Blood 1. Blood Blood is not an epithelial tissue, and it’s not loose or dense connective tissue;...
-
Upload
cassandra-sherman -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Blood 1. Blood Blood is not an epithelial tissue, and it’s not loose or dense connective tissue;...

BloodBlood
11

BloodBlood Blood is not an epithelial tissue, and Blood is not an epithelial tissue, and
it’s not loose or dense connective it’s not loose or dense connective tissue; it’s classified as a “special tissue; it’s classified as a “special connective tissue”. connective tissue”.
You have about 5 liters of blood, but You have about 5 liters of blood, but that is only half of the body fluid. that is only half of the body fluid.
The other half includes fluid around The other half includes fluid around each cell, and joint fluids, etc.each cell, and joint fluids, etc.
22

Blood plasma circulates Blood plasma circulates outside of the blood vessels outside of the blood vessels
too!too!
PLASMA EXTRACELLULAR FLUID ↑↓ ↓↑ ↓↑
SYNOVIAL FLUIDS JOINTS CSF
33

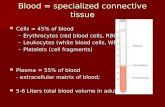
Blood consists of the Blood consists of the following:following:
PlasmaPlasma Red blood cellsRed blood cells White blood cellsWhite blood cells PlateletsPlatelets
44

FUN FACTSFUN FACTS In one day, your blood travels nearly In one day, your blood travels nearly
12,000 miles. 12,000 miles. Your heart beats around 35 million Your heart beats around 35 million
times per year. Your heart pumps a times per year. Your heart pumps a million barrels of blood during the million barrels of blood during the average lifetime -- enough to fill average lifetime -- enough to fill three supertankers. If an artery is three supertankers. If an artery is cut, blood will shoot out 30 feet.cut, blood will shoot out 30 feet.
55

PlasmaPlasma Plasma is what the blood cells float around Plasma is what the blood cells float around
in. If you spin a blood sample in a test in. If you spin a blood sample in a test tube, the red blood cells sink to the tube, the red blood cells sink to the bottom, and you’ll see the yellow plasma bottom, and you’ll see the yellow plasma on top. on top.
Some people who need blood just need Some people who need blood just need the packed RBCs (anemia), some need the the packed RBCs (anemia), some need the platelets (hemophilia), others need the platelets (hemophilia), others need the plasma (burn victims), and some need plasma (burn victims), and some need whole blood (hemorrhage), which is both whole blood (hemorrhage), which is both plasma and RBCs. plasma and RBCs.
66

Overview: Composition of Overview: Composition of BloodBlood
Figure 17.177

88

PLASMA CONTENTSPLASMA CONTENTS Water (90%)Water (90%) Dissolved substances (10%)Dissolved substances (10%)
– ProteinsProteins Albumin (egg white). Most common protein in Albumin (egg white). Most common protein in
blood (needed for homeostasis of blood volume)blood (needed for homeostasis of blood volume) AntibodiesAntibodies Clotting factors; main one is called fibrin.Clotting factors; main one is called fibrin. Lipoproteins (move fats through blood: HDL, LDL)Lipoproteins (move fats through blood: HDL, LDL)
– NutrientsNutrients Glucose (main energy source)Glucose (main energy source) Amino Acids (builds proteins)Amino Acids (builds proteins)
– Wastes (urea)Wastes (urea)– Gases (O2, CO2, Nitrogen)Gases (O2, CO2, Nitrogen)– Electrolytes = ions (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++)Electrolytes = ions (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++)
99

Blood CellsBlood Cells
1010

ERYTHROCYTES ERYTHROCYTES (Red blood cells)(Red blood cells)
5 million 5 million Like a doughnut with the hole not fully Like a doughnut with the hole not fully
cut out. cut out. – These are among the smallest cells in the These are among the smallest cells in the
body body – They have no nucleusThey have no nucleus– Biconcave to increase surface areaBiconcave to increase surface area– Filled with hemoglobin (Hgb), which carries Filled with hemoglobin (Hgb), which carries
O2 throughout the body. Oxygenated Hgb O2 throughout the body. Oxygenated Hgb is bright red, deoxy Hgb is deeper red, is bright red, deoxy Hgb is deeper red, almost a bluish-purple. almost a bluish-purple.
1111

ErythrocytesErythrocytes
1212

Hemoglobin MoleculeHemoglobin Molecule
1313

Hemoglobin MoleculeHemoglobin Molecule
1414
Hemoglobin consists of 2 alpha units and 2 beta units. Hemoglobin abnormalities are classified by which unit is deformed.
The heme group is where the oxygen molecule binds. An iron (Fe++) molecule is in the middle, which attracts the oxygen to the heme group.

ERYTHROCYTES:ERYTHROCYTES:– Average life span is 120 days. Old ones Average life span is 120 days. Old ones
are destroyed in the spleen and liver, are destroyed in the spleen and liver, and Hgb and iron are recycled. and Hgb and iron are recycled.
– In one day, 100 billion of these cells In one day, 100 billion of these cells are destroyed, and 100 billion are are destroyed, and 100 billion are made: where? made: where?
– Red bone marrow.Red bone marrow.
1515

Disorders of RBCsDisorders of RBCs Polycythemia Polycythemia AnemiaAnemia
– Too few RBC’sToo few RBC’s– Iron deficiencyIron deficiency– Hemorrhagic anemia (person lost blood)Hemorrhagic anemia (person lost blood)– Hemolytic anemia (immune disorder, infection, blood Hemolytic anemia (immune disorder, infection, blood
transfusion)transfusion) G6PD deficiencyG6PD deficiency
– Hemoglobin abnormalitiesHemoglobin abnormalities Pernicious (Megaloblastic) anemia (lack of vitamin B12 or Pernicious (Megaloblastic) anemia (lack of vitamin B12 or
intrinsic factor)intrinsic factor) ThalassemiaThalassemia Sickle cell disease Sickle cell disease
1616

PolycythemiaPolycythemiaToo many RBC’s; can cause clots. Need to Too many RBC’s; can cause clots. Need to
donate blood frequentlydonate blood frequently
1717

