Cell Membrane & Cell Transport. About Cell Membranes* 1.All cells have a cell membrane 2.Functions:...
-
Upload
karen-flynn -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
3
Transcript of Cell Membrane & Cell Transport. About Cell Membranes* 1.All cells have a cell membrane 2.Functions:...

Cell Membrane & Cell Transport

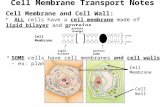
About Cell Membranes*
1.All cells have a cell membrane
2.Functions: a.Controls what enters
and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis
b.Provides protection and support for the cell
TEM picture of a real cell membrane.

Cell Membranes are made of aPHOSPHOLIPID bilayer which isAmphipathic –
Molecules with both hydrophilic
and hydrophobic regionsphosphate
lipid
hydrophilic
hydrophobic

PHOBIC TAILS in center determine what can pass through

*More than just a barrier…
• Expanding our view of cell membrane beyond just a phospholipid bilayer barrier– phospholipids plus…

*A membrane is a collage of different proteins & carbohydrates & cholesterol embedded in the fluid matrix of the lipid bilayer

Proteins
Membrane movement animation
Polar heads love water & dissolve.
Non-polar tails hide from water.
Carbohydrate cell markers
*Fluid Mosaic Model of the
cell membrane

Membrane Proteins• Proteins determine most of membrane’s specific
functions– cell membrane & organelle membranes each have
unique collections of proteins
• Membrane proteins:– peripheral proteins = loosely
bound to surface of membrane– integral proteins = penetrate into
lipid bilayer, often completely spanning the membrane = transmembrane protein

Membrane Carbohydrates • Attached to proteins (glycoproteins)
or lipids (glycolipids)
• Play a key role in cell-cell recognition– ability of a cell to distinguish neighboring cells
from another– important in organ &
tissue development– basis for rejection of
foreign cells by immune system
http://faculty.southwest.tn.edu/rburkett/GB1-osmosis.htm

Types of Cellular Transport
• Passive Transport
cell doesn’t use energy1. Diffusion
2. Facilitated Diffusion
3. Osmosis
• Active Transport
cell does use energy1. Protein Pumps
2. Endocytosis
3. Exocytosis
high
low
This is gonna be
hard work!!
high
low
Wee!!!

*Molecules need to move across membranes in cells
Image modiified from: http://www.accessexcellence.org/AB/GG/importProt.html
INfoodcarbohydratessugars, proteinsamino acidslipidssalts, O2, H2O
OUTwasteammoniasaltsCO2
H2O products

*Diffusion: movement directly through membrane. What molecules can get through directly?
inside cell
outside cell
Small non-polar molecules (O2 & CO2) and hydrophobic molecules (fats & other lipids)
can slip directlythrough the phospholipid cell membrane, but…
lipid
salt
aa H2Osugar
NH3
O2
What about other stuff?

Diffusion
• Passive transport– No energy needed
• High to low concentration
• Small, nonpolar molecules
• Continues until equilibrium and then moves randomly

*Diffusion• 2nd Law of Thermodynamics
governs biological systems– Universe tends towards disorder
• Diffusion– movement from [higher] [lower] concentration
Animatioin from: http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/diffusion-animated.gif

*Diffusion will also happen across a cell membrane as long as there is a difference in concentration and the membrane will let the molecule pass through until equilibrium and then moves randomly

The Special Case of Water
Movement of water across the cell membrane =
OSMOSIS

Osmosis is diffusion of water• Water is very important, so we talk about
water separately
• Diffusion of water from high concentration of water to low concentration of water– across a
semi-permeable membrane
– Passive– Uses no energy

Concentration of water• Direction of osmosis is determined by
comparing total solute concentrations– Hypertonic - more solute, less water– Hypotonic - less solute, more water– Isotonic - equal solute, equal water
hypotonic hypertonic
water
net movement of water

Solute concentration
Lower outsidethan inside
Equal outsideand inside
Greater outsidethan inside
HYPOTONIC ISOTONIC HYPERTONIC
What will happen to an animal cell placed in different solutions?

