Lecture 24 MOSFET Basics (Understanding with no math) Reading ...
Basics of Mosfet
-
Upload
tonymathew03 -
Category
Documents
-
view
237 -
download
0
Transcript of Basics of Mosfet
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
1/25
MOS Transistor (MOSFET)
n+ n+
p-
SOURCE DRAIN
GATE
SUBSTRATE
GATE OXIDE
CHANNEL
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
2/25
MOS Transistor Operation
Channel is normally non-conducting (open-circuit):No bias voltage (or small voltage) applied to Gate
Source and Drain junctions are reverse-biasedrelative to the substrate
Depletion regions surround the Source and Drain
Channel is depletedof mobile charge carriers
Channel starts to conduct when:Gate voltage VGS exceeds the Threshold VoltageVTMobile charge is present in the channel
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
3/25
p Substrate
S DG
VDS +
_
Source Depletion
Region
Drain Depletion
Region
mA
IDS = 0
n+ n+
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
4/25
p Substrate
S DG
VDS +
_
mA
VGS < VT
+_
Channel
in Depletion
IDS = 0
n+ n+
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
5/25
MOSFET Operation 0 < VGS < VT
Channel in DepletionMajority carriers in p-type substrate (holes) are
repelled by positive charge on the Gate
No current flows in the channel VGS VT
Channel in Inversion
Electrons (minority carriers in substrate) are drawninto channel by positive charge on the Gate
Current flows in the channel
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
6/25
p Substrate
S DG
VDS +
_
mA
VGS < VT
+_
Channel
in Depletion
IDS = 0
n+ n+
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
7/25
p Substrate
S DG
VDS +
_
mA
VGS VT
+_
Channel
in Inversion
IDS 0
n+ n+
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
8/25
Mobile charge concentration in the channel isproportional to that part of the gate-source voltagewhich exceeds the threshold voltage VT, that is by
(VGS - VT). In this way the gate-source voltagecontrols the drain-source current.
MOS TRANSISTOR MODEL
Capacitance of gate-oxide-substrate capacitor is CG
Mobile charge (electrons) in the channel is given by:
( )TGSG VVCQ =
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
9/25
Formation of the Inversion Layer
GATE OXIDE SILICON
+ve
Charge
-ve
Charge
NA
z
Charge Density
GATE OXIDE SILICON
+veCharge
-ve
Charge
NA
z
Charge Density
Inversion
Layer
(Electrons)
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
10/25
is mean transit timefor electrons to cross the channel
All mobile charge in the channel is swept through the
drain once per transit time; hence drain current is:
( )
=
= TGSGDSVVCQ
I
average drift velocity of the electrons in the channelunder the influence of an electric field E is:
Ev =
is the mobilityor velocity per unit field strength
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
11/25
Let the length of the channel (distance from source todrain) be L; then if the velocity v is constantthroughout the channel we can write:
=Lv
Assume E is uniform along the entire length of the
channel, and that it is created by a voltage VDSbetween drain and source, then:
L
V
EDS
=
[Note: It will be explained later that this condition is only
fulfilled if VDS
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
12/25
The transit time is
DS
2
V
L
=
Substitute into previous equation for IDS:
( ) DSTGS2G
DS VVV
L
CI
=
Gate capacitance CG = Cox.WL, where Cox is the gateoxide capacitance per unit area and WL is the area of
the channel. Therefore:
( ) DSTGSoxDS VVVL
WCI =
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
13/25
MOS Transistor
n+ n+
L
W
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
14/25
For VDS
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
15/25
Triode Region 0 < VDS < (VGS - VT)
( )
= 2
VVVVL
WCI
2
DSDSTGSoxDS
The voltage in the channel varies between Source andDrain now that VDS is getting bigger; as a result the
charge concentration in the channel also varies withdistance from the Source
This equation reduces to the earlier one if VDS is small.
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
16/25
Saturation Region VDS (VGS - VT)
( )2
TGSoxDS VVL
WC2
1I =
When VDS reaches (VGS - VT) the end of the channelclosest to the drain pinches off and the drain currentsaturates.
The amount of charge induced in the channel cannotbe increased beyond this level.
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
17/25
MOS Channel Pinch-Off
n+ n+
Electron
Density
Depletion
Region
Inversion
Layer
S
G
D
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
18/25
MOSFET Transfer Characteristic
0
20
40
60
80
100
0 1 2 3 4 5
VGS (V)
IDS
(A)
VT
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
19/25
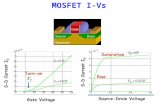
MOSFET Drain Characteristics
VDS (V)
0
ID
S
(A)
2 4 6 8 10 12
200
400
600
(VGS VT) = 4V
3V
2V
1V
Triode
RegionSaturation
Region
800
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
20/25
MOSFET Transfer Characteristic
VDS = 10V
T
Gate-Source Voltage (V)
0.00 2.50 5.00 7.50 10.00
DrainCurre
nt(A)
0.00
5.43
10.86
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
21/25
MOSFET Drain CharacteristicsT
Input voltage (V)
0.00 2.50 5.00 7.50 10.00
Current
(A)
0.00
6.00
12.00VGS = 10V
VGS = 8V
VGS = 6V
VGS = 4V
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
22/25
MOSFET Circuit SymbolsD
G
S
Substrate
n-channel
Enhancement Mode
MOSFET
D
G
S
Substrate
p-channel
Enhancement Mode
MOSFET
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
23/25
MOSFET TransconductanceThe transconductance parameter gm is defined
as:
GS
DSm
V
Ig
=
Enhancement MOSFET in saturation:
( ) ( )2TGS2TGSoxDS VV2VVLWC21I ==
L
W
Cox=Where
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
24/25
MOSFET Transconductance
( )TGSGSDS
m VVV
I
g =
=
( ) =DS
TGS I2VV
DSm I2g =
-
8/4/2019 Basics of Mosfet
25/25