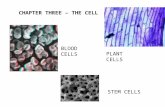
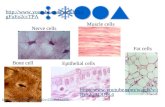
Cells
description
Transcript of Cells

Cells The Building Blocks of Life

The Cell
A cell is defined as the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms.
It is the smallest living building block of all organisms
Some cells are single organisms
Some cells group together to form living tissues of a larger, more complex organism

Robert Hooke
The first person to name the cell was Robert Hooke in 1665
He used an early version of a microscope to look at cork and described the little boxes as cells (as in a jail cell)
He believed only plants had “cells”From: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/history/hooke.html

Van Leeuwenhook
A Dutch inventor who created the microscope that we recognize today
In 1678, he was the first person to discover a single celled protozoa
He called these “Little Animals” He also looked at blood cells

Cell Theory All organisms
are made of one or more cells
The cell is the basic unit of all living things
All cells come from existing cells
From : http://www.answers.com/topic/cell-theory-1
Cell theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure in every living thing. Development of this theory during the Mid 1600s was made possible by advances in microscopy. This theory is one of the foundations of biology. The theory says that new cells are formed from other existing cells and the cell is a fundamental unit of structure, function and organization in all living organisms.

Types of Cells
Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
Think “Eu” = YouYou have eukaryotic cells just like all animals and most plants.
Think ProMeans NO!No nucleus

Prokaryotes
Think ProMeans NO!No nucleus

Prokaryote Cell Cells that DO NOT have a nucleus. These single cells are molecules
surrounded by a membrane and cell wall. Prokaryotic cells lack typical “organelles”, but may contain a membrane system inside a cell wall. Examples include simple bacteria

Eukaryotes
Think “Eu” =YouYou have eukaryotic cells just like all animals and most plants.

Eukaryotes Eukaryotic Cell
Cells that have a nucleus and usually have organelles that perform specific jobs for the cell.
Example – Plant and Animal Cells are Eukaryotic
Eukaryotic cells usually are 10 times larger than Prokaryote cells.
See the visible nucleus (dark spot)

Typical Eukaryotic Cell
Eukaryotic Cell

Difference between cell types

Eukaryotes have organelles Organelles are the structures (PARTS)
inside of a cell that perform the functions necessary for the cell to survive.
Example: Think about your heart, lungs and liver… They are all organs inside of your body. The cell has parts like this inside of its cell that are called
organelles.

Organelles have specific jobs

Cell Membrane The cell membrane is the protective layer
that covers the cell’s surface. It acts like the fence around a yard. It is
like the skin on your body. It keeps some things out and lets other things in.

Functions of the cell membrane Support Protection Controls movement of materials in/out of
cell Barrier between cell and its environment Maintains homeostasis

Cell Wall Cell Wall: not found in animal cells Gives support to the cell Is a second layer or “fence” like the cell
membrane.

Found in : plant, fungi, and some bacteria, but not animal cells
Description : Outer layer that is rigid
& strong Made of cellulose
Function –Support and protection of cell
not found in animal cells

Nucleus Nucleus: An organelle inside of the cell
that directs the activity in the cell. It holds the DNA (chromosomes)
This is the blue print material (directions) for the cell.
It tells how to reproduce and perform all of the cells jobs.
nucleus

The Nucleus is like your brain!
The nucleus tells all the other cell parts what to do.

Mitochondria Mitochondria The organelle that releases
energy in the cell. (The powerhouse of the cell)
Breaks down sugar (glucose) molecules to release energy

Chloroplasts (plants only)
Chloroplasts Organelle that produces chlorophyll. ( The chemical of photosynthesis) to power the plant cell. Chlorophyll traps the energy of sunlight, which
is then used by the plant cell to make sugar for energy.
Only found in PLANT cells.

Function of the chloroplasts Uses energy from sun to make food
(glucose) for the plant Process called photosynthesis Responsible for the conversion ofCarbon dioxide toCarbohydrates Similar to themitochondria of the animal cells

Cytoplasm Cytoplasm The gel-like material inside of
the cell membrane. Found in all cells Keeps organelles in place

Cell Movement Some single celled
organisms must move about to search for food.
They can move by:1. Cilia2. Flagella (whip-like
tails)3. Pseudopods (false
feet)
1
2
3

Movement Examples
Pseudopod movement

Cells and your body
The cells in your body function similar to the way your entire body works
The nucleus (brain) tells the cell what to do The organelles each perform a specific
task to help the body survive All living things are made up of cells.

Responsible for intracellular digestion and the release of cellular waste products.
In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small.
Large in plant cells and play a role in turgor pressure.

Ribosomes Site of protein synthesis, it may be free in the cytoplasm
or attached to membranes.
LysosomesContains digestive enzymes, if it breaks it will kill the cell
Endoplasmic ReticulumInterconnection channels that store and transport
materials around the cell.

Questions for Thought
Why are cells considered the most basic level of life?
Why are Eukaryotes considered more advanced than Prokaryotes?
Name some cells in your body. Are they all alike or different?
How would our bodies work differently if we had chloroplasts in our body cells?

AliensAliens are often shown as being green creatures? Can you guess why?

Answer Many scientists believe if there is life on other planets
that it would have evolved differently than life on Earth. One belief is that life forms would be a cross between animals and plants and, therefore, aliens would have the ability to use sunlight as a source of food. Cool!

References
http://www.williamsclass.com/SeventhScienceWork/CellTheoryParts.htm