Biology C15. Describe the basic structures of an animal cell, including the nucleus, cytoplasm,...
-
Upload
briana-hampton -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
3
Transcript of Biology C15. Describe the basic structures of an animal cell, including the nucleus, cytoplasm,...

7th Grade CMT
Review

Biology

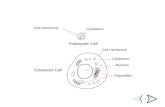
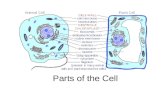
C15. Describe the basic structures of an animal cell, including the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria and cell membrane, and how they function to support life.
What are the functions of the:• cell membrane• cytoplasm• mitochondria• nucleus

The digestive system is composed the mouth/teeth, esophagus, epiglottis, stomach, small intestine, large intestine. It’s helper organs are the liver, gallbladder and pancreas
C16. Describe the structures of the human digestive, respiratory and circulatory systems and explain how they function to bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells and expel waste materials.
The respiratory system is composed of the nose, trachea, pharynx, bronchi, lungs, alveoli and diaphragm.
The circulatory system is composed of the heart, blood and blood vessels (arteries, capillaries, veins).
1. How does the digestive system provide nutrients for cells and expel waste materials?
2. How does the respiratory system provide oxygen for cells and expel waste materials?
3. How does the circulatory system participate in providing needed materials and removing waste?

C17. Explain how the human musculoskeletal system supports the body and allows movement.
The skeletal system provides support for the body. It has joints to allow movement.
1. What is a joint?
2. What type of joint is shown in each picture?
3. What type of movement does it allow?
4. Can you think of another example?
5. What are the 3 types of muscles?
6. Where are they found?
A
B
C
7. How do muscles and bones work together
to move the body?

Feel the Beat
How and why does activity level impact pulse rate?

Food Preservation

C21. Describe how freezing, dehydration, pickling and irradiation prevent food spoilage caused by microbes.
Bacteria grows best with water, a temperature between 40 ˚F and 140 ˚F, low salt and neutral pH (no acid). Controlling these conditions can prevent bacteria from growing in food.
Things to think about:
1. What is involved in each food preservation process?
2. How does each process affect bacteria?
dehydration freezing pickling irradiation

Chemistry

C1. Describe the properties of common elements such as O, H, C, Fe and Al.
Properties on the periodic table include:
mass, number of protons, number of electrons, number of neutrons, state of matter, metal-nonmetal- metalloid
Things to think about:
1. Can you find numbers of P, N, and e?2. How can you tell state of matter?3. How will the density change as state of matter changes?4. Where are metals, nonmetals and metalloids on the table?5. What are some properties of metals, nonmetals and metalloids?

C2. Describe how properties of simple compounds, such as H2O and NaCl, are different from the properties of the elements of which they are made. 1. What is the main difference between a chemical change and a physical change?
2. What is some evidence that a chemical change has happened?
Na: explosive, shiny, metalCl: deadly, yellow-green, gas
Does salt have these properties?
H: explosive, gas, very low densityO: supports combustion, gas, very low density
Does water have these properties?

C3. Explain how mixtures can be separated by using properties of the substances from which they are made. Which can be separated—elements, compounds, mixtures,
solutions? Explain.
What property was used?
1. Pepper was removed from a mixture of pepper and water using a funnel and filter paper.
3. Salt was removed from a salt water solution by boiling it on a hot plate.
2. Different types of plastic were separated by putting them in water. Some floated and some sank.
4. A mixture of salt and sand was separated by putting it in water and stirring.

Earth Science

C18. Describe how folded and faulted rock layers provide evidence of gradual up and down motion of the earth’s crust.
Folds and faults are caused by movement of the earth’s crust and can make features such as mountains, ridges and valleys.
1. What is a fold?2. What type of
land forms can folds create?
1. What is a fault?2. What type of land forms
can faults create?

C19. Explain how glaciation, weathering and erosion create and shape valleys and floodplains.
Glaciation, weathering and erosion slowly change earth’s surface
1. When do glaciers form?
2. Why are they called “nature’s bulldozers?
3. What kind of changes can they make to Earth’s surface?
1. What is weathering?
2. What are the 2 kinds of weathering?
3. Do all rocks weather at the same rate?
1. What is erosion?
2. What are two causes of erosion?
3. What type of land forms are created by erosion?

C20. Explain how the boundaries of tectonic plates can be inferred from the location of earthquakes and volcanoes.
Earth’s crust is broken into tectonic plates. They float on molten rock and move very slowly. This movement is referred to as continental drift. It is caused by convection currents in the hot liquid mantle beneath the crust.
What are the 3 ways plate boundaries interact? What features occur at each type of boundary?
A. B. C.