Splash Screen 2 Contents CHAPTER FOCUS SECTION 1Ancient African Kingdoms SECTION 2The Middle...
-
Upload
brenda-ryan -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Splash Screen 2 Contents CHAPTER FOCUS SECTION 1Ancient African Kingdoms SECTION 2The Middle...

Splash Screen

2
Contents
CHAPTER FOCUS
SECTION 1 Ancient African Kingdoms
SECTION 2 The Middle Kingdoms
SECTION 3 East African Civilizations
SECTION 4 Path to the Americas
SECTION 5 Mesoamerica
SECTION 6 The Incas
CHAPTER SUMMARY & STUDY GUIDE
CHAPTER ASSESSMENTClick a hyperlink to go to the corresponding section.
Press the ESC key at any time to exit the presentation.

3
Chapter Focus 1
Overview
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• Chapter 8 focuses on the development of civilization in Africa and the Americas. – Section 1 discusses the Kush and Aksum
civilizations.
– Section 2 describes West African kingdoms.
– Section 3 describes the contributions of the East African civilizations.
– Section 4 explains why people migrated to the Americas.
– Section 5 summarizes the civilizations of Mesoamerica.
– Section 6 analyzes the Inca civilization of South America.

4
Chapter Focus 2
Objectives
• discuss how the ancient civilizations of Kush and Aksum passed along their culture.
After studying this chapter, you will be able to:
• summarize how West African and East African kingdoms developed because of trade.
• explain how bands of people crossed into the Americas.
• describe the civilizations that developed in Mesoamerica.
• discuss Inca culture.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

5
Chapter Focus 3
Read to Discover
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. The Chapter Focus is on page 129 of your textbook.
• How the ancient African civilizations of Kush and Aksum passed along elements of their culture
• How West African kingdoms and East African civilizations grew because of trade
• How Native Americans developed farming and other skills
• What kinds of civilizations developed in Mesoamerica
• What life was like for the Inca of South America

6
Terms to Learn
People to Know
Chapter Focus 4
• silent barter • pilgrimage • population
explosion • quipus
• Sunni Ali • Askia Muhammad • Montezuma II • Pachacuti
People to Know (cont.)
• Meroë • Timbuktu • Zimbabwe • Bering Strait • Tenochtitlán • Kilwa
Places to Locate
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Click the Speaker On button to listen to the words.
• Kashta • Piankhi • Ezana • Sundiata Keita • Mansa Musa

7
While armies carved out empires in the Middle East, civilizations developed in Africa south of the Sahara and in the Americas. Through conquest and trade, Africans and early Americans built great kingdoms and empires that rivaled civilizations elsewhere in the world.
Chapter Focus 5
Why It’s Important
Click the Speaker On button to replay audio.

End of Chapter Focus

9
Section 1-1
Ancient African Kingdoms• Other civilizations besides Egypt flourished
in ancient Africa.
• Less is known about them than about Egypt.
• However, archaeologists have discovered enough remains to be able to tell what African civilizations were like.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Section 1 begins on page 129 of your textbook.

10
Section 1-2
Kush
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• The first of these African civilizations was Kush, which lay south of Egypt on the Nile River in present-day Sudan.
• About 2000 B.C., the Kushites were nomadic cattle herders, grazing long-horned cattle on a savannah, or grassy plain.
• During the New Kingdom, Egyptian armies conquered Kush.
• About 1160 B.C., Egypt’s power declined and the Kushites won back their independence and set up a capital at Napata.

11
Section 1-3
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• About 750 B.C., the Kushite king Kashta set out to conquer Egypt.
• His son Piankhi completed the conquest and founded a dynasty that ruled Egypt for 70 years.
• However, during the 600s B.C., the Assyrians invaded Egypt, and drove the Kushites back to the south.
• Despite their losses, the Kushites did gain something: they learned the secret of iron-smelting from the Assyrians.
Kush (cont.)

12
Section 1-4
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• Soon, Kushite farmers, using iron hoes, were growing large amounts of grain.
• Around 540 B.C., the Kushites moved their capital to Meroë.
• Kush remained a great trading country for some 600 years, and then began to decline.
• As it declined, Aksum, in present-day Ethiopia, rose to take its place.
• About 350 A.D., Aksumite armies burned Meroë to the ground.
Kush (cont.)

