Ch 7.2 Cell Structure. How is a cell organized? -All Eukaryotic (Animal/Plant) cells have 3 main...
-
Upload
marybeth-jones -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
1
Transcript of Ch 7.2 Cell Structure. How is a cell organized? -All Eukaryotic (Animal/Plant) cells have 3 main...

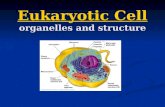
Ch 7.2Cell
Structure

How is a cell organized?
- All Eukaryotic (Animal/Plant) cells
have 3 main parts:
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Cell Membrane

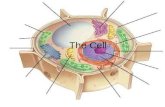
Organelles - Literally means “tiny organs”- Are membrane-bound compartments- Have specialized jobs in a cell- Can be compared to the machines in a factory

Nucleus
- Is the control center of a cell
- Contains a cell’s DNA- DNA in the form of chromatin- DNA bound to proteins
- Sends coded instructions for making proteins and other molecules

Nuclear Envelope- A two-layer membrane- Covers and protects the contents of the nucleus

Nuclear Pores- Small holes in the nuclear membrane- Allow molecules in and out of the nucleus

Nucleolus- Where ribosomes are assembled

Building Proteins

Ribosomes- Build proteins- Use instructions that come from DNA

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Where lipids and proteins are assembled and transported
- Rough ER- Covered in ribosomes = “rough”- Synthesize proteins
- Smooth ER- No ribosomes = “smooth”- Synthesize lipids- Detoxify drugs

Golgi Apparatus
- Receives proteins from ER
- Give proteins an “address tag”
- Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials
- Sends proteins to final destination


Storing and Cleaning Up
Vacuoles and Vesicles- Vacuoles store water, salts,
proteins, and carbs- Vesicles store and move
materials between organelles
Lysosomes- Filled with enzymes- Breakdown lipids, carbs, and
proteins, and other organelles- Remove “junk” from cell

Providing Support and Structure
Cytoskeleton- Maintains cell shape
- Helps with cell movement
- Consists of Microfilaments and Microtubules

How do cells get their energy?


Chloroplasts
- Perform photosynthesis- Capture energy from sunlight and
convert it into food (sugars)

Mitochondria- Perform cellular respiration- Convert the chemical energy in food into cellular
energy (ATP)

Cell Wall
- Strong, supportive layer that surrounds plant cells
- Made of cellulose
- Also found in prokaryotes, but theirs is not made of cellulose
- Allow water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and most nutrients to pass through

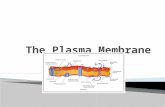
Cell Membrane- Regulates what enters and
leaves the cell
- Protects and supports the cell
- Is made of a double layer of lipids called a lipid bilayer

Lipids in the Membrane- Have regions that are hydrophilic
- “love” water
- Have regions that are hydrophobic- “fear” water
- Orient themselves so the hydrophilic parts face the water and the hydrophobic parts face away from it
- Make the membrane selectively permeable
- Some things can cross it, but others can’t

Fluid Mosaic Model- Proteins, carbohydrates and other molecules
are embedded in the lipid bilayer
- This makes the membrane look like a mosaic
- Since molecules can float and move in the membrane, it acts like a fluid

Differences Between Plant and Animal CellsPlant- Have cell walls- Have chloroplasts
Animal- No cell walls- No chloroplasts