4. hydrops fetalis; pedatric pathology
-
Upload
krishna-tadepalli -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
291 -
download
9
Transcript of 4. hydrops fetalis; pedatric pathology

Pediatric PathologyPediatric Pathology
Dr. Krishna Tadepalli, MD, www.mletips.com
1

4. Hydrops Fetalis4. Hydrops Fetalis
Dr. Krishna Tadepalli, MD, www.mletips.com
2

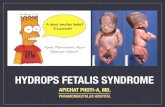
Fetal Hydrops• Accumulation edema fluid; Non-immune causes (CVS,
Chromosomal and Fetal anemia) are MC; Hydrops fetalis = generalized edema;
• Immune type
• Nonimmune type
• Three major causes – parvovirus B19– α-thalassemia – cardiovascular defects, chromosomal anomalies, and fetal anemia
Dr. Krishna Tadepalli, MD, www.mletips.com
3

Fetal Hydrops• Accumulation edema fluid; Non-immune causes (CVS, Chromosomal and Fetal
anemia) are MC; Hydrops fetalis = generalized edema;
• Immune type
Dr. Krishna Tadepalli, MD, www.mletips.com
4

Fetal Hydrops• Immune type• MC is Rh (mainly D Antigen) incompatibility between mother and fetus• Incidence is decreased in urban societies ( why?)
• Factors influence immune response =
– Concurrent ABO incompatibility protects
– depends on the dose of immunizing antigen (> 1 ml of Rh-positive fetal red cells)
– subsequent pregnancy has the risk
• Pathology
– Anemia due to hemolysis (extramedullary hematopoiesis )
– Jaundice due to hemolysis ( unconjugated bilirubin) kernicterus
– hypoxic injury to the heart and liver cardiac decompensation and failure generalized edema and anasarca
Dr. Krishna Tadepalli, MD, www.mletips.com
5

Fetal Hydrops• Nonimmune type (table-10.4)• Three major causes (cardiovascular defects, chromosomal anomalies, and fetal
anemia ;- α- thalassemia &parvovirus B19)
• Morphology– stillborn, die within the first few days, or recover – Pale fetus and placenta (due to fetal anemia)– liver and spleen are enlarged ( due to congestion from cardiac failure)
– bone marrow hyperplasia of erythroid precursors & extramedullary hematopoiesis (compensatory)
– Erythroblastosis fetalis =large numbers of immature red cells, including reticulocytes, normoblasts, and erythroblasts in peripheral circulation
– blood bilirubin level greater than 20 mg/dL in term infants– Kernicterus =most serious; brain is enlarged and edematous and bright yellow in
color; affects mainly basal ganglia, thalamus, cerebellum, cerebral gray matter, and spinal cord
• Clinical = vary with the severity of the disease from Hepatosplenomegaly to Kernicterus
• Rx = for mild cases -phototherapy (visual light oxidizes unconjugated bilirubin ) and total exchange transfusion for severe cases
Dr. Krishna Tadepalli, MD, www.mletips.com
6

Hydrops FetalisHydrops Fetalis
Dr. Krishna Tadepalli, MD, www.mletips.com
7

KernicterusKernicterus
Dr. Krishna Tadepalli, MD, www.mletips.com
8

9

9