ANEMIA Any condition of RED BLOOD CELLS
in which the blood’s capacity for carrying oxygen is diminished.
HYPOXIA is lack of oxygen to tissues.– It can be caused from:
Ischemia (reduced blood flow to a tissue)Ischemia (reduced blood flow to a tissue) Malfunctioning hemoglobinMalfunctioning hemoglobin Increasing altitudeIncreasing altitude
1818

AnemiaAnemia Characteristic sign of anemia: see Characteristic sign of anemia: see
reticulocytes in the blood reticulocytes in the blood (immature red blood cells). (immature red blood cells).
Remnants of the nucleus are still in Remnants of the nucleus are still in the cell.the cell.
1919

ReticulocytesReticulocytes
2020

Anemia can be caused by many things. Anemia can be caused by many things. One type of anemia is from too few One type of anemia is from too few
RBC’s.RBC’s.
2121

Anemia can also be caused Anemia can also be caused from Iron Deficiencyfrom Iron Deficiency
2222

IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA that was treated with blood
transfusion
These are the healthy RBCs from blood transfusion
2323

Hemolytic AnemiaHemolytic Anemia Hemolysis means rupture of RBC’s. Hemolysis means rupture of RBC’s.
– Hereditary (born with the genes that Hereditary (born with the genes that cause the disease) cause the disease) Immune disorders and G6PD deficiency.Immune disorders and G6PD deficiency.
– AcquiredAcquired Infections (malaria), and receiving the wrong Infections (malaria), and receiving the wrong
blood type in a transfusion.blood type in a transfusion.
2424

G6PD DeficiencyG6PD Deficiency Hereditary, X-linked; almost all are malesHereditary, X-linked; almost all are males G6PDH is an enzyme which is important for RBC G6PDH is an enzyme which is important for RBC
metabolism. metabolism. G6PD is the most common human enzyme defect. G6PD is the most common human enzyme defect.
2525
A person with this develops hereditary (NOT acquired) hemolytic anemia in response to a number of causes, most commonly infection or exposure to certain medications, chemicals, or ingestion of fava beans.

HEMOGLOBINOPATHIESHEMOGLOBINOPATHIES Pernicious anemia (megaloblastic
anemia) Thalassemia Sickle Cell Disease
2626

Pernicious anemia (megaloblastic anemia)
Caused by lack of vitamin B12 or intrinsic factorCaused by lack of vitamin B12 or intrinsic factor When a person has gastric bypass surgery, the When a person has gastric bypass surgery, the
stomach is no longer able to produce intrinsic stomach is no longer able to produce intrinsic factor, which is needed to absorb vitamin B12, factor, which is needed to absorb vitamin B12, which is needed to make hemoglobin in RBC’s. which is needed to make hemoglobin in RBC’s.
Without this vitamin, the blood cells are fewer Without this vitamin, the blood cells are fewer and much larger than normal (megaloblastic). and much larger than normal (megaloblastic).
The surgery patient must take vitamin B12 shots The surgery patient must take vitamin B12 shots or sublingual supplements for the rest of their life. or sublingual supplements for the rest of their life.
2727

Megaloblastic AnemiaMegaloblastic Anemia(Large RBCs: Note that the lymphocyte is the same size as the huge RBCs)
2828

TEAR DROP
SPHEROCYTE
TARGET CELLS
Thalassemia Thalassemia A hereditary form of anemia A hereditary form of anemia where the RBCs have abnormal hemoglobin that where the RBCs have abnormal hemoglobin that
deforms the cellsdeforms the cells
2929

Sickle Cell DiseaseSickle Cell Disease Present in Present in African AmericansAfrican Americans more more
than in other groups, and is always than in other groups, and is always characterized by sickled characterized by sickled erythrocytes.erythrocytes.
The sickle shape helps prevent The sickle shape helps prevent malaria infections, but it also causes malaria infections, but it also causes blood clots.blood clots.
3030

Sickle Cell AnemiaSickle Cell Anemia
SICKLE CELL
3131

RBC, Hgb, HctRBC, Hgb, Hct Red blood cell (RBC) Red blood cell (RBC) count is a count of the count is a count of the
actual number of red blood cells per volume of actual number of red blood cells per volume of blood. Both increases and decreases can point to blood. Both increases and decreases can point to abnormal conditions. abnormal conditions.
HemoglobinHemoglobin (Hgb) measures the amount of (Hgb) measures the amount of oxygen-carrying protein in the blood. oxygen-carrying protein in the blood.
Hematocrit Hematocrit (Hct) measures the percentage of (Hct) measures the percentage of red blood cells in a given volume of whole blood. red blood cells in a given volume of whole blood.
3232

HematocritHematocrit A quick screening test for anemia is the A quick screening test for anemia is the
hematocrit.hematocrit. A drop of blood is drawn up a small glass capillary A drop of blood is drawn up a small glass capillary
tube and the tube is centrifuged to pack the red tube and the tube is centrifuged to pack the red blood cells at the bottom with the plasma on top. blood cells at the bottom with the plasma on top.
Hematocrit measures the percentage of blood Hematocrit measures the percentage of blood volume that consists of erythrocytes.volume that consists of erythrocytes.
The hematocrit is the ratio of packed red blood The hematocrit is the ratio of packed red blood cells to total blood volume.cells to total blood volume.
Normal is about 45% (46% for men and 38% for Normal is about 45% (46% for men and 38% for women.)women.)
3333

HematocritHematocrit
3434

Blood DopingBlood Doping Blood doping is the practice of Blood doping is the practice of
boosting the number of red blood boosting the number of red blood cells in the bloodstream in order to cells in the bloodstream in order to enhance athletic performance. enhance athletic performance.
Because such blood cells carry Because such blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the muscles, oxygen from the lungs to the muscles, a higher concentration in the blood a higher concentration in the blood can improve an athlete’s aerobic can improve an athlete’s aerobic capacity and endurance.capacity and endurance.
3535

IOC strips Lance Armstrong of
Olympic medal The winner of seven straight Tour de France titles confessed to Oprah Winfrey to using blood doping during that time.
Two months after the France tournament, he won the bronze medal at the 2000 Sydney Games.
Olympic officials won a suit to have the medal returned.
3636