13
Section 1-5
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• Like Kush, Aksum was a trading country.
• Jewish, Greek, and Arab merchants settled in Aksum.
• It was most likely the Greeks who brought Christianity to Aksum.
• Emperor Ezana, whose armies had destroyed Meroë, converted to Christianity in 324 A.D.
• This heritage was passed down to the present day.
Aksum

14
Section 1-6
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• Aksumites developed a writing system, minted gold coins, and learned to farm on terraces, or raised levels of land.
• Over time, Aksum’s power as a trading country began to decline.
• After Arab armies swept across North Africa in the 600s A.D., the Aksumites retreated toward the interior, or inland areas, of their country.
• There, they lived in isolation for more than 1,000 years.
Aksum (cont.)

15
Section 1-Assessment 1
Section Assessment
How did the Kushites and Egyptians influence each other?
Kushites learned to worship the god Amon-Re, how to work in copper and bronze, and to adapt hieroglyphs to fit their language. Egypt was also ruled for a time by Kush and was also influenced through trade.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

16
Section 1-Assessment 2
Section Assessment (cont.)
Why did the Kushites choose Meroë as their capital?
It was on the Nile, it lay near large deposits of iron ore and trees to fuel smelting furnaces, and it had good grazing land.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

17
Section 1-Assessment 3
Section Assessment (cont.)
Making Generalizations How were the kingdoms of Kush and Aksum influenced by other cultures?
Kushites learned iron-smelting from the Assyrians; they worshiped the same god and built pyramids like the Egyptians; Aksumites took Christianity from the Greeks.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

18
Possible effects: made iron hoes, which increased grain production; made iron knives and spears for trade; moved capital to Meroë, where large deposits of iron ore and trees to fuel smelting could be found; grew into a great trading nation.
Section 1-Assessment 4
Section Assessment (cont.)
Draw a diagram like the one on page 131 of your textbook, and use it to show the effects of iron-smelting on Kush.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

End of Section 1

20
Section 2-1
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Section 2 begins on page 132 of your textbook.
The Middle Kingdoms• Several large trading kingdoms arose in
West Africa after 400 A.D.
• Their rise was aided by the knowledge of iron-smelting.
• This was most likely brought to West Africa by refugees, or people who flee for safety, from Kush.

21
Section 2-2
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
Ghana• The first of these trading kingdoms was
Ghana.
• Legend has it that Ghana was founded about 200 A.D.
• Around 350 A.D., the Ghanians learned how to smelt iron.
• They also gained control over West Africa’s major trade routes.
• The most important traded goods were salt and gold.

22
Section 2-3
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• Caravans carried salt south from Taghaza in present-day Algeria and returned north with gold from Wangara, an area southwest of Ghana.
• Ghanian merchants and Wangara gold miners used a trading technique called silent barter.
• In 1042 A.D., Arabs from North Africa started a war against Ghana.
Ghana (cont.)

23
Section 2-4
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• The Arabs destroyed the capital and made the Ghanians give them tribute.
• Ghana managed to regain its independence but was not strong enough to survive.
Ghana (cont.)

24
Section 2-5
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• By 1240 A.D., Ghana was a part of Mali, the second large trading kingdom in West Africa.
• Sundiata Keita, the king of Mali, did several things to make his kingdom strong:
Mali
– He reestablished the salt-gold trade, which the Arabs had disrupted.
– He organized a permanent army.
– He divided the kingdom into provinces, each headed by a general.
– He moved his capital from place to place.

25
Section 2-6
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• One of the most famous kings of Mali was Mansa Musa I, or King Moses I.
• He led a pilgrimage, or religious journey, to Arabia in 1324–25; it took more than 14 months to cover the 3,000 miles.
• Within 100 years after Mansa Musa’s death, Mali lost its land to others due to weak leadership.
Mali (cont.)

26
Section 2-7
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• The kingdom that replaced Mali as the most powerful in West Africa was Songhai.
• The Sultan Sunni Ali, in 1464, ruled Songhai from the city of Gao.
• Following Sunni Ali’s death, Askia Muhammad came to power in Songhai.
• Songhai was more organized than the other two kingdoms.
• It was divided into provinces with a governor for each.
Songhai

27
Section 2-8
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• Despite its power, Songhai lasted only 100 years.
• In 1591 A.D., a Moroccan army, armed with guns, sought to capture Songhai’s gold mines.
• The Moroccans defeated Songhai’s soldiers, who were armed with swords and spears.
Songhai (cont.)

