Chapter 1 notes - FCSC Library Home Page and Physiology/Chapter 1... · Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 1...
Transcript of Chapter 1 notes - FCSC Library Home Page and Physiology/Chapter 1... · Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 1...

1
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Slides 1.1 – 1.8
Seventh Edition
Elaine N. Marieb
Chapter 1
The Human Body:
An Orientation
Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook
The Human Body The Human Body –– An OrientationAn Orientation
Slide 1.1Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Anatomy – study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts
• Physiology – study of how the body and its parts work or function
Anatomy Anatomy –– Levels of StudyLevels of Study
Slide 1.2aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Gross Anatomy
• Large structures
• Easily observable
Figure 1.1

2
Anatomy Anatomy –– Levels of StudyLevels of Study
Slide 1.2bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Microscopic Anatomy
• Very small structures
• Can only be viewed with a microscope
Figure 14.4
Levels of Structural OrganizationLevels of Structural Organization
Slide 1.3Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 1.1
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.4Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Integumentary
• Forms the external body covering
• Protects deeper tissue from injury
• Synthesizes vitamin D
• Location of cutaneous nerve receptors
Figure 1.2a

3
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.5Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Skeletal
• Protects and supports body organs
• Provides muscle attachment for movement
• Site of blood cell formation
• Stores mineralsFigure 1.2b
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.6Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Muscular
• Allows locomotion
• Maintains posture
• Produces heat
Figure 1.2c
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.7Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
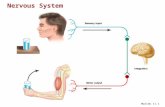
• Nervous
• Fast-acting control system
• Responds to internal and external change
• Activates muscles and glands
Figure 1.2d

4
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.8Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Endocrine
• Secretes regulatory hormones
• Growth
• Reproduction
• Metabolism
Figure 1.2e
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.9Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Cardiovascular
• Transports materials in body via blood pumped by heart
• Oxygen
• Carbon dioxide
• Nutrients
• WastesFigure 1.2f
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.10Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Lymphatic
• Returns fluids to blood vessels
• Disposes of debris
• Involved in immunity
Figure 1.2g

5
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.11Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Respiratory
• Keeps blood supplied with oxygen
• Removes carbon dioxide
Figure 1.2h
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.12Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Digestive
• Breaks down food
• Allows for nutrient absorption into blood
• Eliminates indigestible material
Figure 1.2i
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.13Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Urinary
• Eliminates nitrogenous wastes
• Maintains acid – base balance
• Regulation of materials
• Water
• ElectrolytesFigure 1.2j

6
Organ System OverviewOrgan System Overview
Slide 1.14Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Reproductive
• Production of offspring
Figure 1.2k
Necessary Life FunctionsNecessary Life Functions
Slide 1.15Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Maintain Boundaries
• Movement
• Locomotion
• Movement of substances
• Responsiveness
• Ability to sense changes and react
• Digestion
• Break-down and delivery of nutrients
Necessary Life FunctionsNecessary Life Functions
Slide 1.16aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Metabolism – chemical reactions within the body
• Production of energy
• Making body structures
• Excretion
• Elimination of waste from metabolic reactions

7
Necessary Life FunctionsNecessary Life Functions
Slide 1.16bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Reproduction
• Production of future generation
• Growth
• Increasing of cell size and number
Survival NeedsSurvival Needs
Slide 1.17aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Nutrients
• Chemicals for energy and cell building
• Includes carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals
• Oxygen
• Required for chemical reactions
Survival NeedsSurvival Needs
Slide 1.17bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Water
• 60–80% of body weight
• Provides for metabolic reaction
• Stable body temperature
• Atmospheric pressure must be appropriate

8
HomeostasisHomeostasis
Slide 1.18Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Maintenance of a stable internal environment = a dynamic state of equilibrium
• Homeostasis must be maintained for normal body functioning and to sustain life
• Homeostatic imbalance – a disturbance in homeostasis resulting in disease
Maintaining HomeostasisMaintaining Homeostasis
Slide 1.19aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• The body communicates through neural and hormonal control systems
• Receptor
• Responds to changes in the environment (stimuli)
• Sends information to control center
Maintaining HomeostasisMaintaining Homeostasis
Slide 1.19bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Control center
• Determines set point
• Analyzes information
• Determines appropriate response
• Effector
• Provides a means for response to the stimulus

9
Feedback MechanismsFeedback Mechanisms
Slide 1.20aCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Negative feedback
• Includes most homeostatic control mechanisms
• Shuts off the original stimulus, or reduces its intensity
• Works like a household thermostat
Feedback MechanismsFeedback Mechanisms
Slide 1.20bCopyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Positive feedback
• Increases the original stimulus to push the variable farther
• In the body this only occurs in blood clotting and birth of a baby
The Language of AnatomyThe Language of Anatomy
Slide 1.21Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Special terminology is used to prevent misunderstanding
• Exact terms are used for:
• Position
• Direction
• Regions
• Structures

10
Orientation and Directional TermsOrientation and Directional Terms
Slide 1.22Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Table 1.1
Orientation and Directional TermsOrientation and Directional Terms
Slide 1.23Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Table 1.1 (cont)
Orientation and Directional TermsOrientation and Directional Terms
• Contralateral
- pertaining or relating to the opposite side
• Ipsilateral
- on the same side
• Bilateral
- relating to the right and left sides of the body or of a
body structure such as the right & left extremities

11
Orientation and Directional TermsOrientation and Directional Terms
• Supine
lying on the back; face upward position of the body
• Prone
the body lying face downward; stomach lying
• Volar
relating to palm of the hand or sole of the foot
• Plantar
relating to the sole or undersurface of the foot
Anterolateral Superomedial
Anteromedial Superolateral
Anteroposterior Inferomedial
Posteromedial Inferolateral
Posterosuperior Anterosuperior
Anteroinferior Posterolateral
Posteroinferior
Body LandmarksBody Landmarks
Slide 1.24Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Anterior
Figure 1.5a

12
Body LandmarksBody Landmarks
Slide 1.25Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Posterior
Figure 1.5b
Body PlanesBody Planes
Slide 1.26Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 1.6
Body CavitiesBody Cavities
Slide 1.27Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 1.7

13
Abdominopelvic QuadrantsAbdominopelvic Quadrants
Slide 1.28Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 1.8a
Abdominopelvic RegionsAbdominopelvic Regions
Slide 1.29Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 1.8b
Abdominopelvic Major OrgansAbdominopelvic Major Organs
Slide 1.30Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 1.8c