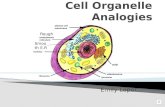
Where found Organelle Plants Animals Analogy Function...
Transcript of Where found Organelle Plants Animals Analogy Function...

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2 Day 6—Major Cell Organelles
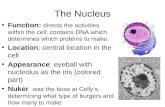
1. Without this organelle, the cell would be unable to repair itself or continue to grow.
2. Without this organelle, if a plant cell lost water, it would shrink.
3. Celery is hard to bend partly because of this organelle.
4. Helps the cell maintain homeostasis by selectively allowing certain substances into or out of the cell.
5. A. What color is a chloroplast?
B. Why?
6. The nucleus from Cell A is removed and replaced by the nucleus from Cell B. Afterwards, which
cell’s characteristics will Cell A have?
7. A cell needs certain molecules to function. These come from outside the cell.
A. What organelle will allow or disallow these molecules to get in?
B. Which organelle moves these molecules around the cell.
C. Which organelle will make these molecules into proteins?
D. Where the plans for making the proteins is stored (and comes from)?
E. Which organelle makes energy for these molecules to be used?
F. Which organelle will then moves the finished proteins around the cell?
G. Which organelle will break up these materials when the cell is done with them?
8. Plants actually have two organelles that make energy. Which ones?
9. If this organelle is removed, a cell loses its ability to function.
Where found
Organelle Plants Animals Analogy Function Looks like
Nucleus x x brain holds DNA (blueprint) The big blob in the middle
Ribosomes x x factory makes proteins from mRNA's blueprint little dots (chocolate chips)
Mitochondria x x energy plant makes ATP (energy) for cell hot dog with mustard
chloroplast x green house performs photosynthesis stacked M&M's in a bubble
cell membrane x x skin protects cell and allows passing
of materials into cell at the edge of the cell
cell wall x walls of a room like skeleton - gives rigidity -
holds up a plant cell very edge of a plant cell
lysosomes x x clean up crew breaks down left over and
worn out material
Central vacuole
x toilet holds waste products;
maintains water pressure in cell.
Golgi apparatus (or complex)
x x post office redistributes materials to rest of cell Stack of pancakes
Endoplasmic reticulum
x x Conveyor belt for assembly line
moves materials from ribosomes to golgi
Folded fruit roll up

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2
Respiration vs. Photosynthesis
6 12 6 2 2 2C H O + O CO + H O + energy→2 2 6 12 6 2CO + H O + energy C H O + O→
Energy in
Energy out
(Heat)
Oxygen
Carbon Dioxide
O2
CO2
Out
In
Photosynthesis
and
Respiration Water vapor
Photosynthesis
Glucose
(plant sugar)
Respiration
Glucose
(food)
In photosynthesis plants use
sunlight, carbon dioxide and water
to produce oxygen and glucose
(plant sugar). Plants breathe in
carbon dioxide an give off oxygen.
In respiration animals burn
glucose and oxygen to produce
carbon dioxide, water, and heat.
Respiration is a Combustion Reaction
because it uses oxygen and makes water! Plants do respiration, too – cellular respiration,
making ATP in a plant cell’s mitochondria!
Out
In
10. Photosynthesis or Respiration?
A. ___ Occurs in the lungs of animals.
B. ___ Occurs only in plants.
C. ___ Carbon dioxide is a product
D. ___ Takes in sunlight.
E. ___ Uses glucose as energy.
F. ___ Carbon dioxide is a reactant.
G. ___ Produces oxygen.
H. ___ Produces water.
I. ___ Occurs in both plants and animals.
J. ___ Makes glucose.
K. ___ Uses water as a reactant.
These next questions are still from the above notes. Read carefully.
11. Where is ATP created in a cell?
12. What is the proof that respiration is a combustion reaction?
Day 6B — Respiration vs. Photosynthesis

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2
Inserted: Cell membrane helps maintain homeostatis.

