Brain Stem Anatomi
-
Upload
nor-ubudiah-seti -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
0
Transcript of Brain Stem Anatomi
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
1/55
Brainstem & Cranial Nerves
Maryann Martone, Ph. D.
NEU 256
October 13, 2005
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
2/55
Review: Levels of the Spinal Cord
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
3/55
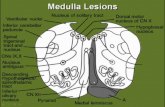
Ventricles in brainstem
Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct
Metencephalon 4th ventricle
Mylencephalon 4th ventricle
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
4/55
vermis
Occipital
LobeThalamus
Corpus callosum
Hypothalamus
Fornix
Anterior
commissure
Optic nerve
4th ventricle
Posterior commissure
pyramid
Mammillary body
Quadrigeminal
cistern
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
5/55
internal capsulebasal ganglia
optic nerveoptic tract
hypothalamusmammillary body
cerebral peduncle
interpeduncular fossa
flocculus
inferior olivary
nuclear complex
cerebellum
cerebellar tonsil
pyramid
pyramidal decussation
pons
optic chiasm
Anterior view of brainstem
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
6/55
optic tract
optic nerve
hypothalamus
optic chiasm
middle cerebellar peduncle
trigeminal nerve
vestibulocochlear nerve
flocculus
cuneate tubercle
inferior olivary nuclear complex
anterior median fissure pyramid
pons
cerebral
peduncle
Lateral view of brainstem
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
7/55
Middle cerebellar
peduncle
Superior colliculus
Inferior colliculusCerebral
peduncle
Superior cerebellar
peduncle
Inferior cerebellar
peduncle
Medulla
4th ventricle
Posterior view of brainstem
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
8/55
Components of the brainstem
Sensory ascending pathways (dorsal)
Motor descending pathways (ventral)
Cerebellar pathways Cranial nerve sensory and motor tracts
CPGs: rhythmic chewing, respiration,cardiovascular regulation & gain adjustments
for reflexes Modulatory systems: locus coeruleus, raphe
& substantia nigra
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
9/55
Ascending sensory pathways
Fine discriminitive touch, conscious proprioception
Fasciculus gracilis: Terminates in the nucleus gracilis (medulla) Fasciculus cuneatus: Terminates (medulla) in the cuneate and
accessory cuneate nuclei
Sensations ofpain and temperature
Lateral Spinothalamic Tract origin dorsal horn cells of the gray matter
Fibers cross contralaterally through the anterior commissure andascend to the VPL nucleus
Transmits sensations oftouch
Ventral Spinothalamic Tract
origin cells of the posterior horn
Fibers cross to the opposite side in the anterior commissure
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
10/55
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
11/55
Descending motor pathways
Voluntary movement
Lateral Corticospinal Tract Originates in large pyramidal cells (precentral gyrus)
cross to the opposite side of the cord at the pyramidal decussation &terminate in the dorsal horn cells
Ventral Corticospinal Tract
Originates in the pyramidal cells (motor area of the cortex)
Impulses related to equilibrium and antigravity reflexes
Vestibulospinal Tract
Fibers originate in the vestibular nuclei of the medulla and terminate
at level of the sacral spinal nerves
Connects vestibular complex and head and eye movementcoordination center in medulla
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
Contains both ascending and descending fibers
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
12/55
Motor HierarchyLateral group (extremities;
fine motor control)
Corticospinal tract
Rubrospinal tract
Medial group (axialmusculature; rhythmic and
postural movements)
Vestibulospinal tract
Tectospinal tract
Reticulospinal tract
Final common path:
motor pool
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
13/55
Reticular Formation
Core of brainstem(midbrain, pons and medulla)composed of looselyorganized neurons, outside of
the major nuclear groups ofthe brainstem.