Lance Armstrong (right)
3737

BLOOD TYPING: BLOOD TYPING: The ABO The ABO SYSTEMSYSTEM
Blood typing is the technique for Blood typing is the technique for determining which specific protein type determining which specific protein type is present on the RBC membranes. is present on the RBC membranes.
Only certain types of blood transfusions Only certain types of blood transfusions are safe because the cell membranes of are safe because the cell membranes of the red blood cells carry certain types the red blood cells carry certain types of proteins that another person’s body of proteins that another person’s body will think is a foreign body and reject it. will think is a foreign body and reject it.
3838

BLOOD TYPINGBLOOD TYPING These proteins are called antigens (something These proteins are called antigens (something
that causes an allergic reaction). There are two that causes an allergic reaction). There are two types of blood antigens: Type A and Type B.types of blood antigens: Type A and Type B.
A person with Type A antigens on their blood A person with Type A antigens on their blood cells have Type A blood.cells have Type A blood.
A person with Type B antigens have Type B A person with Type B antigens have Type B blood.blood.
A person with both types has type AB blood.A person with both types has type AB blood. A person with neither antigen has type O A person with neither antigen has type O
blood.blood.
3939

4040

BLOOD TYPINGBLOOD TYPING If a person with type A blood gets a transfusion of type If a person with type A blood gets a transfusion of type
B antigens (from Type B or Type AB, the donated B antigens (from Type B or Type AB, the donated blood will clump in masses (coagulation), and the blood will clump in masses (coagulation), and the person will die.person will die.
The same is true for a type B person getting type A or The same is true for a type B person getting type A or AB blood.AB blood.
Type O- blood is called the universal donor, because Type O- blood is called the universal donor, because there are no antigens, so that blood can be donated to there are no antigens, so that blood can be donated to anyone. anyone.
Type AB+ blood is considered the universal acceptor, Type AB+ blood is considered the universal acceptor, because they can use any other type of blood. This because they can use any other type of blood. This blood type is fairly rare.blood type is fairly rare.
The rarest blood type is AB negative.The rarest blood type is AB negative.
4141

RH FACTORRH FACTOR There is another term that follows the There is another term that follows the
blood type. The term is “positive” or blood type. The term is “positive” or “negative”. This refers to the “negative”. This refers to the presence of another type of protein, presence of another type of protein, called the Rh factor. A person with called the Rh factor. A person with type B blood and has the Rh factor is type B blood and has the Rh factor is called B positive.called B positive.
A person with type B blood and no Rh A person with type B blood and no Rh factor is called B negative.factor is called B negative.
4242

RH FACTORRH FACTOR The reason this is so important is that if The reason this is so important is that if
an Rh- mother has an Rh+ fetus in her an Rh- mother has an Rh+ fetus in her womb (from an Rh+ father), her womb (from an Rh+ father), her antibodies will attack the red blood antibodies will attack the red blood cells of the fetus because her body cells of the fetus because her body detects the Rh protein on the baby’s detects the Rh protein on the baby’s red blood cells and thinks they are red blood cells and thinks they are foreign objects. This is called Hemolytic foreign objects. This is called Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN).Disease of the Newborn (HDN).
4343

4444

HDNHDN This can be prevented if the doctor knows This can be prevented if the doctor knows
the mother is Rh- and the father is Rh+, the mother is Rh- and the father is Rh+, because that means the baby has a 50% because that means the baby has a 50% chance of being Rh+ like the father. chance of being Rh+ like the father.
Therefore, anytime a mother is Rh-, even Therefore, anytime a mother is Rh-, even if the mother says the father is Rh-, you if the mother says the father is Rh-, you can’t be sure who the father is, so they can’t be sure who the father is, so they will proceed as though the baby may be will proceed as though the baby may be Rh +. Rh +.
They will give her an injection of a They will give her an injection of a medicine (Rhogam) that will prevent her medicine (Rhogam) that will prevent her immune system from attacking the baby.immune system from attacking the baby.
4545

RhogamRhogam Rhogam is given at 18 weeks into the pregnancy and Rhogam is given at 18 weeks into the pregnancy and
again within 72 hours after giving birth.again within 72 hours after giving birth. It is usually given within 2 hours after giving birth It is usually given within 2 hours after giving birth
since you can’t trust the patient to return after they since you can’t trust the patient to return after they leave the hospital.leave the hospital.
The first baby is not at risk; during the first birth (or The first baby is not at risk; during the first birth (or miscarriage), the placenta tears away and that’s miscarriage), the placenta tears away and that’s when the baby’s blood cells get into the mother’s when the baby’s blood cells get into the mother’s bloodstream.bloodstream.
She then forms antibodies against the Rh factor, She then forms antibodies against the Rh factor, which are ready to attack the second fetus.which are ready to attack the second fetus.
The baby does not make the Rh factor until about 18 The baby does not make the Rh factor until about 18 weeks into the pregnancy.weeks into the pregnancy.
4646

ReynoldsUnwrapped.com offers FANTASTIC, inexpensive daily email subscriptions, where you can receive a HILARIOUS new cartoon every day, and it is a MARVELOUS idea for a UNIQUE gift for your family and friends as well. That is how I learned about this...one of my fellow teachers gave me a subscription as a birthday present.
He also has FUNNY greeting cards and BEAUTIFUL paintings for sale as well.You can also get reprints suitable for framing, or originals. Here is more info about his work and a YOUTUBE video.https://nccnews.expressions.syr.edu/?p=11515
4747

LEUKOCYTES LEUKOCYTES (White blood (White blood cells)cells)
all fight infectionall fight infection BASOPHILSBASOPHILS
– MAST CELLMAST CELL EOSINOPHILSEOSINOPHILS NEUTROPHILSNEUTROPHILS MONOCYTESMONOCYTES
– MACROPHAGESMACROPHAGES LYMPHOCYTESLYMPHOCYTES
– B CELLSB CELLS– T CELLST CELLS
4848
too many is ___philiatoo few is ___penia

Basophils – only about Basophils – only about 0.5% of all leukocytes0.5% of all leukocytes– Granules secrete Granules secrete
histamineshistamines (vasodilation; (vasodilation; more WBCs can get to the more WBCs can get to the infection site)infection site)
– Antihistamines interfere Antihistamines interfere with the function of with the function of basophils.basophils.
– Mast Cell: a basophil that Mast Cell: a basophil that leaves the blood vessel leaves the blood vessel and enters the tissues. and enters the tissues.
BASOPHILSBASOPHILS
4949

