Acute Cholecystitis in Cirrhotic Patients Seeking advice ... gs for rayong.pdf · Acute...
Transcript of Acute Cholecystitis in Cirrhotic Patients Seeking advice ... gs for rayong.pdf · Acute...

Acute Cholecystitis in Cirrhotic Patients Seeking advice from Surgeons
Taned Chitapanarux, MD
Chiang Mai University

Clinical Question
• Diagnosis?
• When is the optimal time for consultation or surgery?
• LC/OC?
• Clinical factors predict a successful laparoscopic surgical outcome?

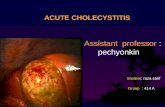
Acute Cholecystitis
• Inflammation of GB
• 90% of cases result from obstruction of cystic duct by GS or by biliary sludge
• 5-10%: acute acalculous cholecystitis
• Acute cholecystitis develops in 1-3% of patients with symptomatic GS

Clinical features of acute cholecystitis

Acute cholecystitis
Acute Calculous Cholecystitis
• Obstruction of the cystic duct from stone impaction
• Unresolved cystic duct obstruction, infection of the stagnant pool of bile
• Ischemia and necrosis of GB
• Gangrenous, emphysematous
Acute Acalculous Cholecystitis
• Obstruction of the cystic duct in the absence of frank stones
• Concentration of biliary solutes and stasis in GB
• Fulminant, gangrene (50%) and perforation (20%)
• Thickened gallbladder wall, with pericholecystic fluid

Pathogenesis of acute cholecystitis

Pathogenesis and risk factors for AAC

Pathological classification Edematous cholecystitis: 1st stage (2–4days) • Edematous GB wall with interstitial fluid, dilated capillaries and lymphatics.
Necrotizing cholecystitis: 2nd stage (3–5days) • Areas of hemorrhage and necrosis
• Elevated internal pressure
• Obstructed blood flow
• Vascular thrombosis and occlusion
Suppurative cholecystitis: 3rd stage (7–10days) • Intramural abscesses, pericholecystic abscesses: WBC infiltration
• Contract GB with thickened GB wall (fibrous proliferation)
Chronic cholecystitis: • Repeated occurrence of mild cholecystitis
• Mucosal atrophy and fibrosis of GB wall

Special forms of Acute Cholecystitis
• Acalculous cholecystitis
• Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
– Xanthogranulomatous thickening of GB wall
– Rupture of Rokitansky-Achoff sinus
– Granulomatous formation
• Emphysematous cholecystitis
– Gas-forming anaerobes infection

Advance forms and complications
• Perforation of GB: ischemia and necrosis of GB, tumor
• Biliary peritonitis
• Pericholecystic abscess
• Biliary fistula: large stone

Gallstone
• Cholesterol stone – Cholesterol and calcium
– Pure cholesterol
• Pigment stone – Black stone: hemolytic conditions and cirrhosis
– Brown stone (bile duct): biliary motility, bacterial infection

Natural History of Gallstones
• Asymptomatic gallstone patients are at low risk of developing symptoms. – 10% and 20% will become symptomatic within 5 and
20 years of diagnosis.
• The average risk of developing symptomatic gallstones is low (2.0-2.6% per year).
• Aging is the most significant factor: higher incidence of acute cholecystitis.
• Incidence of complications is 0.3% per year. • Risk for gallbladder cancer is 0.02%.
Attili AF, et al. Hepatology 1995; 21: 656-660.

Conditions Associated with GS
• Chronic hemolytic disease (sickle cell anemia, spherocytosis)
• Obesity • Ileal resection or disease • Cystic fibrosis • Chronic liver disease • Prolonged parenteral nutrition • Prolonged fasting or rapid weight reduction • Pregnancy • Abdominal surgery

Prevalence of Gallstone in CLD
0
10
20
30
40
50
Bouchier1969,autopsy
Iber1977,autopsy
Iber1990,autopsy
Fornari1990,ultrasound
Pre
vale
nce
of
galls
ton
e (
%)
CLD
Control
The incidence of GS in patients with cirrhosis is twice that general population • increased intravascular hemolysis • decreased GB motility and emptying

