Vertebral Column
description
Transcript of Vertebral Column

Vertebral Column

Do NowType 2 Writing4 minutes to write 5 things from last class

SpineThe spine (vertebral column) spans from the
base of the spine, all the way to the pelvisFunction – Major core support and protects the
spinal cordCurvature
Kyphosis (hunch back) Lordosis

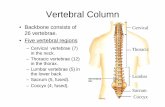
Spine24 single vertebrae make up the spine
An additional 2 fused bones at the bottom (sacrum and coccyx) help provide a flexible curved structure
What are the 3 different types of vertebrae? Cervical Vertebrae Thoracic Vertebrae Lumbar Vertebrae

Cervical Vertebrae7 Cervical Vertebrae
C1 – C7
Superior portion of the spineC1 and C2 are commonly referred to as…
Atlas Axis
Smaller than the rest of the vertebrae

Thoracic Vertebrae12 Thoracic Vertebrae
T1 – T12
The only vertebrae that articulate with the ribsBody of the Vertebrae is slightly larger than
that of the Cervical Vertebrae

Lumbar Vertebrae5 total lumbar vertebrae
L1 – L5
Large, block-like bodiesMost sturdy of all the vertebrae

SpineTo help remember the number of bones in the
vertebrae, remember common meal times 7am 12 noon 5pm

Intervertebral DisksBetween each vertebrae lie intervertebral disksEach disk is composed of strong, fibrous tissue
Inside the fibrous tissue lies a semifluid nucleus
Function – Shock absorption

Injuries of the SpineHerniated DiskCervical Sprain (Whiplash)Spina Bifida

Herniated DiskDisks, specifically lumbar, are subjected to
constant, intense stressStress can cause degeneration, tears and
cracks in fibrous disk tissueTears in the tissue can cause the fluid to fall
out and compress the nerves of the spinal cord

Disk Herniation

Cervical Sprain (Whiplash)Occurs from a sudden snap of the headPain might not be present initially, but almost
always appears the day after the trauma

Spina BifidaA birth defect when the vertebrae do not form
around the spinal cordMild cases might not need treatmentSevere cases can require surgery

Spina Bifida

HomeworkAnswer Questions 14-16 on pg. 158 (?)