Bacterial Structure Beheshtimaal
-
Upload
harishkumar-kakrani -
Category
Documents
-
view
111 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Bacterial Structure Beheshtimaal

Bacterial Morphology Arrangement1. Bacilli
a.Streptobacilli
b. Bacilli
2. Cocci
a. Cocci
b. Doplococci
c. Streptococci
d. Staphylococci
e. Sarcina ( 3D )
f. Gaffkya ( 2D ) 1Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Common Shapes & Arrangement
2Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Bacterial morphologies (1)
3Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Bacterial morphologies (2)
4Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Bacterial morphologies (3)
5Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Bacterial Morphology Arrangement
3 Spirl
a. Vibrio
b. Spirillum
c. Spirochete
6Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Bacterial morphologies (4)
7Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Bacterial Cell Structures & Functions
8Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Size relationships among prokaryotes
9Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Bacterial Cell Structure
Appendages - fdlagella, pili or fimbriae
Surface layers - capsule, cell wall, cell
membrane
Cytoplasm - nuclear material, ribosome,
mesosome, inclusions etc.
Special structure - endospore
10Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Bacterial Cell Structure
11Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Appendages
1. flagella
Some rods and spiral form have this.
a). function: motility
b). origin : cell membrane flagella attach to the
cell by hook and basal body which consists of set(s) of
rings and rods
Gram - : 2 sets of ring and rods, L, P, S, M rings and
rods
e.g. E. coli
Gram + : S, M rings and rods
e.g. B. megaterium12
Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish Kakrani

Organ of bacterial locomotion
13Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Structure of the flagellum
14Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Flagella movement(1)
15Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Flagella movement(2)
16Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Flagella movement(3)
17Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

b).Origin (continued)
– The structure of the bacterial flagella allows it to spin
like a propeller and thereby propel the bacterial cell;
clockwise or counter clockwise ( Eucaryotic , wave
like motion.
– Bacterial flagella provides the bacterium with
mechanism for swimming toward or away from
chemical stimuli, a behavior is knows as
CHEMOTAXIX, chemosenors in the cell envelope
can detect certain chemicals and signal the flagella to
respond.
18Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

c). position
monotrichous
lophotrichous
peritrichous
d). structure
protein in nature: subunit flagellin
19Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

2. Pili or Fimbriae
Shorter than flagella and straighter , smaller.
Only on some gram- bacteria.
a). function: adhere. One of the invasive
mechanism on bacteria. Some pathogens
cause diseases due to this. If mutant
(fimbriae) not virulent. Prevent phagocytosis.
20Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

pili - sex factor. If they make pili, they are + or
donors of F factor.
It is necessary for bacterial conjugation
resulting in the transfer of DNA from one cell to
another.
It have been implicated in the ability of
bacteria to recognize specific receptor sites on
the host cell membrane. In addition, number of
bacteria virus infect only those bacteria have F
pilus. 21Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

b). Origin: Cell membrane
c). Position: common pili , numerous over
the cell, usually called fimbriae sex pile, 1-
4/cell
d). Structure: composed of proteins which can
be dissociated into smaller unit
Pilin . It belongs to a class of protein Lectin
which bond to cell surface polysaccharide.22
Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish Kakrani

II. CELL SURFACE LAYER
1. Capsule or slime layer
Many bacteria are able to secrete material that adheres to the bacterial cell but is actually external to the cell.
It consists of polypeptide and polysaccharide on bacilli. Most of them have only polysaccharide. It is a protective layer that resists host phagocytosis. Medically important.
23Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

2. Bacterial Cell Wall
General structure: mucopolysaccharide i.e. peptidoglycan. It is made by N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid. tetrapeptide ( L-alanine- isoglutamine-lysine-alanine) is attached. The entire cell wall structure is cross linked by covalent bonds. This provide the rigidity necessary to maintain the integrity of the cell.
N-acetylmuramic acid is unique to prokaryotic cell.
24Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Cell walls of bacteria(2)
25Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Cell walls of bacteria(3)
26Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Cell walls of bacteria(4)
27Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Cell walls of bacteria(1)
28Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Structure of peptidoglycan(1)
29Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Structure of peptidoglycan(2)
30Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