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2
1. Which of the badgers below are most closely related?
A. North American Badgers – Taxidea taxus B. Palawan Badger – Mydaus marchei
C. Eurasian Badgers – Meles meles C. Javan Stink Badger – Mydaus javanensis
2. Which are more closely related: organisms of the same family or same class?
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Most general Most specific.
Less related More closely related
The farther to the right that the words are the same,
the closer the species are:
Roses and Humans - different Kingdoms
Worms and Humans - different Phylums
Eagles and Humans – different Classes
Horses and Humans – different Order
Monkeys and Humans – different Family
Neanderthals and Humans – different Species
(but very closely related)
All scientific names have two parts; genus and species:
Ex: Human (Homo sapiens):
Genus Species
Kingdom # of cells Characteristics
Prokaryotes (no nucleus)
Archeabacteria unicellular (1) Live in extreme environments (very hot, no oxygen)
Eubacteria unicellular (1) common bacteria, live on and around us/ some are beneficial (like in our stomachs).
Plants multicellular sexual or asexual/ don't move/ cell wall of cellulose/
true roots, stems, leaves/ Autotrophs (producer own food)
Animals multicellular move/ sexual reproduction/ heterotrophs (eats other organisms)
Fungi mostly
multicellular sexual or asexual reproduction/ cell wall of chitin (like mushrooms)/ decomposers/ Heterotrophs or saprobes (digests outside of body)
Protista multi or uni sexual or asexual reproduction/ animal or plant-like/
auto or heterotrophs/ no cellulose or true leaves or stems
Eukaryotes (with a nucleus)
Day 7A—Taxonomy/ Kingdoms
3. Which kingdom (might be more than one)?
A. Flat worms.
B. Ferns.
C. A bacteria that lives in a thermal vent at the bottom of the ocean.
D. Made up of decomposers with a spongy cell wall.
E. Makes there own food.
F. Live with humans and even help with digestion.

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2 Day 7B—Cellular Processes
4. If Tank A is full of water and Tank B is empty, which way does the
water flow?
5. If Tank A has a pressure of 20 pascals and Tank B has a pressure of
55 Pascals, which way does air flow?
/ote: ALL of nature works in this way: thing move from high to low. Objects
roll down hill (high to low). Air moves from high pressure to low pressure (like
letting out a filled balloon). It requires energy to go the opposite way.
6. A) In which region is there more table salt (by percent)?
B) In which region is there more water (by percent)?
C) If there is a semi-permeable membrane around A than allows only water to flow,
does water flow from A to B or from B to A?
D) Over time, does A swell (get bigger) or shrink (get smaller)?
E) This flow of water is known as:
F) If the salt were moving, it would be known as d_________.
(/ote: This is why a fresh water fish (A) would die if placed in salt water (B).
It would lose water and shrink.)
Diffusion—Movement of molecules from high to low concentration (how a smell spreads out around a room).
Osmosis—Movement of water thru a membrane from an area of high water concentration to low.
Semi-permeable membrane—Allows some things thru, but not others (cell wall does this).
Homeostasis— constant, stable internal conditions when the cell is able to thrive. (When it is “happy”.) All the above help
maintain homeostasis in a cell. Humans maintain homeostasis by eating and drinking, etc.
Tank A Tank B
Connecting
hose
30%
NaCl
20%
NaCl
7. Give two examples of humans maintaining homeostasis. (Do not use the same examples as above.)
8. We usually think that if an organism moves, then it is alive. Really the organism is trying to maintain
homeostasis. Give two examples of an organism moving to maintain homeostasis.

