USING CLINICAL PATHWAYS, MONITORING FOR VARIANCES.
-
Upload
ryan-barnett -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of USING CLINICAL PATHWAYS, MONITORING FOR VARIANCES.

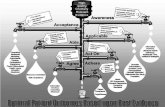
USING CLINICAL PATHWAYS, MONITORING FOR VARIANCES

Choosing the pathway, choosing the patient
1. What is the working diagnosis?
2. Do we have a pathway for this diagnosis?
3. Is the patient eligible to be in this pathway?

Activating the pathway
1. AP/RIC signs at the bottom
2. NIC acknowledges
What do these signatures signify?
Pathways are activated one time interval at a time.Pathways are subdivided into either time intervals (day 1, day 2, etc) or units of care (e.g., NSD pathway)
Pathways are activated one time interval at a time.Pathways are subdivided into either time intervals (day 1, day 2, etc) or units of care (e.g., NSD pathway)

Filling out patient informationWho fills these out?

Indicate date for interval or phaseWho fills this out?

Fill out SOAP
Who fills out the SOAP?

With the pathway soap filled out, is a Patient Database Form still needed?
a.Not anymoreb.Optional c.Only when there’s additional information to supplement the pathway SOAPd.Always


Reviewing orders
Who reviews the orders?
Mandatory orders need to be carried out once the pathway is activated.
How would you indicate that you want Protime to be carried out?
a.Put X on the bullet
b.Encircle the bullet
c.Do nothing
d.Underline the order
Remember: bulleted orders
are carried out automatically
once the pathway is
activated.
Remember: bulleted orders
are carried out automatically
once the pathway is
activated.

Reviewing orders
Mandatory orders need to be done 100% of the time. True or false?
False. They may be deferred. How?
a.Putting X on the bullet
b.Crossing out the order and signing
c.Writing the word “defer” beside the order
smv

How would you indicate that you want 12-L ECG to be done? Show how on your pathway form.
a.Shade the boxb.Write “X” on the boxc.Check the box
Optional orders that are checked will be carried out automatically.

9. If pain reliever is not ordered, how would it be indicated? Show how on your pathway form.a.Cross out the orderb.Write “X” on the boxc.Do nothingd.Write “Defer” beside the order
Unwanted optional orders are left blank.

10. If you have carried out an order, how would you indicate it? Show how on your pathway form.
a.Order has been crossed out and signedb.The word “OK” is written and signedc.The word “Done” is written and signedd.Signed and timed in Sign column
PRV10:35am
PRV11:20am

Summary so far…
What pathways are How to use pathways
Activating Reviewing orders Mandatory & optional orders Deferring mandatory orders Signifying that the order has been carried
out

Variances

What are variances
Any mandatory or checked optional intervention that was not done
An abnormal finding An unmet outcome within the time
frame An outcome met earlier than expected

TMC variance codesA. Patient/family 1. Patient’s medical condition 2. Patient/family decision 3. Patient/family availability 4. No funds 5. Other reasons B. Physician 1. Medical order 2. Provider(s) decision 3. Provider(s) response time 4. Other reasonsC. TMC System 1. Results/Data availability 2. Supplies/Equipment related 3. Appointment Availability 4. Weekend/Holiday 5. Other reasons D. Outside TMC 1. Transportation availability 2. Home Care availability 3. Other reasons

Documenting variances
• Who▫ Any member of the health care team who
noted them• Where
▫ Variance code is written on the pathway’s Var column
• How▫ Variance notes may be written on progress
or nursing notes▫ Documented in the Variance Monitoring
Form

1. Is 12-L ECG ordered? Yes No2. Patient refused the test. Is this a
variance? Yes No3. What is the variance code?4. Where is the variance code written?
Show it on your pathway form.
A2
Surgical floorDr. Goellegue
4 hrs
JEO6:05pm
A2PRV10:35am
The single sheet of the pathway shows
•The orders
•The orders that were carried out
•The order that were not done
•The reason/s why the order was not done

Arterial blood gas was requested. It wasn’t done because the procedure is not covered by the HMO.
1. Is this a variance? What is the variance code? Show on your pathway form how this will be documented.

Reviewing outcomes

Outcomes
• The measurable outcomes that a patient is expected to experience is specified in the pathway for every time interval (e.g., daily, per shift).
• Pre-determined by the pathway developers• Listed in discharge planning section• If not met, should signal calling the
attention of the AP so that interventions can be modified, added, discontinued in a timely way.

Reviewing outcomes: MD’s roleAll care team members must review the
problem list, variances and outcomes daily. Pathways ensure that the members of the care team are looking at the same plan of care.
AP and all referred MDs are accountable for reviewing the patient’s progress against intermediate and discharge outcomes on a daily basis.
And for revising the plan of care based on the review of patient’s outcomes.

Reviewing outcomes: nurse-in-charge’s role
Reviews patient’s progress daily against intermediate and discharge outcomes
Review variances daily and report them to the AP and the rest of the care team.
Ensures that all variances result in re-evaluation of plan of care by appropriate disciplines.

Patient outcomes, day 1
Day 1
1. Can the next time interval (Day 2) be activated for this patient?
2. Why? Why not?

Patient outcomes, Day 1 1.Can the next time interval (Day 2) be
activated for this patient?2.Why? Why not?3. Is this a variance? Document.

Day 4 outcomes1.Are all patient outcomes met? Yes No2.Is patient for discharge? Yes No3.Document the disposition on your pathway form.4.Is this a variance? Document.
Patient’s length of stay exceeded
that of the pathway. This is a
variance.Patient’s length of stay exceeded
that of the pathway. This is a
variance.
A1PRV10:35
am

Discontinuing the pathway

Discontinuing the pathway
The pathway will be discontinued whenever: The patient’s primary diagnosis changes The patient’s condition significantly worsens The patient fails to meet clinical outcomes
for 24-48 hoursTo discontinue the pathway, a progress note
(SOAP) is written by the MD outlining the patient’s new plan of care and new orders. A new nursing plan of care is also written. The pathway is then filed in the patient record.

Think about this:
Why should pathway be discontinued if the primary diagnosis changed?
Why should pathway be discontinued if the patient’s condition significantly worsens?
Why should pathway be discontinued if outcomes are not met within the time frame?

Summary
What pathways are How to use pathways
Activating & acknowledging Mandatory & optional orders Deferring mandatory orders Signifying that the order has been carried
out Identifying variances Reviewing outcomes Discontinuing the pathway