EosinophilsEosinophils Eosinophils – Eosinophils –
compose 1-4% of all compose 1-4% of all WBCsWBCs– Play roles in: Play roles in:
Ending Ending allergic allergic reactionsreactions, , parasitic parasitic infectionsinfections
During these During these conditions they conditions they increase in numbers: increase in numbers: eosinophiliaeosinophilia
5050

Neutrophils – most Neutrophils – most numerous WBCnumerous WBC
First to respond to First to respond to infectioninfection– Phagocytize and destroy Phagocytize and destroy
bacteriabacteria– Also destroy bacterial Also destroy bacterial
toxins in body fluidstoxins in body fluids– Nucleus – has two to six Nucleus – has two to six
lobeslobes
NeutrophilsNeutrophils
5151

White Blood Cell White Blood Cell PhagocytosisPhagocytosis
VIDEO http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JnlULOjUhSQ
5252

NeutrophilsNeutrophils Neutrophils are the white blood cells that Neutrophils are the white blood cells that
contribute to immunity mainly by contribute to immunity mainly by engulfing BACTERIA and foreign bodies engulfing BACTERIA and foreign bodies (thorns, dirt, etc) in a process called (thorns, dirt, etc) in a process called phagocytosis. phagocytosis.
They release the contents of their They release the contents of their lysosomes onto the invader, dissolving it.lysosomes onto the invader, dissolving it.
When a bacterium has a capsule, it When a bacterium has a capsule, it makes it hard to phagocytize, so the makes it hard to phagocytize, so the neutrophil requires opsonization by neutrophil requires opsonization by antibodies.antibodies.
5353

OpsonizationOpsonization Some bacteria have evolved a slippery Some bacteria have evolved a slippery
capsule around them as a defense capsule around them as a defense against phagocytosis. The neutrophil against phagocytosis. The neutrophil cannot engulf this type of bacteria. cannot engulf this type of bacteria. Neither can a macrophage.Neither can a macrophage.
When an antibody attaches to this type When an antibody attaches to this type of bacteria, the neutrophil can now of bacteria, the neutrophil can now grab onto the antibody like a handle, grab onto the antibody like a handle, enabling it to phagocytize the bacteria.enabling it to phagocytize the bacteria.
This process of facilitation of This process of facilitation of phagocytosis is called opsonization.phagocytosis is called opsonization.
5454

When an invading bacteria has the antibody When an invading bacteria has the antibody attached to its cell membrane, the entire attached to its cell membrane, the entire structure is now called an antigen-antibody structure is now called an antigen-antibody complex.complex.
If a bacterium does not have a capsule, the If a bacterium does not have a capsule, the neutrophil can destroy it without opsonization. neutrophil can destroy it without opsonization. The antibody can also destroy the bacterium by The antibody can also destroy the bacterium by itself by popping the cell membrane.itself by popping the cell membrane.
But when a capsule is present, the neutrophil But when a capsule is present, the neutrophil and antibody work best together.and antibody work best together.
Neutrophils are also the ones that Neutrophils are also the ones that primarily destroy the dissolved toxins that primarily destroy the dissolved toxins that bacteria secrete into body fluids.bacteria secrete into body fluids.
5555

MonocytesMonocytes Comprise about 5% of all WBC’s.Comprise about 5% of all WBC’s. Like neutrophils, they Like neutrophils, they
phagocytize (eat) bacteria, old phagocytize (eat) bacteria, old cells, and foreign bodies.cells, and foreign bodies. They They have more types of lysosome have more types of lysosome enzymes than neutrophils so enzymes than neutrophils so they are better at killing difficult they are better at killing difficult pathogens.pathogens.
They also use antibodies for They also use antibodies for opsonization.opsonization.
When they leave the When they leave the bloodstream and enter the bloodstream and enter the tissues, they are calledtissues, they are called MACROPHAGES.MACROPHAGES.
5656

WBC’s leave the blood vessel WBC’s leave the blood vessel to enter the tissuesto enter the tissues
5757

20–45% of WBCs20–45% of WBCs– The most important cells of The most important cells of
the immune systemthe immune system– There are two types of There are two types of
lymphocytes; one type is lymphocytes; one type is effective in fighting infectious effective in fighting infectious organisms like body cells organisms like body cells infected with infected with virusesviruses
– Both types of lymphocytes act Both types of lymphocytes act against a against a specific foreign specific foreign molecule (antigen)molecule (antigen)
LymphocytesLymphocytes
5858

Two main classes of lymphocyte Two main classes of lymphocyte – B cells – Originate in the bone marrow, B cells – Originate in the bone marrow,
mature into plasma cells. mature into plasma cells. A mature A mature plasma cell fights infection by plasma cell fights infection by producing antibodiesproducing antibodies
– T cells – Originate in the thymus gland. T cells – Originate in the thymus gland. They attack foreign cells directly They attack foreign cells directly ((including organ transplants!). including organ transplants!). They can also kill viruses.They can also kill viruses.
LymphocytesLymphocytes
5959

B cells – mature into plasma cellsB cells – mature into plasma cells Plasma cells secrete antibodies; the plasma Plasma cells secrete antibodies; the plasma
cell’s antibodies are what kills the attacking cell’s antibodies are what kills the attacking cell.cell.
Antibodies attack in three ways:Antibodies attack in three ways:– They attach to bacteria and pop the cell They attach to bacteria and pop the cell
membranemembrane– They attach to encapsulated bacteria to help They attach to encapsulated bacteria to help
neutrophils and macrophages to phagocytize neutrophils and macrophages to phagocytize them.them.
– They agglutinate (clump all over the bacteria, They agglutinate (clump all over the bacteria, binding their receptor sites so they cannot cause binding their receptor sites so they cannot cause harm)harm)
LymphocytesLymphocytes
6060

MononucleosisMononucleosis: Epstein Barr virus : Epstein Barr virus attacks B lymphocytes. It is attacks B lymphocytes. It is characterized by inflammation of characterized by inflammation of lymph vessels (lymphangitis).lymph vessels (lymphangitis).
– LymphangitisLymphangitis: lymph vessel : lymph vessel inflammation; usually from infection.inflammation; usually from infection.
Infected lymphocytes have a Infected lymphocytes have a characteristic scalloped characteristic scalloped edge where they touchedge where they touchRBC’sRBC’s
Disorder of B-cell Disorder of B-cell LymphocytesLymphocytes
6161