Gallstone prevalence in Cirrhotic according to Child-Pugh’s class
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Conte Fornari Elzouki
Child A
Child B
Child C

Diagnostic criteria for acute cholecystitis
A. Local signs of inflammation (1) Murphy’s sign (2) RUQ mass/pain/tenderness
B. Systemic signs of inflammation (1) Fever (2) elevated CRP (3) elevated WBC count
C. Imaging finding Imaging finding characteristic of acute cholecystitis
Suspected Dx: one item in A + one item in B Definite Dx: one item in A + one item in B+C Acute hepatitis, other acute abdominal disease and chronic cholecystitis should be excluded
TG 13

Diagnostic criteria for acute cholecystitis
In the critically ill, who may be intubated and sedated,
Unexplained fever
Leukocytosis
or Vague abdominal discomfort
may be the only clue to diagnosis acute cholecystitis.

Normal GB
Sonography Pencil-thin echogenic line GB wall thickness depends on the degree of GB distention Pseudothickening: postprandial state CT scan Thin rim of soft-tissue density Enhances after contrast injection

Thickened GB wall
• US: GB wall > 3 mm with a layered appearance
• CT: a hypodense layer of subserosal edema that mimics pericholecystic fluid

GB wall thickening Cholecystitis Liver cirrhosis
• acute/chronic Hepatitis
• acalculous CHF, Rt-sided
• xanthogranulomatous Renal failure
GB carcinoma Pancreatitis
Adenomyomatosis
Edema of GB wall • elevated portal venous pressure • elevated systemic venous pressure • decreased intravascular osmotic pressure

Criteria for AAC
Ultrasound
Major
GB thickening (>3mm)
Striated GB (edema)
Sonographic Murphy sign
Pericholecystic fluid (no ascites or hypoalbuminemia)
Mucosal sloughing
Intramural gas
Minor
GB distention (>5mm in transverse diameter)
Echogenic bile (sludge)
CT scan
Major
GB thickening (>3mm)
Subserosal halo sign (intramural lucency caused by edema)
Pericholecystic fat infiltration
Pericholecystic fluid
Mucosal sloughing
Intramural gas
Minor
GB distention
High-attenuation bile (sludge)
Two major or One major and two minor criterion

Severity Grading for Acute Cholecystitis
• Grade III (severe ) acute cholecystitis
• Grade II (moderate) acute cholecystitis
• Grade I (mild) acute cholecystitis

Severity Grading for Acute Cholecystitis
Grade III (severe ) acute cholecystitis Associated with dysfunction of any one of the following organs/ systems
1. Cardiovascular Hypotension (DA ≥ 5mcg/min or any dose of NE)
2. Neurological Decrease level of consciousness
3. Respiratory PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 300
4. Renal Oliguria, Cr > 2.0 mg/dl
5. Hepatic PT-INR > 1.5
6. Hematologic Platelet count < 100,000/mm3

Severity Grading for Acute Cholecystitis
Grade II (moderate) acute cholecystitis Associated with any one of the following conditions
1. Elevated WBC > 18,000/ mm3
2. Palpable tender mass in RUQ
3. Duration of complaints > 72 hr.
4. Marked local inflammation: gangrenous cholecystitis, pericholecystic abscess, hepatic abscess, biliary peritonitis, emphysematous cholecystitis

Severity Grading for Acute Cholecystitis
Grade I (mild) acute cholecystitis
• Does not meet the criteria of “Grade III” or “Grade II”
• Defined as acute cholecystitis in a healthy patient with no organ dysfunction and mild inflammatory changes in GB
• Making cholecystectomy a safe and low-risk operative procedure

Management of acute cholecystitis
• Supportive care with IVFs, bowel rest and antibiotic
• Almost half of patients have positive bile culture
• E. coli is the most common organism
• Enterobacteria family (e.g., a second-generation cephalosporin or a combination of a quinolone and metronidazole); activity against enterococci is not required.
• Cholecystectomy is the definite therapy.

