The Skull and Vertebral Column
-
Upload
ala-yassin -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
4
Transcript of The Skull and Vertebral Column
11/23/2009
1
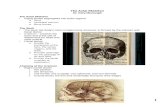
Skeletal System Continued pg29 in Study Guide
Figure 7.1a
Skull
Thoracic cage
(ribs andsternum)
(a) Anterior view
Facial bonesCranium
Sacrum
Vertebral
column
ClavicleScapulaSternumRibHumerusVertebraRadiusUlnaCarpals
PhalangesMetacarpalsFemurPatella
TibiaFibula
TarsalsMetatarsalsPhalanges
11/23/2009
2
The Skull=22 bones
Two sets of bones – cranial and facial
1. Cranial bones (8)
○ Enclose the brain in the cranial cavity
○ Provide sites of attachment for head and
neck muscles
○ Provide support
The Skull
2. Facial bones (14 bones)
○ Framework of face
○ Cavities for special sense organs for sight,
taste, and smell
○ Openings for air and food passage
○ Sties of attachment for teeth and muscles of
facial expression
11/23/2009
3
Figure 7.2a
Bones of cranium (cranial vault)
Lambdoid
suture
Facial
bones
Squamous
suture
(a) Cranial and facial divisions of the skull
Coronal
suture
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 7.4a
Parietal bone
Nasal bone
Sphenoid bone
Temporal bone
Ethmoid bone
Lacrimal bone
Zygomatic bone
Maxilla
Mandible
Mental
foramen
(a) Anterior view
Frontal bone
Middle nasal
concha
Vomer
Perpendicular
plate
Ethmoid
bone
11/23/2009
4
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Coronal suture Frontal bone
Sphenoid bone
(greater wing)
Ethmoid bone
Lacrimal bone
Nasal bone
Zygomatic
bone
Maxilla
Alveolarmargins
Mandible
Mental foramen
Parietal bone
Lambdoidsuture
SquamoussutureOccipital
bone
OccipitomastoidsutureExternal acousticmeatusMastoid processStyloid process
Mandibular condyle
Mandibular notch
Mandibular ramus
(a) External anatomy of the right side of the skull
Mandibular angle Coronoid process
Zygomaticprocess
Temporal bone
Figure 7.5a
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Cranial Bones=8
• Frontal bone
• Parietal bones (2)
• Occipital bone
• Temporal bones (2)
• Sphenoid bone
• Ethmoid bone
11/23/2009
5
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Facial Bones=14
• Mandible
• Maxillary bones
(maxillae) (2)
• Zygomatic bones (2)
• Nasal bones (2)
• Lacrimal bones (2)
• Palatine bones (2)
• Vomer
• Inferior nasal conchae
(2)
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Sutures
• Become more complex with age
• At birth bones of skull are held together by
soft regions of connective tissue-fontanelles
• Loose joining permits?
11/23/2009
6
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Hypophyseal fossa
of sella turcica
Temporal bone
Parietal bone
Occipital bone
Foramen magnum
(a) Superior view of the skull, calvaria removed
Frontal bone
Olfactory foramina
Optic canal
Internal acoustic
meatus
Cribriform plateEthmoid
boneCrista galli
SphenoidLesser wing
Greater wing
View
Figure 7.7a
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 7.15
Frontal
sinus
Ethmoidal
air cells
(sinus)
Maxillary
sinus
Sphenoid
sinus
Frontal
sinus
Ethmoidal
air cells
Maxillary
sinus
Sphenoid
sinus
(a) Anterior aspect (b) Medial aspect
11/23/2009
7
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 7.12
Greater horn
Lesser horn
Body
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
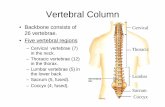
Functions of the Vertebral Column
• Pg 30
11/23/2009
8
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 7.18
Posterior
Anterior
Lamina
Superior
articular
process
and
facet
Transverse
process
Pedicle
Spinous
process
Vertebral
arch
Vertebral
foramenBody
(centrum)
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Developmental Errors of the Skull
pg 11 study guide
• Microcephalus-premature closure of anterior
fontanelle
• Hydrocephalus
• Cleft palate
11/23/2009
9
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Disorders of the spinal column
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
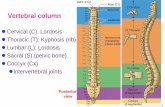
Vertebral Column: Curvatures
• Increase the resilience and flexibility of the spine
• Two posteriorly concave curvatures
• Cervical and lumbar
• Two posteriorly convex curvatures
• Thoracic and sacral
• Abnormal spine curvatures
• Scoliosis (abnormal lateral curve)
• Kyphosis (hunchback)
• Lordosis (swayback)
11/23/2009
10
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 7.16
Cervical curvature
(concave)
7 vertebrae, C1–C7
Thoracic
curvature
(convex)
12 vertebrae,
T1–T12
Lumbar curvature
(concave)
5 vertebrae, L1–L5
Sacral curvature
(convex)
5 fused vertebrae
sacrum
Coccyx
4 fused vertebrae
Anterior view Right lateral view
Spinous
process
Transverse
processes
Intervertebral
discs
Intervertebral
foramen
C1
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
scoliosis
11/23/2009
11
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
lordosis
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
kyphosis
11/23/2009
12
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 7.17a
Supraspinous ligament
Intervertebral
disc
Anterior
longitudinal
ligament
Intervertebral foramen
Posterior longitudinal
ligament
Anulus fibrosus
Nucleus pulposus
Sectioned body
of vertebra
Transverse process
Sectioned
spinous process
Ligamentum flavum
Interspinous
ligament
Inferior articular process
Median section of three vertebrae, illustrating the composition
of the discs and the ligaments
Normal intervertebral discs
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 7.17c
Vertebral spinous process
(posterior aspect of vertebra)
Spinal nerve root
Anulus fibrosus
of disc
Herniated portion
of disc
Nucleus
pulposus
of disc
Spinal cord
(c) Superior view of a herniated intervertebral disc
Transverse
process