Function of a B LymphocyteFunction of a B Lymphocyte
Figure 17.6b6262

T cells – coordinate the immune response by T cells – coordinate the immune response by recruiting other white blood cells. recruiting other white blood cells.
They can directly destroy bacteria by popping They can directly destroy bacteria by popping their cell membrane.their cell membrane.
T cells can also directly destroy foreign cells by T cells can also directly destroy foreign cells by popping the cell membrane. popping the cell membrane.
They do not need to phagocytize the invading They do not need to phagocytize the invading cell. They do not need the assistance of cell. They do not need the assistance of antibodies.antibodies.
T-cells can therefore kill a body cell that has T-cells can therefore kill a body cell that has become infected with viruses.become infected with viruses.
T-cell LymphocytesT-cell Lymphocytes
6363

T-CellT-Cell
6464

T cells are the cells that attack T cells are the cells that attack organ transplants!organ transplants!
Immunosuppression drugs are designed to Immunosuppression drugs are designed to inhibit the action of T cells. inhibit the action of T cells.
T cells are attacked by the HIV (AIDS) T cells are attacked by the HIV (AIDS) virus.virus.
The thymus gland secrets certain The thymus gland secrets certain hormones which can cause T cells to hormones which can cause T cells to become immunocompetent (makes become immunocompetent (makes the cells mature and start to work)the cells mature and start to work)
T-cell LymphocytesT-cell Lymphocytes
6565

T CellsT CellsThere are several types of T cells. The main types areThere are several types of T cells. The main types are Cytotoxic (Killer) T cellsCytotoxic (Killer) T cells
– Go out and directly kill bacteria or infected Go out and directly kill bacteria or infected host cells host cells
Helper T cellsHelper T cells– Release chemicals called “cytokines” to call in Release chemicals called “cytokines” to call in
more white blood cells of all types to join in the more white blood cells of all types to join in the war. They also present the macrophage’s war. They also present the macrophage’s antigen to a B cell, which causes it to produce antigen to a B cell, which causes it to produce antibodies against that particular bacteria. The antibodies against that particular bacteria. The B cell is now called a plasma cell B cell is now called a plasma cell
Suppressor T cellsSuppressor T cells– Stop the immune process when it is over.Stop the immune process when it is over.
6666

Killer T-Killer T-CellCell
6767

Virus-Infected CellVirus-Infected Cell
6868

Function of a T- LymphocyteFunction of a T- Lymphocyte
Figure 17.6a6969

Neutrophil
Macrophage(Monocyte in
bloodstream)
B-Cell Killer T-Cell
Helper T-Cell
Suppressor T-Cell
Plasma Cell
Lymphocytes
Phagocytosis
Bacteria
Virus
Presentation
Y YY
Antibodies
Y
Y
Pops the cell
Capsule
Cytokines
Pops the cell
STOP
Opsonization
Bacteria
Presentation
70

LEUKEMIALEUKEMIA Cancer of the blood is called leukemia. It actually Cancer of the blood is called leukemia. It actually
only involves the white blood cells. only involves the white blood cells. Something goes wrong in one stem cell, and it Something goes wrong in one stem cell, and it
starts making huge amounts of clones of itself starts making huge amounts of clones of itself which don’t work right and not enough normal which don’t work right and not enough normal white blood cells are made. Therefore, the body white blood cells are made. Therefore, the body cannot fight infection. So, the immature white cannot fight infection. So, the immature white cells are sent into the bloodstream. It’s better to cells are sent into the bloodstream. It’s better to send a young cell with no weapons to the war send a young cell with no weapons to the war than to send nothing at all!than to send nothing at all!
Think of Leukemia as too few mature white Think of Leukemia as too few mature white blood cells. blood cells.
Even though the WBC count is high, they are all Even though the WBC count is high, they are all immature forms.immature forms.
7171

Disorders of WBCsDisorders of WBCs Disorders of leukocytesDisorders of leukocytes
– Leukemia – too few mature WBC’s (may Leukemia – too few mature WBC’s (may see increase in immature forms); a form see increase in immature forms); a form of cancerof cancer
– Classified as Classified as lymphoblastic lymphoblastic (too many (too many immature lymphocytes) or immature lymphocytes) or myeloblasticmyeloblastic (too many immature (too many immature neutrophils)neutrophils)
7272

Bone Marrow Transplant People with severe leukemia may need a
bone marrow transplant. First, all of their WBC’s have to be killed off
with a medicine because they are mostly malfunctioning anyway.
A donor has a small cylinder of bone removed from their hip. This is ground up and given by i.v. to the recipient.
The new WBC’s may kill the patient or it may save their life. It is done as a last resort.
7373

WBC Count WBC Count White blood cell (WBC) White blood cell (WBC) count is a count of the count is a count of the
actual number of white blood cells per volume of actual number of white blood cells per volume of blood. Both increases and decreases can be blood. Both increases and decreases can be significant. significant.
White blood cell differential White blood cell differential looks at the types of looks at the types of white blood cells present. There are five different types white blood cells present. There are five different types of white blood cells, each with its own function in of white blood cells, each with its own function in protecting us from infection. The differential classifies protecting us from infection. The differential classifies a person's white blood cells into each type: neutrophils a person's white blood cells into each type: neutrophils (also known as segs, PMNs, granulocytes, grans), (also known as segs, PMNs, granulocytes, grans), lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
7474

AntibodiesAntibodies AntibodiesAntibodies (also known as (also known as
immunoglobulinsimmunoglobulins, abbreviated , abbreviated IgIg) are ) are proteins made by plasma cells.proteins made by plasma cells.
They are used to identify and neutralize They are used to identify and neutralize foreign objects, such as bacteria and foreign objects, such as bacteria and viruses. viruses.
They are typically made of basic structural They are typically made of basic structural units—each with two large heavy chains units—each with two large heavy chains and two small light chains—to form a unit and two small light chains—to form a unit shaped like the letter “Y”shaped like the letter “Y”
7575