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2
9. Give two examples of humans maintaining homeostasis. (Do not use the same examples as above.)
- keeping warm
- sleeping when tired
- defending our selves
- vomiting when sick (trying to expel poisons)

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2
4. Will it cause a mutation of the species?
A. _____A gene mutation occurs when a skin cell is replicated.
B. _____A mutation happens during meiosis.
C. _____ If the sequence is copied perfectly.
D. _____ If the sequence is off by one nitrogen base when making a sperm cell.
E.______ If the mutation occurs during mitosis.
F.______ If the mutation ends up in a gamete cell.
5. If the gamete cell has 28 chromosomes, how many chromosomes are in the zygote?
T
G
C
G
A
DNA DNA
A
C
G
G
T
DNA RNA
D.A – Found in the nucleus of all cells. Contain the characteristics of a cell.
P
D
P
D
A T
C G
P
D
P
D
P
R
P
R A U
C G
P
D
P
D
D.A r.A
DNA has two sides (double helix [ladder])
Lad
der
sid
es: Phosp
hat
e
and d
eoxyribose
(su
gar
)
/ucleotide
(P, D, and a
nitrogen base)
4 nitrogen bases.
Always pair: A&T;
C&G. Sequence con-
tains the genetic code.
RNA has only 1 side.
It has Uracil instead of Thymine.
Lad
der sid
es: Phosp
hate
and a rib
ose su
gar.
Gametes—Egg or sperm; has only 1/2 the chromosomes of a full cell.
Zygote—fertilized egg. Has the full set of chromosomes.
Mitosis—Cell division for regeneration (exact copies to replace aging body cells).
Meiosis—Cell division for sexual reproduction: produces gametes (egg or sperm).
DNA Mutation—Occurs when the nitrogen base sequence is copied wrong.
Doesn’t cause a permanent mutation unless it occurs in the gametes and is passed
on to the offspring.
1. A. On the diagram at the right circle each individual nucleotide.
B. How many nucleotides are there in the diagram?
2. DNA, RNA (could be both).
3. Given the following genetic
codes give the paired sequence.
A. ______Contains nitrogen bases.
B. ______Found in the nucleus of a cell.
C. ______Double helix structure.
D. ______A goes with T
E. _____ Has a sugar on its side.
F. _____ Has uracil
G. _____ Has a phosphate backbone
H. _____ Has ribose as a sugar
Day 8—D.A/R.A Structure

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2
4. Will it cause a mutation of the species?
A. N ___A gene mutation occurs when a skin cell is replicated.
B. Y ___A mutation happens during meiosis.
C. N ___ If the sequence is copied perfectly.
D. Y ___ If the sequence is off by one nitrogen base when making a sperm cell.
E. N ___ If the mutation occurs during mitosis.
F. Y ___ If the mutation ends up in a gamete cell.
5. If the gamete cell has 28 chromosomes, how many chromosomes are in the zygote?
52 chromosomes (28 from egg/ 28 from sperm)
T
G
C
G
A
A
C
G
C
T
DNA DNA
A
C
G
G
T
U
G
C
C
A
DNA RNA
D.A – Found in the nucleus of all cells. Contain the characteristics of a cell.
P
D
P
D
A T
C G
P
D
P
D
P
R
P
R A U
C G
P
D
P
D
D.A r.A
DNA has two sides (double helix [ladder])
Lad
der
sid
es: Phosp
hat
e
and d
eoxyribose
(su
gar
)
/ucleotide
(P, D, and a
nitrogen base)
4 nitrogen bases.
Always pair: A&T;
C&G. Sequence con-
tains the genetic code.
RNA has only 1 side.
It has Uracil instead of Thymine.
Lad
der sid
es: Phosp
hate
and a rib
ose su
gar.
Gametes—Egg or sperm; has only 1/2 the chromosomes of a full cell.
Zygote—fertilized egg. Has the full set of chromosomes.
Mitosis—Cell division for regeneration (exact copies to replace aging body cells).
Meiosis—Cell division for sexual reproduction: produces gametes (egg or sperm).
DNA Mutation—Occurs when the nitrogen base sequence is copied wrong.
Doesn’t cause a permanent mutation unless it occurs in the gametes and is passed
on to the offspring.
1. A. On the diagram at the right circle each individual nucleotide.
B. How many nucleotides are there in the diagram? four
2. DNA, RNA (could be both).
3. Given the following genetic
codes give the paired sequence.
A. Both__Contains nitrogen bases.
B. DNA _Found in the nucleus of a cell.
C. DNA _Double helix structure.
D. DNA _A goes with T
E. Both _ Has a sugar on its side.
F. RNA_ Has uracil
G. Both _ Has a phosphate backbone
H. RNA_ Has ribose as a sugar
D.A/R.A Structure—KEY