(a). Gram positive bacterial cell wall
Thick peptidoglycan layer
pentaglycin cross linkage.
Teichoic acid: ribitol TA &
glycerol TA
Some have peptioglycan
teichoic acid.
All have lipoteichoic acid. 31
Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish Kakrani

Function of TA:
* Antigenic determinant
* Participate in the supply of Mg to
the cell by binding Mg++
* regulate normal cell division.
For most part, protein is not found as
a constituent of the G+ cell wall except
M protein on group streptococci
32Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Structure of the Gram-positive Cell Wall
33Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

(b) Gram -
Thin peptidoglycan
Tetrapeptide cross linkage
A second membrane structure: protein and
lipopolysaccharide.
Toxicity : endotoxin on lipid A of
lipopolysaccharide. glucosamine- glucosamine-long
polysaccharide- repeated sequences of a few sugars
(e.g. gal- mann-rham) n=10-20 O antigen
34Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Structure of peptidoglycan(3)
35Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Toxicity : endotoxin on lipid A of
lipopolysaccharide.
glucosamine- glucosamine-long
FA FA FA FA
polysaccharide- repeated sequences of
a few sugars (e.g. gal- mann-rham)
n=10-20 O antigen36
Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish Kakrani

Chemistry of LPS
37Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

The Gram-negative outer membrane(1)
38Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

The Gram-negative outer membrane(2)
39Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

2. Cell Membrane
Function:
a. control permeability
b. transport e’s and protons for cellular metabolism
c. contain enzymes to synthesis and transport
cell wall substance and for metabolism
d. secret hydrolytic enzymes
e. regulate cell division. Fluid mosaic model. phospholipid bilayer and
protein (structure and enzymatic function). Similar to eukaryotic cell membrane but some differs. e.g. sterols such as cholesterol in Euk not in Prok. 40
Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish Kakrani

The cytoplasmic membrane
41Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Functions of the cytoplasmic membrane(1)
42Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Functions of the cytoplasmic membrane(2)
43Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Transport proteins
44Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Classes of membrane transporting systems(1)
45Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Classes of membrane transporting systems(2)
46Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Classes of membrane transporting systems(3)
47Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

III. Cytoplasm
80% water, nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, lipid
and inorganic ions etc.
1. Bacterial chromosomes
a single large circular double stranded DNA no histone
proteins. The only proteins associated with the
bacterial chromosomes are the ones for DNA
replication, transcription etc.
2. Ribosome
protein synthesis 48
Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish Kakrani

The bacterial chromosome and supercoiling
49Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

3. Mesosomes
A large invaginations of the plasma membrane,
irregular in shape.
a. increase in membrane surface, which may be
useful as a site for enzyme activity in respiration
and transport.
b. may participate in cell replication by serving as a
place of attachment for the bacterial chromosome.
50Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

4. Inclusions
Not separate by a membrane but distinct.
Granules of various kinds:
* glycogen,
*polyhydroxybutyric acid droplets (PHB)
i.e. fat droplets
* inorganic metaphosphate (metachromatic granules) - in
general, starvation of cell for almost any nutrients
leads to the formation of this to serve as an
intracellular phosphate reservoir.
51Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

PHBPHB
52Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

5. Chromatophores
Only in photosynthetic bacteria and blue green algae.
Prok. no chloroplast, pigment found in lamellae
located beneath the cell membrane.
53Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

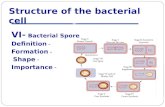
IV. Special Structure
* Endospores
Spore former: sporobactobacilli and sporosarcinae - no medical importance. bacillus and clostridium have medical importance.
* Position: median, sub-terminal and terminal have small water, high calcium content and dipicolinic acid (calcium dipicolinate)
extremely resistant to heat, UV, chemicals etc. may be due to many S containing A.A for disulfide groups.
54Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

• After the active growth period approaching the stationary growth phase, a structure called forespore develops within the cells.
• It consists of coat, cortex and nuclear structure.
The process of endospore formation
55Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Endospores
56Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Negatively Stained Bacillus: (A) Vegetative Cell (B) Endospore
57Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Dipicolinic acid
58Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Vegetative/spore-containing cells(1)
59Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Vegetative/spore-containing cells(2)
60Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Detailed stepsin endospore formation(1)
61Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Detailed stepsin endospore formation(2)
62Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani

Detailed stepsin endospore formation(3)
63Purvi Kakrani & Dr. Harish
Kakrani