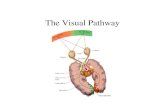
Overview of Visual Pathway and Processing
-
Upload
christiane-riedinger -
Category
Education
-
view
3.018 -
download
0
Transcript of Overview of Visual Pathway and Processing

Ganglion cells Bipolar cells LGN Visual Cortex
V1V2V3V4V5V6V7
Dorsal pathway: Where?To post. parietal cortexMOTION (+ motion illusions)
Ventral pathway: What?To inferior temporal cortexColour and form (+ illusory contours)
Overview of Visual Processing
= 4C-alpha, simple cell?
= 4C-beta, complex cell?
light
rods and cones
horizontal cellsbipolar cellsamacrine cells
ganglion cells
(onto optic nerve)
The retina:
Lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus:
1* visualcortex:
Midget
Amacrine?+?
Parvocellular cellsmajority, smaller receptive fields, slower, colour vision, sustained response
Magnocellular cells larger receptive fields, convergence, faster, more sensitive, detect motion, transient reponse
4 parvocellular layers
2 magnocellular layers
spiny stellate neurons4th layer of sublayer A
spiny stellate neurons,4th layer of sublayer B
LGN (optic radiation)
What?
Where?
http://www.circadian.org/biorhyt.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two-streams_hypothesis

Cortical columnscortical column (somatosensory):a vertical column of the cortical layers that has a near identical receptive field, but each layer corresponds to a different modality.
orientation column: is a vertical column in which each layer displays the same orientational preference for the stimulus, every 1mm a different orientation
ocular dominance:0.5mm wide cortical strips that prefer input from either retina
hypercolumn: 1-2mm^2 cortical column responding to all orientations of a stimulus, both retinae and performing colour analysis of differently sized visual fields
tiger stripe:organisation of ocular dominance columns
pinwheels:organisation of orientation columns
amblyopia: disorder of the visual system resulting from a deficiency in optic information from one eye reaching the cortex, which results in cortical development that makes it impossible to recover the function
http://www.pnas.org/content/102/11/4158/F2.expansion.html
http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Consciousness_Studies/The_Neuroscience_Of_Consciousness