*How Organisms Deal with Osmotic Pressure
•Bacteria and plants have cell walls that prevent them from over-expanding. In plants the pressure exerted on the cell wall is called tugor pressure.
•A protist like paramecium has contractile vacuoles that collect water flowing in and pump it out to prevent them from over-expanding.
•Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they do not dehydrate.
•Animal cells are bathed in blood. Kidneys keep the blood isotonic by remove excess salt and water.

*Grocery stores spray water on their veggies to “plump them up”
http://www.painetworks.com/photos/gt/gt0461.JPG

Animal cells
http://www.stchs.org/science/courses/sbioa/metenergy/bloodcells.gif
= CYTOLYSIS = CRENATION

Plant cellshttp://www.stchs.org/science/courses/sbioa/metenergy/aplantturgor.gif
= PLASMOLYSISCell wall keepsplant cell from bursting

http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_vacuole.html
*Loss of water from central vacuole= plants “wilt”
Vacuole full of water gives plant support (turgor pressure)
Turgid = very firmFlaccid = limp

*Managing water balance• Isotonic
– animal cell immersed in isotonic solution• blood cells in blood• no net movement of water across
plasma membrane• water flows across membrane, at
same rate in both directions• volume of cell is stable

Facilitated diffusion• Move from HIGH to LOW concentration with
aid of membrane transport proteins – passive transport
• no energy needed
– facilitated = with help– Medium size molecules;
monomers

Ion Channels
Move from HIGH to LOW concentration with aid of membrane transport proteins
- passive transport- no energy needed
-facilitated = with help-Small, charged molecules

*Carriers and Channels are specific
inside cell
outside cell
sugaraaH2O
saltNH3
. . . BUT STILL MOVES FROM [HIGHER] to [LOWER]

Active transportUses energy from ATP to move molecules
against concentration gradient
– Moves from [lower] → [higher]
– Uses protein pumps
OR
vesicles
Animations from: http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/cell-movement.htmlhttp://www.cat.cc.md.us/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit1/eustruct/images/sppump.gif

Active transportSODIUM-POTASSIUM PUMPSets up difference in charge across membranes
Pumps 3 Na+ outand 2 K+ in
Makes cells more + outside more - inside
Animation from: http://www.cat.cc.md.us/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit1/eustruct/images/sppump.gif

• ACTIVE transport– Requires energy (ATP)
• Uses vesicles
*BULK TRANSPORT
Animation from: http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBooktransp.html

Endocytosis
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor-mediated endocytosis
“Cell eating” large molecules;whole cells
“Cell drinking”Fluids;Small molecules
triggered byligand signal

*PHAGOCYTOSISAnimation from: http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/cell-movement.html
http://www.accs.net/users/kriel/chapter%20nine/
“Cell eating” takes in large molecules;whole cells
See phagocytosis in action:

*Example in cells:WHITE BLOOD CELL ENGULFING BACTERIA using Phagocytosis
http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/255/255ion/fig14x28.jpg

*PINOCYTOSIS
“Cell drinking”
Takes in fluids;
Small molecules
http://student.ccbcmd.edu/~gkaiser/biotutorials/eustruct/pinocyt.html

EXOCYTOSIS• Active transport (requires ATP)• Uses vesicles• Releases substances to outside
INSULIN being released by pancreas cells using exocytosis

*GOLGI BODIES USE EXOCYTOSIS
Animation from: http://www.franklincollege.edu/bioweb/A&Pfiles/week04.html
Video: http://www.southtexascollege.edu/tdehne/BC_ShockwaveAnimations/07SWF-TourOfTheCell/07-16-EndomembraneSystem.swf

*Transport summary

*PROBLEM for Cells?
Cell membranes areSELECTIVELY PERMEABLE