cation(+ ion) movement in and out cell– Provide antigenic specificity– Play role in cell growth
Figure 4.13b

GRAM _________ CELL WALL• PG - thin• _______________
– Structure• Lipopolysaccharides• Lipoproteins• Phospholipids• Porins
– Function• ____________
– Helps evade phagocytosis– Helps evade complement action– Barrier to certain antibiotics (penicillin),
lysozyme, detergents, metals, some dyes

ATYPICAL BACTERIAL CELL ______• _______________ sp.
– Lack cell walls– Sterols in plasma membraneEx. Mycoplasma pneumoniae
• ___________– Wall-less, or– Walls of pseudomurein (lack PG): (lack NAM and D-amino acids)

DAMAGE to BACTERIAL CELL WALLS
Some methods include:• ________- digests bonds between
disaccharides in peptidoglycan.– In G+, results in _____plasts (totally wall-less cells).– In G-, results in ______plasts (semi wall-less cells).
• _______- inhibits formation of peptide bridges in peptidoglycan.– G+ bacteria more susceptible than G- bacteria

• Thick peptidoglycan• _______ acids• In acid-fast cells,
mycolic acid present
Gram __________
Figure 4.13b–c
Thin peptidoglycan _________________ Periplasmic space
Gram __________
BACTERIAL CELL WALL SUMMARY

PRINCIPLE of __________• Crystal violet-iodine (CV-I) crystals
form in cell• Gram-________
– ________ dehydrates peptidoglycan– CV-I crystals do not leave
• Gram-___________– _________ dissolves outer__________ and leaves holes in __________________– CV-I _______________

___________ CELL MEMBRANE MODEL• STRUCTURE: PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER +
__________• FUNCTION: controls ________ into and out of cell,
PERMEABILITY DAMAGE to PLASMA Membrane- Results in leakage of cell contents/CELL DEATH– Caused by:
Alcohols, Ammonia (detergents), Polymixin antibiotics
Figure 4.14b

INTERNAL COMPONENTS OF ____KARYOTIC CELLS_____________
substance inside the plasma
membrane
Figure 4.6a, b
NUCLEAR AREA (___________ region)
Genetic materialSingle, circular chromosomeRIBOSOMES(____)Function in protein synthesis

_____KARYOTIC INCLUSIONS
• Metachromatic granules (volutin)
• Polysaccharide granules
• Lipid inclusions
• _________ granules
• ______________
• Gas vacuoles
• ____________
•Phosphate reserves
•Energy reserves•Energy reserves•Energy reserves
•Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase for CO2 fixation
•________________•Protein covered cylinders
Iron oxide (destroys ____)

ENDOSPORES
____________ cells•Resistant to desiccation, ______, chemicals•Bacillus sp., Clostridium sp.•___________: Endospore formation•Germination: Return to __________ state

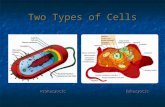
____KARYOTIC CELL
What groups of microorganisms are eukaryotic?

BASIC COMPARISON of ___________ CELL STRUCTURE

Flagella and ______**no _____ in _____karyotic cells
Figure 4.23a, b
___karyotic Flagellum: Structure
Microtubules Tubulin9 pairs + 2 arrangement

EUKARYOTIC _________ PROPERTIES*• Function
- ______, __________• Structure (lack ____________ acid)
– Carbohydrate• Cellulose, chitin, glucan, mannan
– Plants, algae, fungi
Cell walls _____ present in ______ cellsGlycocalyx
– Carbohydrates extending from animal plasma membrane
– Bonded to proteins and lipids in membrane

EUKARYOTIC PLASMA _____________STRUCTURE - Phospholipid bilayer + ________ -Sterols (may be present)- protection against lysis -Carbohydrates-serve as -attachment + recognition sitesFUNCTION -Selective ___________- allows
passage of some molecules: water, simple sugars, oxygen, amino acids, carbon dioxide
-Enzymes for ATP production

CYTOPLASMIC STRUCTURES of __KARYOTIC CELLS
• _____________– Substance inside plasma membrane and outside
nucleus• Cytosol
– ____ portion of cytoplasm• Cyto__________*
– microfilaments – Intermediate filaments– microtubules provide support and movement for cytoplasm
• Cytoplasmic ___________*– Movement of cytoplasm throughout cells