Cholecystectomy
1886: First open cholecystectomy
First half of 20th century: supportive care with delayed open cholecystectomy
1970: Early open cholecystectomy (Golden 72 hr.)
1980: LC (major bleeding, wound infection, bile leak, bile injury)
Mini-laparoscopic cholecystectomy, single-incision laparoscopic surgery

LC vs. OC
0
10
20
30
40
50
LC OC
Mo
rbid
ity
rat
e (
%)
Primary endpoint: hospital mortality, morbidity, length of hospital stay
16% of LC need conversion to OC
P= 0.005
Lancet 1998

Timing of Surgery
• Early surgery:
– within 72 hr. after admission or onset of symptom
• Delay surgery:
– supportive care followed by discharge and readmission in 6-12 weeks for surgery
• Base on patient’s overall risk of surgery
• American society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) scale is a guide for decisions on surgery.

Early VS Delay LC
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
Early Delay
Complication
Conversion
Gangrenous
American Surgery 2000
• Increase chance of gangrene of GB after 72 hr. • If > 72 hr., risk of conversion to open cholecystectomy

Clinical predictive factors
• CRP, duration of symptoms, WBC count: preoperative parameters that predict the severity of inflammation
• Parameters determine type of surgery: CRP, WBC, ASA class, duration of symptom, age
• Surgery within 48 hr. of admission: successful LC.

Probability of GS-related event by Time From Discharge
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
6 wk 12 wk 6 mo 1 y 2 y 3 y 4 y 5 y
• Of 25,397 patients with AC, 10,304 (41%) did not undergo cholecystectomy on the first admission.
• 30%: biliary tract obstruction or pancreatitis, greater morbidity potential than initial cholecystitis episode.
14
19
29
Delayed elective cholecystectomy

Age and GS-related event (the first year following discharge)
• Risk of GS-related event is highest for younger patients (18-34 years old). • Early cholecystectomy in the nonelderly.
J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2013

Preoperative Length of Stay before Cholecystectomy
Outcome variable
0 d (n=2620) 1 d (n=1757) 2 d (n=498) 3 d (n=204) >4 d (n=189)
30-d mortality 0.8% 0.9% 1.8% 2.0% 5.3%
30-d morbidity 6% 7.6% 12.7% 15.2% 19.1%
Open cholecystectomy
16.3% 21.3% 28.9% 30.9% 37.0%
Operative time (min)
82 87 89 91 98
• No significant association between timing of operation and 30-d postoperative mortality or overall morbidity
• Patients who underwent operation later were more likely to require an open procedure and longer postoperative LOS.
Immediate cholecystectomy is preferred for patients who require hospitalization for AC.
J Trauma Acute Care Surg, 2013

Cholecystectomy on the same day of admission (same-admission hereafter)

Management of Acute Cholecystitis
TG 13

Cirrhosis and Cholecystectomy (Past)
• 1980, rate of morbidity and mortality in patients with cirrhosis: 35%, 25%
• Postoperative death: blood loss, sepsis, liver failure
Cirrhosis was contraindication for LC Garrison, 1983; Schwartz, 1981

Cirrhosis and Cholecystectomy (Today)
• Favorable morbidity and minimal to no mortality in patients with Early cirrhosis (CTP class A and B) – Less operative blood loss, shorter operative time, decrease
LOS
• Advanced cirrhosis (CTP class C) – Lack of controlled trial, Poor outcome
– Replacement of clotting factors to minimize intraoperative bleeding
– Care when placing trocars to avoid the "caput medusa" of large collateral vessels in the abdominal wall
– Percutaneous cholecystostomy, cystic duct stent
Puggioni, 2013

Cholecystectomy
• CTP class A and B
– Symptomatic gall stone and/or acute cholecystitis
– LC by experienced surgeons
• CTP class C
– Surgery should be deferred until liver disease is under better control
– Alternative intervention: percutaneous cholecystectomy or endoscopic stenting

Summary points
• AC is the most often caused by GS
• Patients suspected of having AC should be referred to hospitalization immediately
• First line treatments include fasting, IV fluid and analgesia
• Cholecystectomy within 24-48 hr. of admission (early) is preferable to delayed or interval surgery
• PC is a safe alternative to cholecystectomy for very ill patients or those unfit to undergo surgery

THANK YOU