28
Section 2-Assessment 1
Section Assessment
What were two important trade goods in West Africa?
Two important trade goods were salt and gold.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

29
Section 2-Assessment 2
Section Assessment (cont.)
How was the kingdom of Songhai organized?
It was divided into provinces, each with a governor. Everyone used the same weights, measures, and legal system.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

30
Section 2-Assessment 3
Section Assessment (cont.)
Making Inferences Why do you think Ghanian merchants set up a system called silent barter?
Answers will vary but might include that Ghanian merchants might have been dealing with people who did not speak their language.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

31
Section 2-Assessment 4
Section Assessment (cont.)
Draw a diagram like the one on page 134 of your textbook, and use it to summarize the accomplishments of the three great West African kingdoms.
Accomplishments should reflect the policies established by the rulers of each kingdom, particularly the growth of trade and encouragement of learning.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

End of Section 2

33
Section 3-1
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Section 3 begins on page 136 of your textbook.
East African Civilizations• The growth of trading kingdoms in West
Africa was matched by the rise of trading kingdoms and city-states in East Africa.
• Goods moved from the interior of East Africa to coastal markets, which, in time, became large city-states.
• Each of these had its own ruler and government.

34
Section 3-2
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• One of the best-known trading kingdoms was Zimbabwe.
• Their ancestors, the Shona, once lived in present-day Nigeria in West Africa.
• About 100 A.D., a population explosion, or a large and sudden growth in population, took place forcing some people to move.
• The Shona settled in Zimbabwe in East Africa about 700 A.D., where they built towns of stone.
Zimbabwe

35
Section 3-3
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• The people of Zimbabwe viewed their chief as a god-king.
• Officials imitated him; if he coughed, they coughed; when he ate, they ate.
• Zimbabwe’s people traded gold, copper, and ivory from the interior to merchants from cities along Africa’s east coast.
Zimbabwe (cont.)

36
Section 3-4
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• Another important trading city-state in East Africa was Kilwa.
• The people of Kilwa collected heavy taxes from traders of other countries.
• They used their wealth to extend their power over neighboring city-states.
• A culture known as Swahili–a mix of African and Arabic cultures–developed in Kilwa and other East African city-states.
Kilwa

37
Section 3- Assessment 1
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
How did the people of Zimbabwe view their leader?
They viewed him as a god-king.
Section Assessment

38
Section 3- Assessment 2
Section Assessment (cont.)
How did the people at Kilwa use their wealth?
They used their wealth to extend their power over neighboring city-states, to dress in fine cotton and silk, and to fill their houses with riches from India and China.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

39
Section 3- Assessment 3
Section Assessment (cont.)
Understanding Cause and Effect A population explosion among the Shona caused many of these people to leave their homeland. What are some of the events or conditions that might cause people to leave their homelands today?
People might leave their homelands because of war, famine, disease, religious persecution, or simply hope of a better life.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

40
Section 3- Assessment 4
Section Assessment (cont.)
Draw a diagram like the one on page 137 of your textbook, and use it to show features of Swahili culture.
Swahili culture was made up of city-states, traded with people across the Red Sea and Indian Ocean, and spoke a language created from Arabic and Bantu.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

End of Section 3

42
Section 4-1
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Section 4 begins on page 137 of your textbook.
Path to the Americas• Until about 25,000 years ago, there were no
people in the Americas.
• Then, bands of people began to cross into the Americas from Asia over a land bridge formed during the last Ice Age.
• Today, this bridge is covered by the waters of the Bering Strait.
• Experts believe people reached the southern tip of South America by about 9000 B.C.

43
Section 4-2
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
Path to the Americas (cont.)
• About 7000 B.C., the last Ice Age ended and the climate became hotter and drier.
• By 6000 B.C., people in the Tehuacán Valley south of present-day Mexico City had developed farming.
• By 3000 B.C., there were thousands of small farming villages all through the Americas.
• Between 3000 B.C. and 1000 B.C., people developed such skills as weaving and pottery making.