__KARYOTIC CELL ORGANELLES*• Membrane-bound:
– __________ Contains chromosomes, genetic information; histone
proteins**– ER Transport network between
plasma and nuclear membranes
– ____ complex Membrane formation,
distribution, protein packaging
– Lysosome Digestive enzymes– Vacuole Brings food into cells and
provides support
– Mitochondrion Cellular _________ (70S ribosomes)– Chloroplast(plants) _____________ (70S ribosomes)– Peroxisome Oxidation of fatty acids; destroys
H2O2

EUKARYOTIC CELL ORGANELLES
• Not membrane-bound:– _______________
• Protein synthesis (80S*)– _______________*
• Cell division• Consists of protein fibers and centrioles
– ______________*• Cell division• Mitotic spindle formation

COMPARISON OF PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS: AN
OVERVIEW_________________•One circular chromosome, not in a membrane•No histones•No organelles•_______: peptidoglycan cell walls•Archaea: pseudomurein cell walls•Divides by ________ fission
________________•_________ chromosomes, in nuclear membrane•Histones•Organelles•Polysaccharide cell walls, when present•Divides by ________

_______________________ THEORY
• __karyotes evolved from ____karyotes
• Prokaryotes develop a___________
• Eukaryotes ingest ________ bacteria – become _____________________
• Eukaryotes ingest photosynthetic bacteria – become chloroplast Figure 10.2

PLASMA ___________
• _________ transport NO ATP needed
– Simple diffusion– Facilitated diffusion– Osmosis
• __________ transport –
ATP needed– Transporter protein– Group translocation– Endocytosis
• Phagocytosis: Pseudopods extend and engulf particles
• Pinocytosis: Membrane folds inward bringing in fluid and dissolved substances
FunctionSelective __________ – allows passage
of some molecules via the following transport mechanisms:

Movement Across MembranesPASSIVE TRANSPORT
• Simple ______________: – Movement of a solute from an area of high
concentration to an area of low concentration.
• ________________ diffusion: – Movement of a solute from an area of high
concentration to an area of low concentration.– Solute combines with a _________ ________ in the
membrane.

Movement Across Membranes____________ TRANSPORT
• __________ ___________: – Movement of a solute from an area of high
concentration to an area of low concentration.

MOVEMENT ACROSS MEMBRANESFacilitated Diffusion (Passive Transport)
Figure 4.17
__________ combines with a transporter protein in the membrane.

MOVEMENT ACROSS MEMBRANES• ___________ (passive transport)
– Movement of __________ across a selectivelypermeable membrane from an area of higherwater concentration to an area of lower water conc.
• Osmotic pressure– The pressure needed to stop the movement of water across the membrane.
Figure 4.18a

Figure 4.17d
MOVEMENT OF WATER ACROSS MEMBRANES- Osmosis (Passive Transport)
• Movement of water from a ______ concentration of ________ to a lower concentration of water
( favorable gradient)a. through a phospholipid bilayer.b. through __________ (water transporting protein channels).

Figure 4.18a–b
THE PRINCIPLE OF ___________

THE EFFECT of ________ on _____

MOVEMENT ACROSS MEMBRANES
• ___________ transport – Transport of substances
requires a transporter protein and ATP.
Group translocation – Transport of substances
requires a transporter protein and PEP.

ENDOCYTOSIS & EXOCYTOSIS__________ TRANSPORT

________ vs. ______ TRANSPORTCLASSIFICATION of TRANSPORT
TRANSPORT PROTEIN
DIRECTION of MOVEMENT
REQUIRES ATP TYPE of TRANSPORT
SIMPLEDIFFUSION
____ Withconcentrationgradient
No ____________
FACILITATEDDIFFUSION
___ – carrierProteins or channel proteins
___________concentrationgradient
No Passive
ACTIVETRANSPORT
Yes – carrierProteins
_______concentrationGradient
________ Active

COMPARISON of PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC CELLSCELL PART FUNCTION PROKARYOTIC CELL* EUKARYOTIC CELL
Cell Wall Support/Protection Present* ________ only
Plasma membrane
Homeostasis/Transport
Present Present
Nucleus Control Center Absent Present
Genetic Material Cell Function/Properties Circular _________________
Histones Gene regulation/organization
Absent Present
Ribosomes Protein Synthesis Present (_______) Present (________)
____________ Internal Structure Absent Present
Mitochondrion Energy Production Absent Present
Chloroplast Photosynthesis Absent* Present*
EndoplasmicReticulum
Intracellular transport/chemical reactions
Absent Present
Golgi Apparatus Protein packaging/transport
Absent Present
___________ Digests Material Absent Present in some
Vacuole Storage Absent Present