Medial-to-lateral: raphenuclei, gigantocellular region,small cell region
Participate in widespread
connections Rostral continuation of
interneuronal network foundin spinal cord
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
14/55
Cerebellar pathways
Conduct impulses from the leg and trunk muscles for
unconscious proprioception
Dorsal & Ventral Spinocerebellar Tracts
Enter cerebellum via inferior cerebellar peduncle
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
15/55
Brainstem Internal Anatomy
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
16/55
Components of the brainstem
Sensory ascending pathways (dorsal): Relay nuclei, tracts
Motor descending pathways (ventral) Tracts, motor nuclei brainstem
Cerebellar pathways Tracts, cerebellar afferent and efferent nuclei
Cranial nerve sensory and motor tracts Cranial nerve nuclei, nerve entry and exit points
CPGs: rhythmic chewing, respiration, cardiovascularregulation & gain adjustments for reflexes
Modulatory systems: locus coeruleus, raphe &substantia nigra
Chemically coded nuclei
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
17/55
Tracing through the brainstem:
Dorsal Column/Medial Lemniscal
System
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
18/55
Corticospinal Tract
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
19/55
Caudal Medulla
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
20/55
Caudal Medulla
Closed medulla
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
21/55
Medulla
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
22/55
Rostral Medulla
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
23/55
Rostral Medulla
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
24/55
Medulla-Pons Junction
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
25/55
Mesencephalon
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
26/55
The Cranial Nerves
The head and neck are not innervatedby spinal nerves
Sensory information is received and
motor information is sent via 12 cranialnerves
Considered part of the PNS they
convey messages to and from thebody's muscles and glands.
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
27/55
Each cranial nerve.
Can be referred to by a name ornumber!
Has a general function
Has at least a motor, sensory orparasympathetic component
Some have more than one component
Has associated brainstem nuclei Innervates a structure(s)
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
28/55
I
I
II
IIIIV
V
VI
VIIIVII
IXX
XI XII
Cranial nerves can be identifiedon the ventral surface of the brain
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
29/55
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
30/55
I Olfactory On Some
II Optic Old Say
III Occulomotor Olympus Marry*
IV Trochlear Towering Money
V Trigeminal Tops ButVI Abducens A My
VII Facial Frenchman Brother*
VIII Auditory/Vestibulocochlear And Says
IX Glossopharyngeal German Big*
X Vagus Viewed Business*XI Spinal/Accessory Some Makes
XII Hypoglossal Hops Money
Some tricks to learning cranial nerve
numbers, names & components
S = Sensory
M = Motor
B = Both/Mixed Sensory & Motor
* = Parasympathetic
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
31/55
Arrangement of
brainstem
cranial nervenuclei in
columns
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
Insert picture with
different levels
differentiated
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
32/55
General Rules of Thumb
Most motor nuclei are
associated with a singlecranial nerve
Afferent nuclei often receive
fibers from several cranial
nerves
All associated with a
single function however,
e.g., nucleus of solitary
tract
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
33/55
Functions of Cranial Nerves
www.neurophys.com/EMG/Cranial_Nerves/
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
34/55
Cranial Nerve I: Olfactory
Component: Sensory
Function: Smell
Tract: Olfactory cells of nasal mucosa
Olfactory Bulbs pyriform cortex
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
35/55
Cranial Nerve II: Optic
Component(s): Sensory
Function: Vision
Tract: retinal ganglioncells opticchiasmthalamusprimary visualcortex in
occipital lobe
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
36/55
Cranial Nerve III: Oculomotor
Component #1: Motor
Function(s): Movement of eyeball &
lens accomodation
Structure(s)
Innervated:
4 eyeball muscles & 1
eyelid muscle
Component #2: Parasympathetic
Nucleus location: midbrain
Function: pupil constriction
Structure(s)
Innervated:
ciliary muscle and
pupillary constrictor
muscles
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
37/55
Cranial Nerve III: Oculomotor
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
38/55
Cranial Nerve IV: Trochlear