44
Section 4- Assessment 1
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
How did hunting-and-gathering bands travel to the Americas?
They came across a land bridge over the Bering Strait.
Section Assessment

45
Section 4- Assessment 2
Section Assessment (cont.)
How long may it have taken for people to spread out over North and South America?
It may have taken from 23,000 B.C. to 9000 B.C., or about 14,000 years to spread out.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

46
Section 4- Assessment 3
Section Assessment (cont.)
When and where did farming first appear?
By about 6000 B.C., people in the Tehuacán Valley south of present-day Mexico City had developed farming.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

47
Section 4- Assessment 4
Section Assessment (cont.)
Understanding Cause and Effect What do you think caused hunting-and-gathering bands to push farther south into the Americas?
Answers will vary but could include the need for food, safety from attack, weather, or curiosity.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

48
Section 4- Assessment 5
Section Assessment (cont.)
Draw a diagram like the one on page 138 of your textbook, and use it to show the cause and effects of the invention of farming in Mesoamerica.
cause–end of the last Ice Age and the disappearance of most large game
effects–rise of farming villages, development of weaving and pottery making, construction of irrigation ditches, population growth
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

End of Section 4

50
Section 5-1
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Section 5 begins on page 138 of your textbook.
Mesoamerica• As the number of people grew, societies
became more complex.
• Several great civilizations rose in Mesoamerica, or Middle America, before 900 A.D. and others later.

51
Section 5-2
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
The Olmecs• One of the earliest civilizations in
Mesoamerica was that of the Olmecs which came into being around 1000 B.C.
• About 900 years later, it disappeared mysteriously.
• They developed planned cities, hieroglyphic writing, and a calendar.
• The Olmecs lived along the southern coast of the Gulf of Mexico.

52
Section 5-3
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• Another great civilization, that of the Mayas, began in Mesoamerica about 500 B.C.
• It reached its peak between 300 and 900 A.D.
• The Mayas lived in present-day southeast Mexico, Belize, and Guatemala.
• The Mayas were great traders and their cities were linked by roads paved with white cement.
The Mayas

53
Section 5-4
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• The Maya adapted their own hieroglyphs from the Olmecs.
• Mayan mathematicians came up with the idea of zero and a counting system based on 20.
• They also made cotton cloth and paper. • About 900 A.D., most Mayas abandoned
their cities and disappeared.
• No one knows exactly why.
The Mayas (cont.)

54
Section 5-5
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• Later, a third great civilization, that of the Aztecs, rose in Mesoamerica.
• About 1200 A.D., the Aztecs began moving south into the central valley of Mexico.
• By 1400 A.D., the Aztec Empire had 5 million people.
• Tenochtitlán, their capital, was built on an island in Lake Texcoco and was home to about 300,000 people.
• Causeways, or paved roads, connected the island to the mainland.
The Aztecs

55
Section 5-6
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• To feed the people, they filled in parts of the lake and dug drainage canals to create more farmland.
• To the Aztecs, war and religion were closely connected.
• The people worshiped two major gods–the rain god who stood for the peaceful life of farming and the sun god who stood for war and expanding empire.
• The Aztecs believed that the sun god needed human sacrifices.
The Aztecs (cont.)

56
Section 5-7
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• The Aztec Empire reached its height in the early 1500s under Montezuma II.
• Easily defeated by the Spaniards, the Aztecs lost their empire.
The Aztecs (cont.)

57
Section 5- Assessment 1
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
What were some of the accomplishments of the Olmec?
They farmed and built stone cities.
Section Assessment

58
Section 5- Assessment 2
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
How did the Aztec Empire come to an end?
The Spaniards, who had guns and horses, defeated the Aztecs.
Section Assessment

59
Section 5- Assessment 3
Section Assessment (cont.)
Drawing Conclusions Why do you think Mayan civilization ended?
Answers will vary but could include disease, conquering army, poor farming, and bad weather conditions.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

60
Section 5- Assessment 4
Section Assessment (cont.)
Draw a diagram like the one on page 140 of your textbook, and use it to summarize the accomplishments of the three great Mesoamerican civilizationsOlmec–planned cities, hieroglyphic writing, calendar; Maya–religious cities, cement roads for trade, hieroglyphic writing, idea of zero and counting system based on 20, ability to predict eclipses, 365-day calendar, production of cotton cloth and paper; Aztec–construction of huge empire, monumental architecture of Tenochtitlán, use of drainage canals and aqueducts
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

End of Section 5

62
Section 6-1
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information. Section 6 begins on page 140 of your textbook.
The Incas• About the same time the Aztecs moved
south into central Mexico, the Incas moved out from Peru.
• They established an empire that stretched along the west coast of South America for about 2,500 miles.
• By the 1500s, there were 12 million people in the Inca Empire.