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2 Day 9A—Protein Synthesis
A
B
C
E F
D
G
U C A G
U
UUU Phenylalanine
UCU
Serine
UAU Tyrosine
UGU Cysteine
U
UUC UCC UAC UGC C
UUA Leucine
UCA UAA Ochre UGA Opal A
UUG UCG UAG Amber UGG Tryptophan G
C
CUU
Leucine
CCU
Proline
CAU Histidine
CGU
Arginine
U
CUC CCC CAC CGC C
CUA CCA CAA Glutamine
CGA A
CUG CCG CAG CGG G
A
AUU
Isoleucine
ACU
Threonine
AAU Asparagine
AGU Serine
U
AUC ACC AAC AGC C
AUA ACA AAA Lysine
AGA Arginine
A
AUG Methionine ACG AAG AGG G
G
GUU
Alanine
GCU
Alanine
GAU Aspartic acid
GGU
Glycine
U
GUC GCC GAC GGC C
GUA GCA GAA Glutamic acid
GGA A
GUG GCG GAG GGG G
First Nitrogen Base (1st letter)
Second Nitrogen Base (2nd letter)
Third
Nitro
gen Base (3
rd le
tter)
3. The picture at the left shows the steps in protein synthesis in an
animal cell.
1. Translation (TL) or Transcription (TS)?
A. ____ When mRNA is turned into tRNA.
B. ____ When DNA is turned into mRNA.
C. ____ Occurs in the nucleus.
D. ____ Occurs at the ribosomes.
2. The three nitrogen base code that tells the r___________ which a_______ a______ to make is called a:
A. The double coiled molecule at letter A is called the
________.
B. The double coiled molecule is unzipping and giving its
code to the single stranded molecule at letter B. This
single stranded molecule is the ________.
C. The process in which molecule A becomes molecule C
is called t______________.
D. Molecule F is called the ________.
E. When D becomes F is called t______________.
F. Letter E shows the chaining of amino acids to make a
p____________.
G. Two of the cell’s major organelles are shown in grey.
i. A, B, and C are in the _____________.
ii. G shows the ____________.
4. From the codon chart at
the left, what amino acid
comes from the follow-
ing codons:
i. CAG:
ii. AGC:
iii. GUA:
Transcription: Process in which DNA is copied into mRNA. (Before it can ride it must transcribe.)
Translation: Process in which proteins are made from tRNA. (Before it can create it must translate.)
Ribosomes: Cell organelle where proteins are created.
Amino Acids: Building blocks of proteins.
Codon: Code of tree nitrogen bases that tells the ribosome what amino acid to make. Ex. AGA