A Typical A Typical AntibodyAntibody
The tips of the “Y” have receptors that are specific for a particular antigen.
The stem of the “Y” can be grasped by a phagocyte.
7676

7777
Precipitation/agglutination#1 #3#2

IMMUNITYIMMUNITY Most people are sick more often as Most people are sick more often as
children than as adults in their 20s children than as adults in their 20s through 30s because we build up through 30s because we build up many varieties of memory many varieties of memory lymphocytes during childhood, lymphocytes during childhood, providing immunity from more and providing immunity from more and more antigens during adulthood.more antigens during adulthood.
7878

PLATELETSPLATELETS(thrombocytes)(thrombocytes)
Very small compared to all other blood cells. Very small compared to all other blood cells. These are pieces of another cell found in the These are pieces of another cell found in the red marrow called a red marrow called a MEGAKARYOCYTE.MEGAKARYOCYTE.
Pieces break off of a megakaryocte and are Pieces break off of a megakaryocte and are known as platelets. known as platelets.
When a platelet encounters a broken blood When a platelet encounters a broken blood vessel it uses clotting factors (made in the vessel it uses clotting factors (made in the liver and circulating in the blood) to form a liver and circulating in the blood) to form a web to clots blood.web to clots blood.
Platelets are responsible for Platelets are responsible for clot formationclot formation. .
7979

PlateletsPlatelets Cell fragmentsCell fragments
– Break off from Break off from megakaryocytesmegakaryocytes
Function in clotting Function in clotting of bloodof blood
Megakaryocyte
Platelets
8080

Platelets Platelets need certain proteins in the
plasma called CLOTTING FACTORS in order for them to become activated and form a clot.
The main clotting factor is called FIBRIN, but there are many other types as well.
8181

Blood Blood ClotClot8282

Vitamin KVitamin K Found in green, leafy vegetables.Found in green, leafy vegetables. Needed for blood clotting factors.Needed for blood clotting factors. Some types of rat poisons work by Some types of rat poisons work by
eliminating the blood clotting ability.eliminating the blood clotting ability. In case of accidental ingestion of rat In case of accidental ingestion of rat
poison, a child needs an I.V. of vitamin K.poison, a child needs an I.V. of vitamin K. It works for accidental poisoning in dogs, It works for accidental poisoning in dogs,
too!too!
8383

AspirinAspirin One baby aspirin a day can help prevent One baby aspirin a day can help prevent
blood clots.blood clots. It blocks the ability of an enzyme called It blocks the ability of an enzyme called
COX (cyclo-oxidase) to make a substance COX (cyclo-oxidase) to make a substance called prostaglandin.called prostaglandin.
Prostaglandins are needed for Prostaglandins are needed for inflammatory reactions. However, they also inflammatory reactions. However, they also INCREASE blood clotting time.INCREASE blood clotting time.
8484

Disorders of PlateletsDisorders of Platelets
Excess platelets: Excess platelets: thrombocytophiliathrombocytophilia
Few platelets: Few platelets: thrombocytopeniathrombocytopenia
Abnormally low Abnormally low concentration of concentration of plateletsplatelets
Blood does not clot Blood does not clot properly properly
8585

HEMOPHILIAHEMOPHILIA A hereditary disease of males, where they A hereditary disease of males, where they
are unable to clot properly because they are unable to clot properly because they are missing some clotting factors.are missing some clotting factors.
When they get even a slight bump or When they get even a slight bump or bruise they have to have an intravenous bruise they have to have an intravenous infusion of clotting factors or they will infusion of clotting factors or they will bleed to death. bleed to death.
This is probably the disease that was in This is probably the disease that was in the genes of Henry VIII, which caused all of the genes of Henry VIII, which caused all of his male children to become weak and die his male children to become weak and die in infancy.in infancy.
8686

Blood ClotsBlood Clots ThrombusThrombus
– A clot in a vessel A clot in a vessel EmbolismEmbolism
– a thrombus that broke away a thrombus that broke away and travels in the blood and travels in the blood stream. stream.
– It usually lodges in a smaller It usually lodges in a smaller blood vessel and blocks blood vessel and blocks circulation distal to that point.circulation distal to that point.
8787

Blood ClotsBlood Clots ThrombusThrombus EmbolismEmbolism
8888

ThrombusThrombus
8989

ThrombusThrombus
9090

Prothrombin Time (PT) and Prothrombin Time (PT) and Partial Thromboplastin Time Partial Thromboplastin Time
(PTT)(PTT) The PTT test is used to investigate unexplained bleeding or clotting. The PTT test is used to investigate unexplained bleeding or clotting.
It may be ordered along with a PT (Prothrombin Time) test to It may be ordered along with a PT (Prothrombin Time) test to evaluate evaluate hemostasis hemostasis (the process of clot formation). The PTT (the process of clot formation). The PTT evaluates the coagulation factors XII, XI, IX, VIII, X, V, II evaluates the coagulation factors XII, XI, IX, VIII, X, V, II (prothrombin), and I (fibrinogen). A PT test evaluates the coagulation (prothrombin), and I (fibrinogen). A PT test evaluates the coagulation factors VII, X, V, II, and I (fibrinogen). By evaluating the results of the factors VII, X, V, II, and I (fibrinogen). By evaluating the results of the two tests together, a doctor can gain clues as to what bleeding or two tests together, a doctor can gain clues as to what bleeding or clotting disorder may be present.clotting disorder may be present.
These tests are used to monitor heparin anticoagulant therapy. These tests are used to monitor heparin anticoagulant therapy. Heparin is a drug that is given intravenously (IV) or by injection to Heparin is a drug that is given intravenously (IV) or by injection to prevent and to treat blood clots. IV’s are also flushed with heparin to prevent and to treat blood clots. IV’s are also flushed with heparin to prevent clot formation. When it is administered for therapeutic prevent clot formation. When it is administered for therapeutic purposes, it must be closely monitored. If too much is given, the purposes, it must be closely monitored. If too much is given, the treated person may bleed excessively; with too little, the treated treated person may bleed excessively; with too little, the treated person may continue to clot.person may continue to clot.
9191