63
Section 6-2
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• The Incas started out as farmers and shepherds.
• In 1438, the Inca ruler Pachacuti conquered several neighboring peoples and founded the Inca Empire.
• Pachacuti had a huge system of stone-paved roads built for military and government use.
History

64
Section 6-3
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• A ruler, known as the Inca, determined the way of life.
• Land belonged to the ruler and not to the people who worked it.
• Special accountants used quipus, or counting devices, to keep track of people and goods.
• The wealth of the Inca Empire was evident in the Inca’s extravagant surroundings.
Inca Way of Life

65
Section 6-4
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• His palace, the size of a town, had hundreds of rooms and thousands of servants.
• A desire for this wealth was part of the reason the Spaniards destroyed the Inca Empire in the early 1500s.
Inca Way of Life (cont.)

66
Section 6- Assessment 1
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
How big was the Inca Empire at its peak?
The Inca Empire had 12 million people.
Section Assessment

67
Section 6- Assessment 2
Section Assessment (cont.)
How did Pachacuti hold the Inca Empire together?
He ordered conquered peoples to worship the Inca sun god, made Quechua the official language, and moved people who had been living under Inca rule into newly conquered lands.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

68
Section 6- Assessment 3
Section Assessment (cont.)
Demonstrating Reasoned Judgment Suppose the Inca had the choice of keeping Pachacuti as their leader or electing a new one. Which choice do you think they would have taken? Explain.
Some people might have preferred to replace him with a less strict, less dictatorial leader. Others may have wanted to keep him as a leader since he provided well for them.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

69
Section 6- Assessment 4
Section Assessment (cont.)
Draw a diagram like the one on page 142 of your textbook, and use it to show the changes that Pachacuti brought to the Incan way of life.
before–made up of farmers and shepherds living in scattered villages
after–a large unified empire connected by roads and customs
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

End of Section 6

71
Chapter Summary 1
Chapter Summary & Study Guide• The Kushites and Egyptians influenced
each other through conquest and trade.
• The Aksumites destroyed Kush and later converted to Christianity.
• The kingdoms of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai built West African empires based on a trade in salt and gold.
• A population explosion led the Shona to build Zimbabwe in East Africa.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.

72
Chapter Summary 2
Chapter Summary & Study Guide (cont.)
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
• Kilwa and other coastal cities handled trade between Africa and Arabia, Persia, India, and China.
• The Olmec and the Maya invented many new ideas, including forms of writing and a calendar.
• The Aztec and the Inca built complex civilizations that lasted until the time of European arrival in the Americas.

End of Chapter Summary

74
Chapter Assessment 1
Understanding the Main Idea
How did Ghana gain control of West African trade routes?
by the use of iron swords and lances
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

75
Chapter Assessment 2
What was the effect of Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage?
News of Mansa Musa and Mali spread as far as Europe. Mansa Musa also met a Spanish architect while in Arabia and convinced him to help build a university in Timbuktu.
Understanding the Main Idea
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

76
Chapter Assessment 3
What was the main difference between the Mesoamerican civilizations that developed before and after 900 A.D.?
The earlier civilizations were peaceful, had rulers interested in learning, religion and trade; later civilizations were warlike, with religions marked by human sacrifice.
Understanding the Main Idea
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

77
Chapter Assessment 4
What did the Olmec contribute to other civilizations?
planned cities, hieroglyphic writing, a calendar
Understanding the Main Idea
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

78
Chapter Assessment 5
How did the Aztec treat the people they conquered?
The Aztecs made them pay tribute and sacrificed some of them to the sun god.
Understanding the Main Idea
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

79
Chapter Assessment 6
Understanding the Main Idea
Who directed and controlled the Incan way of life?
the ruler
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

80
Chapter Assessment 7
How do you think the development of African civilization might have been different if the Kushites did not develop iron-smelting?
Answers will vary.
Critical Thinking
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

81
Chapter Assessment 8
Why was trade important to the growth of African civilization?
Without trade, African civilizations would not have interacted.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
Critical Thinking

82
Chapter Assessment 9
Which Mesoamerican civilization would you choose to live in? Why?
Critical Thinking

83
Chapter Assessment 10
What contributions did early American civilizations make to present-day life in the United States?
Answers will vary.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
Critical Thinking

84
Chapter Assessment 11
Location Compare the maps of early empires found on page 135 and 141 of your textbook. What similarities in location of these civilizations can you find? What differences in location are there between the two areas?Similarities: both are contiguous, close to the Equator, and coastal; Differences: Mesoamerican empires stretched north and bordered the Pacific Ocean; African kingdoms stretched east and bordered the Atlantic and Indian oceans.
Geography in History
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

85
Chapter Assessment 12
You dig up pottery from a past civilization and know that it was made by the Olmec. What evidence helped you reach your conclusion?
The pottery is adobe clay, was found near the ruins of a city, contains kernels of corn, etc.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.

