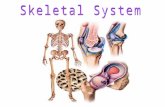
Chapter 15 lecture 1 Skeletal System. Provides support Allows for mobility Protects Vital...
-
Upload
christopher-scott -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
2
Transcript of Chapter 15 lecture 1 Skeletal System. Provides support Allows for mobility Protects Vital...
Skeletal System
• Provides support
• Allows for mobility
• Protects Vital Organs….your brain, spinal column, heart and lungs
• Produces blood cells
• Stores nutrients
From wikipedia.com
1. frontal bone 2. parietal bone (2) 3. temporal bone (2) 4. occipital bone 5. zygomatic bone (2) 6. superior and inferior maxilla 7. mandible
8. cervical vertebrae (7) incl. atlas & axis 9. nasal bone (2)10. Sternum11. hummerus (2) 12. ulna (2) 13. radius (2)14. lumbar vertebrae (5) thoracic vertebrae (12) 15. ilium16. sacrum not labeled coccyx
17. hip joint (joint, not bone) (2) 18. femur (2) 19. patella (2) 20. tibia (2) 21. fibula (2)
22. greater trochanter of femur 23. condyles of femur24. Knee joint not bone
25. clavicle or collarbone (2) 26. condyles of humerus 27. head of radius
28. ribs (2 x 12)29. scapula or shoulder blade (2)
Not Labeled:Palm or metacarpal bones:
metacarpal bones (5 × 2) Finger bones or phalanges:
proximal phalanges (5 × 2) intermediate phalanges (4 × 2) distal phalanges (5 × 2)
Ankle (tarsal) bones: calcaneus (heel bone) (2) talus (2) navicular bone (2) medial cuneiform bone (2) intermediate cuneiform bone (2) lateral cuneiform bone (2) cuboidal bone (2)
Instep bones: metatarsal bone (5 × 2)
Toe bones: proximal phalanges (5 × 2) intermediate phalanges (4 × 2)
distal phalanges (5 × 2)
Bone Formation
• Osseous tissue-type of connective tissue– Osteocytes
– Collagen
• Cartilaginous Tissue- fetal tissue from which bones develop
• Osteoblast- cells that mature and replace cartilage during ossification
• Osteoclasts- breakdown and reabsorb bone tissue
Bone Formation
• Calcium and phosphorus are necessary for formation of bones- enzymatic action causes these two minerals to bind together and produce calcium phosphate
• Vitamin D is also essential for proper absorption of these minerals
Long Bones• Epiphyseal line- growth plate bone gets
longer
• Epiphysis ends of the bones-made of spongy bone
• Diaphysis-shaft of the bone-made of compact bone
• Metaphysis-flared portion
• Periosteum-strong vascular covering of the bone
• Yellow Marrow-fat
• Compact bone-area of the diaphysis
Source: wikipedia.com
Bone Structures
• Head- rounded end of the bone seperated by the neck from the body of the bone
• Tubercle- round process on the bone where tendons or muscles attach
• Tuberosity- lager round process where tendons and muscles attach
• Condyle- knuckle-like process at the joint
Bone Structures- depressions• Fossa- shallow cavity• Foramen- opening for blood vessels or
nerves• Fissure- narrow deep slit on the bone’s
surface• Sinus- a hollow cavity in a bone• Trochanter-large bump on femur• Tubercle-round process where muscle and
tendons attach
•Compact and spongy bone have lots of blood vessels that move through them
• blood vessels pick up new blood cells and deposit minerals for storage
U.S. National Cancer Institute's Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Program (http://training.seer.cancer.gov/index.html)Exact adress
Flat Bone
• Flat bones are found in the skull
• Compact bone sandwiches cancellous bone on each side.
• Provides a shield for internal organs and especially your brain
Source:wikipedia.com
Bone development
• Osteoblasts-osteocytes that replace the cartilage with bone
• Osteoclasts- break down bone to replace it over time
• Minerals attach to the bone structure
Growth of Long Bones
• Epiphyseal line is where the bone presses each direction creating elongation
• Damage to this area during growth causes the bone to be shorter than it should be
Growth of Long Bones
• If the work of the growth plate is interrupted one leg or arm will be shorter than the other
• If growth is interrupted by disease or chemicals of all epiphyseal plates then the person will have a shorter stature and may have problems later in life with bone disease
Bone Growth
source: http://training.seer.cancer.gov/module_anatomy/unit3_3_bone_growth.html
Fracture
• The Diagram is a simple complete fracture
• During a fracture the bone tissue will often bleed just like other wounds in the body
• The tissue will swell to create immobilization and decrease use.
• As the bone heals it creates a callus and is thicker than the bone was before
Fracture Myths
• These are false statements….– You can’t move a broken bone, or the joint
closest to the break– You can tell by looking at a limb that it is
broken– Casting is always necessary for proper healing– Taking vitamins prevents fractures
Male and Female
• Male skeletal system has denser bones
• The pelvic girdle is shaped differently in men and women
• The number of bones in the same
Bone Identification
Be able to divide the bones into the following groups
• Identify the long bones (femur, ulna, radius…)
• Identify the flat bones (skull bones, sternum….)
• Identify Irregular bones (ribs, patella,….)
Joint Basics• bone ends are protected by articular cartilage and a joint capsule
•The outer most edge of the articular cartilage is covered with the synovial membrane which secretes fluid to lubricate the joint