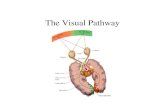
Visual pathway
-
Upload
dr-agarwals-group-of-eye-hospital -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
7.554 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Visual pathway

VISUAL PATHWAY
Dr.S.SoundariConsultant Ophthalmologist
Dr Agarwal’s Eye HospitalChennai

Optic nerve is an outgrowth of the brain
Its fibers posses no neurolemmal cells
Surrounded by meninges unlike any peripheral nerves
Both the primary and second order neurons are in the retina.

VISUAL PATHWAY



Optic nerve
Intraocular part
Intraorbital part
Intracanalicular part
Intracranial part












OPTIC NERVE LESION &
FIELD DEFECTS

Optic nerve field defects
Central scotoma
Enlargement of blind spot
Arcuate field defects
Altitudinal field defects

Paillomacular bundle
Macular fibres enter the temporal aspect of the disc. Defect can lead to
Central scotoma
Centrocecal scotoma
Paracentral scotoma

Causes for central scotoma
Demylineation[retrobulbar neuritis]
Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy
Toxins- tobacco,lead,alcohol,methanol
Vitamin B12 deficiency


Enlargement of blind spot

Altitudinal field defect
Ischaemic optic neuropathy
Branch retinal artery occlusion
Inferior retinal coloboma


CHIASMAL LESION &
FIELD DEFECTS

Chiasma
Lower nasal fibres cross low and anteriorly
Upper nasal fibres cross high and posteriorly
Macular fibres also cross in the posterior part of the chiasm.


Location of chiasma
Central fixation -80%- above the sella
Pre fixed chiasm-10%-located anteriorly-
so pitutary tumour involves the optic tract first [lower temporal fields first]
Post fixed chiasm-10%-located posteriorly- so optic nerve gets involved first[upper temporal fields first]



Pitutary adenoma
Visual fields ; bitemporal hemianopia,junctional scotoma,
bitemporal hemianopic scotomaColour vision; early red deficitVisual acuity tends to reduceOptic disc- bow tie atrophy rarely papilloedemaExtraocular movements: cranial nerve palsies,see saw nystagmus,spasm nutans.

hemifield slip- due to the failure of controlling phoria by fusion.
Post fixation blindness.





Pseudo bitemporal hemianopia
Bilateral sectoral retinitis pigmentosa
Tilted disc
Bilateral inferotemporal retinoschsis.

OPTIC TRACT LESIONS &
ITS FIELD DEFECTS

OPTIC TRACT
Carries ipsilateral temporal fibres and controlateral nasal fibres and pupillary fibres.
So right optic tract lesion will cause left homonymous hemianopia


ASSOCIATIONS
Controlateral pyramidal signs.
Incongruous homonymous hemianopia.
Wernicke's hemianopic pupil
Optic atrophy

OPTIC RADIATION AND ITS FIELD DEFECTS

OPTIC RADIATIONS
The corresponding retinal elements lie progressively closer, so congruous hemianopia.
Passes through the temporal lobe and pareital lobe and ends in the visual cortex.

TEMPORAL LOBE
Controlateral congruous homonymous superior quadrantanopia[pie in the sky]
Controlateral hemisensory disturbance
Mild hemiparesis
Paraxysomal olfactory and uncinate fits.
Formed visual hallucinations
Seizures and receptive dysphasia.

Pie in the sky

PAREITAL LOBE
Controlateral congruous homonymous inferior quadrantanopia[pie on the floor]
Visual perception difficulties
Right-left confusion
Acalculia
Assymmetric OKN.[OKN response diminished towards the side of the lesion.]

Pie on the floor

Striate calcarine cortex
Congruous homonymous hemianopias with macular sparing, macular involvement alone.
Formed visual hallucinations.
Anton's syndrome[ denial of blindness]
Riddoch phenomenon



THANK YOU