Biology 12 – the nucleus. Cell structures Is this eukaryotic? yes Why? nucleus Is this a plant or...
-
Upload
jemimah-grant -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
2
Transcript of Biology 12 – the nucleus. Cell structures Is this eukaryotic? yes Why? nucleus Is this a plant or...
Cell structuresIs this eukaryotic? yes
Why? nucleus
Is this a plant or animal cell? animal
Why? No cell wall or chloroplasts
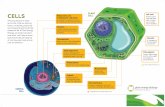
Label the structures
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
The nucleus
From http://www.bio.jhu.edu/~corces/Research2.html
Nucleus contains DNADNA consists of a double helix tightly coiled
DNA is arranged in chunks called chromosomes
Different species have different numbers of chromosomes
Chromosomes are only visible during cell division
Experiments with the nucleus 3
This shows nucleus controls development of special cell structures eg fruiting bodies
Base pairing
Adenine always pairs with ThymineThymine always pairs with AdenineCytosine always pairs with GuanineGuanine always pairs with Cytosine
Why is DNA important
• It can be inherited (passed on in cell divisions)
• It can easily be copied with a high degree of accuracy
• It controls which proteins are made
Definitions• Transcription• Translation• Codon• Anticodon• t-RNA• m-RNA• r-RNA• Protein• Amino acid
Copying of DNA to make RNA
Reading of mRNA to make proteins
3 unit segment of mRNA – codes for particular amino acid
3 unit segment of tRNA (carrying a particular amino acid) that is the reverse of the codon on mRNA
Carries amino acids to the ribosomeHas the set of instructions for the order in which amino acids are to be assembled into proteins
Makes up the ribosomes, where amino acids are assembled into proteins
Long chains of amino acids, usually folded
Building blocks of proteins
Why are proteins important?
Roles of proteins in the body include
• Structural proteins eg collagen, keratin
• Enzymes (organic catalysts) eg digestive enzymes
• Transport proteins eg haemoglobin
• Regulatory proteins eg hormones
• Protective proteins eg antibodies, clotting factors
RNA is made of nucleotidesVery similar to DNA except: Thymine is replaced by UracilThe sugar in the sugar-phosphate backbone is different (ribose)Strands are single not doubleThere are 3 types – mRNA, tRNA and rRNA