African Kingdoms The Post- Classical Era Objective: To understand and analyze the effects of African...
-
Upload
robyn-fowler -
Category
Documents
-
view
242 -
download
2
Transcript of African Kingdoms The Post- Classical Era Objective: To understand and analyze the effects of African...

African Kingdoms The Post- Classical Era
Objective: To understand and analyze the effects of African trading kingdoms
on the Post- Classical Era.
Ms. Costa

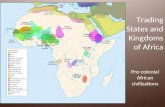
Early Civilizations of Africa:
Great Rift Valley Nile Valley ( Ancient
Egypt) Desertification- Bantu
Migrations Kingdom of Nubia Great Zimbabwe North Africa- Carthage Trade & Camel
Caravans Introduction of Islam
600

Civilizations on the Nile:
Ancient Egypt • Flooding of the Nile-
silt for farming • 5,000 BC people begin
farming- scattered villages
• Ruled by kings & queens (pharaohs = Gods)
• Large burial tombs & pyramids for afterlife
• Use of hieroglyphics • Skill in paper-making,
architecture, medicine and astronomy
Ancient Nubia
• 6000 BC hunting and fishing communities South of Egypt along Nile
• 3100 BC start of kingdoms
• Greatest city Napata- 724 conquered Egypt rule for 60 yrs.
• Later kingdom established South of Nubia
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tp6P_hBnF1s&feature=results_video&playnext=1&list=PL06DEB820AFD029A5


North African Trading Powers Rise and Fall of Carthage
• 800 BC Phoenicians establish Carthage (Tunisia)
• Powerful city-state of N. Africa
• Textiles, metals, slaves, & food
• Dominate Med. Trade 500 BC-200BC
• War with Rome- lose and fall to Roman Empire 146
Roman and Islamic Influences
• Cities grew up in Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia under Roman Empire
• Spread of Christianity • Roman roads• Fall of Rome 476 AD
compete for control of N. Africa
• 600s Arab traders took Egypt and N. Africa- spread of Islam
• N. Africans spread Islam to W. Africa

The Roman Empire


Gold for Salt:
Dominate trans-Saharan trade
Plentiful gold in Ghana, Nigeria & Senegal (Savanna of W. Africa)
North Africa wants gold to make coins (Have Salt)
City of Taghaza salt blocks used to build houses
Salt is going South Gold is going North West Africans trade for
salt- necessity for diets Control of gold supply
=wealthy trade kingdoms

Ghana: “Land of Gold” (700-1000)
Sonike people Between Niger &
Senegal Rivers Use of Iron Lavish court set up Dominate gold/salt
trade Go-between for
North African traders & gold and ivory producers of South
Import: cloth, broaches, copper & salt Export: Gold Trade with Berbers from N. Africa

Ghana: Trade & Islam Ghana’s kings grew
rich- tax on imports/exports
Islam: though in contact with Muslim traders, Ghana kept traditional religion
Tolerant and welcome Muslims
1050 Almoravids- campaign to spread Islam/ invasions


Mali: “Where the King Dwells”(1200-1450)
Mandinke people Famous for weaving, mining,
and architecture Sundiata- founder Takes over old empire-
encompass parts of Ghana Greatest leader Mansa Musa
1312 (takes salt mines to the North)
MM Enlarges empire- Adopts Islam
Assembly of Kings- legal code Timbuktu- center of
scholarship/ wealth Ibn Batutta “There is
complete security in their country.”
Trade: Gold, Salt, cloth, books & Copper :

The Emperor’s Hajj: 1324 sets out for
Mecca with caravan Pass through Cairo Egyptians in Awe –
shows wealth of kingdom
New trading ties Return with Muslim
scholars, artists, writers, teachers & architects
Building of mosques in Gao & Timbuktu
Decline – after MM dies his successor are weak


Songhai: 1300s Founded by Sonni-Ali –
bring trading cities under his control
Great military leader – takes over Timbuktu
Gao = capital Largest empire Asika Muhammad- military
and administration (height of kingdom under him)
Asika makes pilgrimage brings Muslim scholars to Timbuktu
1400 Timbuktu center of learning
1586 invasions from North
Education: Uniform weights & measures, banking and credit


Other Kingdoms of West Africa: Benin
Rose in forests of Guniea near Equator
1300 kingdoms emerge
King is political and religious leader (Ewuare)
3 mile long wall around city
Palace with bronze
The Hausa: 1300 walled cities of clay Thriving commercial
centers Merchants trade with
Arabs and Berbers Develop a written
language based on Arabic
Hausa rulers- some are women
Gain control of Saharan trade routes

East African Trading Kingdoms:
The Post Classical Age

East African Kingdoms Trade with Middle East, Persia, India, China E. African coast good harbors and cities City-States: a large town that has its own government
& usually controls the surrounding countryside Trade at coastal and inland cities – Malindi, Mombasa,
Zanzibar, Mozambique, Mogadishu, Sofala & Kilwa Traders brought slaves, ivory, gold, and animal skins
from interior of Africa to coast Other trade use trade winds to sail across Indian
Ocean using monsoons Arabs bring Islam to E. Africa Development of Swahili (Arab blended with local
lang.)


The Kingdom of Axum:
• Christian missionaries 1st introduce Christianity to Ethiopia AD 300
• AD 500 Spread to Nubia • Kingdom of Axum grew
as Arab & African traders settle on Red Sea
• 600 decline bc Arabs• 1200 re-mergence of
Christian stronghold King Lalaibela
• 11 Rock churches

The Kingdom of
AXUM

BBC: THE LOST KINGDOM OF AXUM
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bkEvbZZ1FuU&feature=related

The Great Kingdom of Zimbabwe: • Inland & South from E.
African City States • Located near Limpopo • Connect to I.O. Trade • Height 1300- rulers
organized large kingdom/Cntrl gold mines
• Zimbabwe = “great stone house”
• Today stone buildings, city walls, fortresses, and homes still stand
• Archeologists found porcelain from China, beads from India
• 1500s power struggle decline


Sources:
• BBC Lost Kingdoms of Africa • Google Images