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2 Day 21—Body Systems
System Function Organs
Circulatory system moves water, oxygen, and nutrients
around the organism heart, veins, arteries, capillaries
Digestive System breaks down food to be absorbed by body. mouth, teeth, throat, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines
Nervous system interprets and sends information
throughout the organism, motor function. brain, spinal cord, nerves (neurons)
Endocrine System secretes hormones to regulate
body functions. testis and ovaries (and others)
Reproductive System produces egg and sperm to propagate (continue) species.
genitals, testicles, ovaries
Integumentary System protects from external environment; skin (also attachments like hair and nails)
Skeletal system supports body, place for muscle attachment,
protects organs bones, ligaments (attachments),
cartilage (nose)
Respiratory System used to exchange CO2 and O2
between blood and air. nose, mouth, wind pipe (trachea), lungs
Muscular system used for locomotion, support, and protection muscles, tendons (for attachment)
Excretory/ Urinary system
used to remove waste products from organism
bladder (storage tank), kidneys (filter), colon
Immune System protects from and fights infections white blood cells, skin (as a barrier)
1. Which body system?
A. The only system that has completely different parts
for males and females.
B. Surrounds the entire body.
C. Attacked by the AIDS virus.
D. Protects your brain.
E. Moves the bones.
F. Stomach and intestines.
G. Causes you to feel anxious.
H. A bird’s feathers.
I. Protects your bones.
J. Helps you get well from the flu.
K. Removes unabsorbed food.
L. Is like the cell membrane for a cell.
M. Makes decisions for the body.
In addition to their primary functions, most body systems interrelate and aid other systems.
B
A
C
2. Which four systems does the heart transport for?
3. Which two systems have been opened when you bleed?
4. Large muscles in the extremities of the body (arms and legs) surround veins and
arteries. When these muscles contract, they squeeze veins and arteries, helping
which system?
5. How does the skin help the immune system?
6. How is the skin part of the nervous system?
7. Circulatory systems can be open or closed. Which do we have?
8. Amphibians allow oxygen thru their skin. Which system is this helping?
9. Some muscles are autonomous (you don’t control them). Give two examples.
10. In the diagram at the left, identify the three organs.
A. B. C.

cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2010, C. Stephen Murray
Name: _____________________
Period: _____________________ Objective 2 Day 21—Body Systems—Key
System Function Organs
Circulatory system moves water, oxygen, and nutrients
around the organism heart, veins, arteries, capillaries
Digestive System breaks down food to be absorbed by body. mouth, teeth, throat, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines
Nervous system interprets and sends information
throughout the organism, motor function. brain, spinal cord, nerves (neurons)
Endocrine System secretes hormones to regulate
body functions. testis and ovaries (and others)
Reproductive System produces egg and sperm to propagate (continue) species.
genitals, testicles, ovaries
Integumentary System protects from external environment; skin (also attachments like hair and nails)
Skeletal system supports body, place for muscle attachment,
protects organs bones, ligaments (attachments),
cartilage (nose)
Respiratory System used to exchange CO2 and O2
between blood and air. nose, mouth, wind pipe (trachea), lungs
Muscular system used for locomotion, support, and protection muscles, tendons (for attachment)
Excretory/ Urinary system
used to remove waste products from organism
bladder (storage tank), kidneys (filter), colon
Immune System protects from and fights infections white blood cells, skin (as a barrier)
1. Which body system?
A. The only system that has completely different parts
for males and females. Reproductive
B. Surrounds the entire body. Integumentary (skin)
C. Attacked by the AIDS virus. Immune
D. Protects your brain. Skeletal
E. Moves the bones. Muscular
F. Stomach and intestines. Digestive
G. Causes you to feel anxious. Endocrine
H. A bird’s feathers. Integumentary (skin)
I. Protects your bones. Muscles
J. Helps you get well from the flu. Immune
K. Removes unabsorbed food. Excretory
L. Is like the cell membrane for a cell. Integumentary
M. Makes decisions for the body. /ervous
In addition to their primary functions, most body systems interrelate and aid other systems.
B
A
C
2. Which four systems does the heart transport for?
Digestive, Respiratory, Immune, Urinary, Endocrine
3. Which two systems have been opened when you bleed? Integumentary, Circulatory
4. Large muscles in the extremities of the body (arms and legs) surround veins and
arteries. When these muscles contract, they squeeze veins and arteries, helping
which system? Circulatory system (muscles help pump blood in the legs and arms)
5. How does the skin help the immune system? As a barrier. Keeps stuff out of body.
6. How is the skin part of the nervous system? Sensory—feeling textures, temperature,
pressure...
7. Circulatory systems can be open or closed. Which do we have? Closed
8. Amphibians allow oxygen thru their skin. Which system is this helping? Respiratory
9. Some muscles are autonomous (you don’t control them). Give two examples.
Heart, lungs, muscles in intestines.
10. In the diagram at the left, identify the three organs.
A. Trachea (wind pipe) B. Lungs C. Intestines (small)