Biology 12 – membranes. Cell structures Is this eukaryotic? Why? Is this a plant or animal cell?...
-
Upload
mark-parks -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Biology 12 – membranes. Cell structures Is this eukaryotic? Why? Is this a plant or animal cell?...

Biology 12 – membranes

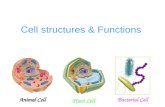
Cell structures
Is this eukaryotic?
Why?
Is this a plant or animal cell?
Why?
Label the structures

Cell structures
Is this eukaryotic?
Why?
Is this a plant or animal cell?
Why?
Label the structures
Yes
It has a nucleus
Plant
Chloroplasts, cell wall, large vacuole
Cell wall
Cell membraneChloroplast
Lysosome
Golgi body Nucleus Nucleolus
DNA

Magnification and field of view 1
magnification x 40 magnification x 400
field of view 4000 m field of view 400 m
Magnification has increased by a factor of 10
Field of view has decreased by a factor of 10

Magnification and field of view 2
magnification x 100 magnification x 400
field of view 1600 m field of view 400 m
Magnification has decreased by a factor of 4
Field of view has increased by a factor of 4

Size of objects under the microscope 1
Magnification x100, field of view 1600 m
~ 4 cells fit across diameterEach cell ~ 400 m

Size of objects under the microscope 2
Magnification x400, field of view for x100 = 1200 m
Field of view for x400 = 300 m ~ 2 cells fit across diameterEach cell ~ 150 m

Cells exchange matter and energy
In: Out:Processes:

Cells exchange matter and energy
In:
Oxygen
Nutrients eg glucose
(carbon dioxide and light energy in plants)
Water
Ions
Out:
Carbon dioxide
Wastes eg urea
(oxygen in plants)
Water
Ions
Heat energy
Processes:
Respiration
Synthesis
Growth
Division
Photosynthesis (in plants)

Unicellular responses to the environment
Give one example that demonstrates unicellular organisms respond to their environment

Unicellular responses to the environment
Give one example that demonstrates unicellular organisms respond to their environment
Engelmann’s experiment
Paramecia and Amoeba changing the rate of their contractile vacuoles depending on salt concentration
Euglena movement towards food & light

Cell membranes
Sketch a typical cell membrane according to the Fluid Mosaic model
Describe the roles of:• Phospholipids
• Proteins
• Carbohydrates

CellsSketch a typical cell membrane according to the Fluid Mosaic model .
Describe the roles of:Phospholipids = A – waterproof, flexible layer, that lets in small particles
Proteins = B – provides channels for larger particles (facilitated diffusions), acts as pumps (active transport), acts as receptor sites
Carbohydrates = C - acts as receptor sites
A
B
C

Diffusion
Draw a diagram to show how materials are exchanged by diffusion

Movement of particles - diffusion
Occurs without energy
Particles will move from higher concentrations to lower concentrations

Osmosis
Draw a diagram to show how materials are exchanged by osmosis

OsmosisMovement of waterThis occurs from areas of high water concentration (low
concentration of solute) to areas of low water concentration (high concentration of solute)

Active transport
Draw a diagram to show how materials are exchanged by active transport

Active transport
Movement against a concentration gradient.Energy is needed

Exchange of material
Show the movements of water and ions that would occur in both these cases
Distilled water Sea water
Water moves in
Water moves out Ions move inIons move out

Determining the components of the cell membrane
Beetroot lab – part A
acid base
water Distilled water
detergent

Beetroot lab part A

Beetroot experiment part A
• What hypothesis is being tested?
• What is the control?
• What is the independent variable?
• What is the dependent variable
• What variables are controlled?
• How will this tell you about the components of the cell membrane?

Beetroot lab results – part A
After 1 hour After 24 hours

Beetroot lab results – part A
After 1 hourAfter 24 hours
Detergent has broken down cell membranes
Detergent has broken down cell membranesThe osmotic difference between distilled water and the cells has caused water to enter and burst cellsAcidic and basic conditions starting to damage cell membranes

Beetroot experiment part B
Beetroot lab – part B• How will you change the temperature? • How many different temperatures will
you test?• How many slices of beetroot will you
use in each test tube?