Complete Blood Count Complete Blood Count (CBC)(CBC)
The complete blood count or CBC test is used as a broad screening test to check for such disorders as anemia, infection, and many other diseases. It is actually a panel of tests that examines different parts of the blood and includes the following:
White blood cell (WBC) count White blood cell differential Red blood cell (RBC) count Hemoglobin Hematocrit platelet count , PT, PTT Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) Red cell distribution width (RDW)
9292

Summary of Formed Summary of Formed ElementsElements
Table 17.1 (1)9393

Summary of Formed Summary of Formed ElementsElements
Table 17.1 (2)9494

Life span, from longest-Life span, from longest-lived to shortest-lived:lived to shortest-lived:
LymphocytesLymphocytes ErythrocytesErythrocytes PlateletsPlatelets NeutrophilsNeutrophils
9595

SepticemiaSepticemia Septicemia (aka bacteremia) is the condition when bacteria invade Septicemia (aka bacteremia) is the condition when bacteria invade
the body and circulate in the blood.the body and circulate in the blood. Bacteria can enter the bloodstream as a severe complication of Bacteria can enter the bloodstream as a severe complication of
infections (like pneumonia or meningitis), during surgery (especially infections (like pneumonia or meningitis), during surgery (especially when involving mucous membranes such as the gastrointestinal when involving mucous membranes such as the gastrointestinal tract), or due to catheters and other foreign bodies entering the tract), or due to catheters and other foreign bodies entering the arteries or veins (including intravenous drug abuse).arteries or veins (including intravenous drug abuse).
Bacteremia can have several consequences. The immune response Bacteremia can have several consequences. The immune response to the bacteria can cause sepsis and septic shock, which has a to the bacteria can cause sepsis and septic shock, which has a relatively high mortality rate (kills 1 person in 5). Bacteria can also relatively high mortality rate (kills 1 person in 5). Bacteria can also use the blood to spread to other parts of the body (which is called use the blood to spread to other parts of the body (which is called hematogenous spread), causing infections away from the original hematogenous spread), causing infections away from the original site of infection. Examples include endocarditis or osteomyelitis. site of infection. Examples include endocarditis or osteomyelitis.
Treatment is with antibiotics, and prevention with antibiotic Treatment is with antibiotics, and prevention with antibiotic prophylaxis can be given in situations where problems are to be prophylaxis can be given in situations where problems are to be expected.expected.
9696

9797

Blood Cell FormationBlood Cell Formation Hematopoiesis – process by which Hematopoiesis – process by which
blood cells are formedblood cells are formed 100 billion new blood cells formed 100 billion new blood cells formed
each dayeach day The plasma proteins are made in the The plasma proteins are made in the
liver.liver. The blood cells are made in the red The blood cells are made in the red
bone marrow.bone marrow.9898

RED BONE MARROWRED BONE MARROW Most blood cells mature in the red Most blood cells mature in the red
bone marrow. bone marrow. When they are almost completely When they are almost completely
mature, they are released into the mature, they are released into the bloodstream. bloodstream.
When they are old, they are When they are old, they are destroyed in the spleen and liver.destroyed in the spleen and liver.
9999

100100

Cell Lines in Blood Cell Cell Lines in Blood Cell FormationFormation
All blood cells originate in bone All blood cells originate in bone marrowmarrow
All originate from one cell type – All originate from one cell type – blood stem cellblood stem cell– Erythroblasts – give rise to red blood Erythroblasts – give rise to red blood
cellscells– Lymphoblasts – give rise to lymphocytesLymphoblasts – give rise to lymphocytes– Myeloblasts – give rise to all other white Myeloblasts – give rise to all other white
blood cellsblood cells101101

Stages of Stages of Differentiation Differentiation of Red Blood of Red Blood
CellsCells
102102

RBC DevelopmentRBC Development ERYTHROBLASTS ERYTHROBLASTS mature until they mature until they
are ready to enter the circulation. The are ready to enter the circulation. The nucleus gets pinched off as it enters nucleus gets pinched off as it enters the blood vessel. the blood vessel.
When a RBC loses its nucleus, it gains When a RBC loses its nucleus, it gains room for more hemoglobin. room for more hemoglobin.
Some bits of its nucleus are still there Some bits of its nucleus are still there for about 2 days, so during this time, for about 2 days, so during this time, they are called they are called RETICULOCYTES.RETICULOCYTES.
103103

ERYTHROBLASTSERYTHROBLASTS These mature into These mature into
RETICULOCYTESRETICULOCYTES, , a RBC with bits of a RBC with bits of nucleus material, nucleus material, which later which later dissolves to make dissolves to make room for more room for more Hgb. It is now Hgb. It is now called an called an EERYTHROCYTERYTHROCYTE. .
104104

LYMPHOBLASTSLYMPHOBLASTSGive rise to lymphocytesGive rise to lymphocytes
105105

MYELOBLASTSMYELOBLASTSThese are the stem cells that mature These are the stem cells that mature
into the other leukocytes:into the other leukocytes:Neutrophil, macrophage, eosinophil, Neutrophil, macrophage, eosinophil,
basophil, platelets. basophil, platelets.
106106

LeukemiaLeukemiaLeukemia is cancer of the stem cells. Leukemia is cancer of the stem cells. See all these different types of stem See all these different types of stem
cells?cells?That’s about how many types of That’s about how many types of
leukemia there are.leukemia there are.
107107

Stages of Stages of DifferentiatioDifferentiatio
n of White n of White Blood CellsBlood Cells
Figure 17.9108108

IMMUNE SYSTEMIMMUNE SYSTEM INFLAMMATORY REACTION: INFLAMMATORY REACTION: When you When you
get stuck by a thorn or have an infected get stuck by a thorn or have an infected cut, the body goes through a series of cut, the body goes through a series of events called an inflammatory reaction. events called an inflammatory reaction.
Four outward signs:Four outward signs:– Redness (erythema or rubor)Redness (erythema or rubor)– Heat (calor)Heat (calor)– Swelling (edema)Swelling (edema)– Pain (dolor)Pain (dolor)
109109

INFLAMMATORY INFLAMMATORY REACTIONREACTION
RednessRedness is caused from the blood vessels is caused from the blood vessels dilating to allow more blood flow to the area. dilating to allow more blood flow to the area.
HeatHeat is caused because of the extra amount of is caused because of the extra amount of warm blood flow to the area.warm blood flow to the area.
SwellingSwelling is caused from the plasma that leaks is caused from the plasma that leaks out of the swollen blood vessels.out of the swollen blood vessels.
PainPain is caused from the pressure of the extra is caused from the pressure of the extra fluid pressing on nerves in the area. fluid pressing on nerves in the area.
110110