Component: Motor
Function: moves eyeball
Nucleus location: midbrain
Structure(s)
Innervated:
superior oblique muscles
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
39/55
Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal
Component #1: Sensory(impulses oftouch, pain, heat and
cold)
Locations of nuclei: pons & medulla
Function: (1) sensations; (2)
general sensory fromtongue; (3)
proprioception
Structure(s)
Innervated:
(1) face, scalp, teeth,
lips, eyeballs, nose &
throat lining; (2) anterior
2/3 of tonque; (3)
muscles of mastication
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
40/55
Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal
Component #2: Motor
Function: chewing
Nucleus location: trigeminal motor nucleusin pons
Structure(s)
Innervated:
muscles of mastication
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
41/55
Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
42/55
Cranial Nerve VI: Abducens
Component: Motor
Function: Eyeball movement
Nucleus: abducens nucleus in
pons
Structure(s)
Innervated:
lateral rectus muscle of
eye
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
43/55
Cranial Nerve VII: Facial
Component #2: Motor
Nucleus location: facial motor nucleus in
ponsFunction: facial expressions
Structure(s)
Innervated:
muscles of the face
Component #1: Sensory
Nucleus location: medulla
Function: (1) taste & (2)
proprioception
Structure(s)
Innervated:
(1) anterior 2/3 of tongue
& (2) face and scalp
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
44/55
Cranial Nerve VII: Facial
Component #3: ParasympatheticNucleus location: Superior salivatory
nucleus in medulla
Function: salivation and lacrimation
(drooling and tears)
Structure(s)
Innervated:
salivary and lacrimal
glands via
submandibular and
pterygopalatine gamglia
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
45/55
Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear(aka acoustic or auditory nerve)
Component: Sensory
Functions: (1) Balance
(2) Hearing
Nucleus: In pons and medulla
Structure(s)
Innervated:
vestibular apparatus of
internal ear
cochlear of internal ear
auditory cortex in the
temporal lobes
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
46/55
Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear(aka acoustic or auditory nerve)
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
47/55
Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal
Component #1: Sensory
Nucleus location: medulla
Function: (1) taste; (2)proprioception for
swallowing & (3) blood
pressure receptors
Structure(s)
Innervated:
(1) posterior two thirds of
tongue; (2) throatmuscles & (3) carotid
sinuses
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
48/55
Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal
Component #2: Motor
Nucleus location: medulla
Function: (1) swallowing and gagreflexes & (2) tear
production
Structure(s)
Innervated:
(1) throat muscles and
(2) lacrimal glands
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
49/55
Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal
Component #3: Parasympathetic
Function: saliva production
Structure(s)
Innervated:
parotid glands
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
50/55
Cranial Nerve X: Vagus
Component #1: Sensory
Nucleus location: medulla
Function: (1) chemoreceptors; (2)
pain receptors; (3)sensations; (4) taste
Structure(s)
Innervated:
(1) blood oxygen
concentration, carotid
bodies; (2) respiratory &
digestive tracts; (3)external ear, larynx &
pharynx (4) tongue
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
51/55
Cranial Nerve X: Vagus
Component #2: Motor
Nucleus location: medulla
Function(s): (1) heart rate & stroke
volume; (2) peristalsis;(3) air flow; (4) speech &
swallowing
Structure(s)
Innervated:
(1) pacemaker &
ventricular muscles; (2)
smooth muscles of thedigestive tract (3) smooth
muscles in bronchial
tubes (4) muscles of
larynx a & pharynx
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
52/55
Cranial Nerve X: Vagus
Component #3: Parasympathetic
Structure(s)
Innervated:
smooth muscles and
glands of the same areas
innervated by motorcomponent, as well as
thoracic and abdominal
areas
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
53/55
Cranial Nerve XI: Spinal Accessory
Component: Motor
Function: head rotation (& shoulder
shrugging!)
Nucleus location: accessory nucleus in
medullaStructure(s)Innervated:
trapezius &sternocleidomastoidmuscles
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
54/55
Cranial Nerve XII: Hypoglossal
Component: Motor
Function: Speech and swallowing
Nucleus location: In medulla
Structure(s)Innervated:
Throat and tonguemuscles
-
7/28/2019 Brain Stem Anatomi
55/55
Cranial Nerve XII: Hypoglossal