End of Chapter Assessment

87
History Online
Explore online information about the topics introduced in this chapter.
Click on the Connect button to launch your browser and go to the Human Heritage: A World History Web site. At this site, you will find interactive activities, current events information, and Web sites correlated with the chapters and units in the textbook. When you finish exploring, exit the browser program to return to this presentation. If you experience difficulty connecting to the Web site, manually launch your Web browser and go to http://www.humanheritage.glencoe.com

88
Global Chronology
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
750 B.C.Kushites conquer Egypt
500 B.C.Mayan civilization begins
200 A.D.Ghana founded

89
Global Chronology
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
1240 A.D.Kingdom of Mali established
700 A.D.Shona settle in Zimbabwe
1400 A.D.Aztec Empire prospers

90
People in History 2.1
A grandson or grandnephew of the warrior king Sundiata Keita, Mansa Musa guided Mali to its height of power. Under his rule, Mali grew to the size of western Europe and, in terms of gold, it outdid the wealth of Egypt. Mansa Musa used his large army to secure safe passage of travelers and traders through his empire and to keep order for nearly 25 years.
Mansa Musa IC. 1337 A.D.
West African Emperor

91
Fun Facts 1.1
One warrior-queen of Meroë, Amanirenas, challenged the Romans who seized Egypt after the death of Cleopatra. The Romans eventually drove Amanirenas back into Meroë, but she fought valiantly and her deeds are recorded in Greek and Roman histories of the time.
A Brave Queen

92
Fun Facts 5.1
Markets played an important part in the economic and social life of the Aztec. The market at Tlateloco was the largest in the ancient Americas. About 60,000 people may have visited the market each day.
Busy Markets

93
Then & Now 6.1
The Aztecs and Incas grew high-protein grains called amaranth and quinoa. Today these grains, native to the Americas, have become important in parts of India, Pakistan, Nepal, and China. Amaranth and quinoa, in the form of flour and cereals, have become common in U.S. health-food stores.
Growing Grains

94
Map Skills 1.1
Reading Latitude
• To measure distances north and south, mapmakers use imaginary lines on maps and globes.
• These are called lines of latitude and they run east and west around Earth.
• Lines of latitude are often called parallels because they never meet and remain the same distance from each other all the way around Earth.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
Continued on next slide.

95
Map Skills 1.2
• Latitude is measured in degrees, as shown by the symbol º.
• The Equator, which is a line of latitude, is marked 0º because all other lines of latitude are measured from it.
• One degree of latitude equals about 69 miles, or 110 kilometers.
• There are 90 lines of latitude from the Equator to each pole.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
Continued on next slide.
Reading Latitude

96
Map Skills 1.3
• Those lines north of the Equator are marked with an N.
• Those lines south of the equator are marked with an S.
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the information.
Continued on next slide.
Reading Latitude

97
Map Skills 1.4
Continued on next slide.
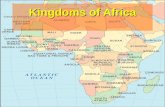
Study the map on page 135 of your textbook showing Early Africa. Then answer the questions that follow.
Reading Latitude

98
Map Skills 1.5
Which civilization was located closest to the Equator?
Mali
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
Continued on next slide.
Reading Latitude

99
Map Skills 1.6
Which city, Timbuktu or Napata, was located closest to the 20º N line of latitude?
Napata
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
Continued on next slide.
Reading Latitude

100
Map Skills 1.7
Which line of latitude runs through the center of the great trading civilization of Zimbabwe?
20º S
Click the mouse button or press the Space Bar to display the answer.
Reading Latitude

End of Custom Shows
End of Custom ShowsWARNING! Do Not Remove
This slide is intentionally blank and is set to auto-advance to end custom
shows and return to the main presentation.

End of Slide Show