ADAPTIVE IMMUNITYADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Two types of Adaptive Two types of Adaptive
ImmunityImmunity– ACTIVE immunityACTIVE immunity
Naturally AcquiredNaturally Acquired Artificially AcquiredArtificially Acquired
– PASSIVE PASSIVE immunityimmunity Naturally Naturally
AcquiredAcquired Artificially Artificially
AcquiredAcquiredYou can also think of it this way
111111

Active ImmunityActive Immunity ACTIVE means the person’s own body ACTIVE means the person’s own body
makes the antibodies.makes the antibodies. Naturally AcquiredNaturally Acquired
– The body is naturally exposed to an The body is naturally exposed to an infectious agent and launches an immune infectious agent and launches an immune reactionreaction
Artificially AcquiredArtificially Acquired– The person is injected with a weakened The person is injected with a weakened
(attenuated) or killed organism, as found in a (attenuated) or killed organism, as found in a vaccinationvaccination
112112

Naturally Acquired Naturally Acquired Active ImmunityActive Immunity
This is when the body is exposed to an This is when the body is exposed to an infectious agent and the body has to work infectious agent and the body has to work to produce antibodies which specifically to produce antibodies which specifically attack that infectious agent. attack that infectious agent.
The white blood cells secrete these The white blood cells secrete these antibodies which will continue to circulate antibodies which will continue to circulate sometimes for years, ready to attack that sometimes for years, ready to attack that type of bacteria and cause them to pop type of bacteria and cause them to pop like a balloon before the body can become like a balloon before the body can become sick. sick.
113113

Naturally AcquiredNaturally AcquiredActive ImmunityActive Immunity
– You catch a cold and eventually get better. You You catch a cold and eventually get better. You can never get the same cold virus twice can never get the same cold virus twice because you will have become immune to it. because you will have become immune to it. Your next cold is from a different virus. There Your next cold is from a different virus. There are hundreds of thousands of cold viruses; are hundreds of thousands of cold viruses; that’s why there is no cure for the common that’s why there is no cure for the common cold.cold.
– Another example is when an unvaccinated Another example is when an unvaccinated child is exposed to the measles at school and child is exposed to the measles at school and gets the disease, but never gets the disease gets the disease, but never gets the disease again. again.
114114

However, there are some diseases that you However, there are some diseases that you don’t want to get, even once, such as polio, don’t want to get, even once, such as polio, diphtheria, tetanus, and influenza, because the diphtheria, tetanus, and influenza, because the first exposure could kill or disable you. first exposure could kill or disable you.
For these diseases, we have vaccines which For these diseases, we have vaccines which are made of those organisms which have been are made of those organisms which have been altered (attenuated) so that the body altered (attenuated) so that the body recognizes them as foreign, but they can’t recognizes them as foreign, but they can’t cause disease. cause disease.
That way, if the person is exposed to the real That way, if the person is exposed to the real organism later, the antibodies are already organism later, the antibodies are already there to kill it off without the body getting sick. there to kill it off without the body getting sick.
115115

Artificially Acquired Artificially Acquired Active ImmunityActive Immunity
An example is when a child is vaccinated An example is when a child is vaccinated against measles as a baby, so when he against measles as a baby, so when he gets to school and is exposed to the gets to school and is exposed to the disease, he doesn’t get sick.disease, he doesn’t get sick.
116116

Passive ImmunityPassive Immunity PASSIVE means the person’s body does PASSIVE means the person’s body does
not have to make the antibodies.not have to make the antibodies. Naturally AcquiredNaturally Acquired
– Example is the passing of antibodies from Example is the passing of antibodies from mother to infant in breast milk mother to infant in breast milk
Artificially AcquiredArtificially Acquired– Example is when a person receives an Example is when a person receives an
infusion of antibodies from someone else. infusion of antibodies from someone else.
117117

Active vs. Passive ImmunityActive vs. Passive Immunity Active immunity is long-lived, and Active immunity is long-lived, and
may last for years or even a life time.may last for years or even a life time. Passive immunity is short lived, and Passive immunity is short lived, and
may last only for a few months.may last only for a few months.
NOTE: A vaccination is not the same as receiving an anti-toxin or anti-venom injection. More on that in Micro class. 118118

ALLERGIESALLERGIES From a hypersensitivity to From a hypersensitivity to
substances such as pollen or animal substances such as pollen or animal hair that would not ordinarily cause a hair that would not ordinarily cause a reaction. There are two types of reaction. There are two types of allergic responses:allergic responses:
Immediate Immediate DelayedDelayed
119119

Immediate allergic responseImmediate allergic responseOccurs within seconds of contact with the Occurs within seconds of contact with the
thing causing the allergy. thing causing the allergy. This is the case with anaphylactic allergies, This is the case with anaphylactic allergies,
where someone who is allergic to seafood where someone who is allergic to seafood or peanuts can actually die within or peanuts can actually die within minutes because the allergic reaction is minutes because the allergic reaction is so severe the throat swells shut and they so severe the throat swells shut and they can’t breathe. can’t breathe.
They need an injection immediately of They need an injection immediately of epinephrine that will stop the reaction.epinephrine that will stop the reaction.
120120

121121

Delayed allergic responseDelayed allergic responseDelayed allergic response is when the Delayed allergic response is when the
body’s first exposure to the body’s first exposure to the substance will not cause a reaction, substance will not cause a reaction, but all exposures afterward will but all exposures afterward will trigger the response. trigger the response.
An example is poison ivy. An example is poison ivy. You won’t itch the first time you touch You won’t itch the first time you touch
it.it.
122122

Common Common allergensallergens
123123

124124

AUTOIMMUNE DISEASEAUTOIMMUNE DISEASE A hereditary problem where the body A hereditary problem where the body
thinks its own tissues are foreign thinks its own tissues are foreign bodies, and it constantly tries to kill bodies, and it constantly tries to kill off its own tissues.off its own tissues.
125125
Cats worse than dogs for allergies, http://fxn.ws/O5jueJ

126126