Unit1_3 Phase System
-
Upload
fitri-kyle -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of Unit1_3 Phase System
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
1/53
1
UNIT 1
THREE PHASE SYSTEM
By: INTAN SHAFINAZ BINTI ABD. RAZAK
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
2/53
2
Introduction
What is alternating current???
What is single phase system???
What is three phase system???
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
3/53
3
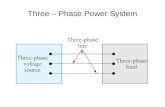
Single-phase electric power
In electrical engineering, single-phaseelectric power refers to the distribution of
electric powerusing a system in which allthe voltages of the supply vary in unison.
Single-phase meaning (2) power lines as an
input source; therefore, only (1) primary and
(1)secondary winding is required to
accomplish the voltage transformation.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_powerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_power -
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
4/53
4
A single-phase load may be powered from a
three-phase distribution system either by
connection between a phase and neutral .
For example, in places using a 415 volt 3
phase system, the phase-to-neutral voltage
is 240 volts, allowing lighting to be
connected phase-to-ground and motors to
be connected to all three phases.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ground_and_neutralhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ground_and_neutral -
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
5/53
5
THREE PHASE AND
SINGLE PHASE POWER SYSTEM
R
Y
B
N
3 phase delta system Single phase(R)3 phase wye system
Single phase
(Y)
Single phase
(B)
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
6/53
66
THREE PHASE AND
SINGLE PHASE POWER SYSTEM
RED
YELLOW
BLUE
LINES
NEUTRAL
PROTECTING
GEAR 3-Phase
415V, 3-Wires(For Motor and
smallindustrialconsular)
Three separate
single-phase 240Vsupplies (For
lighting, heatingand domestic
consumer)
Single- phase
415V supply
BLACK
IR
IY
IB
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
7/53
7
Polyphase system
Polyphase system is the system use
more than one coil to generate the
current. Example: Three phase system
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
8/53
8
HOW TO GENERATE THREEPHASE CURRENT???
Rotating magnetic field , static
winding coil. (Medan magnet berputar,
gegelung kekal.)
Rotating winding coil, static magnetic
field (Gegelung berputar, medan magnet
kekal.)
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
9/53
9
Three phase motor
The rotating
magnetic field of a
three-phase motor
The winding coil is
static
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetic_fieldhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetic_field -
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
10/53
1010
THREE PHASE SYSTEMS(THREE PHASE VOLTAGE)
If three separate coils are spaced 120apart, three voltages 120 out of phasewith each other will be produced whenmagnetic field through the coils.
This manner in which a three-phase
voltage is produced.
http://localhost/var/www/apps/conversion/releases/20121120192253/tmp/VIDEO/e_and_m_3phase_gen.swf -
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
11/53
1111
THREE PHASE SYSTEMS(THREE PHASE VOLTAGE)
Three phase voltage cycle
Result of three-phase voltage cycle as shown below:
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
12/53
12
The waveform
Three-phasenetworks consistof three simplenetworks, eachhaving the sameamplitude andfrequency, and a120 phase
differencebetween adjacentnetworks
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
13/53
13
The phasors diagram
We can also
represent these
voltages withphasors diagram.
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
14/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
15/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
16/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
17/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
18/53
18
18
To reduce the number of wires it is usual to interconnectthe three phases.
Two ways solution:
Star/Wye connection : applied on sources of three
phase supplies (alternators). Higher voltage but lower current (amps)
Delta connection : applied on motors and otherloads.
Lower voltage but mores current (amps).
THREE PHASE SYSTEMS(THREE PHASE CONNECTION)
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
19/53
19
Introduction to delta and wye
three phase system
When you connect a load to the threewires/ lines it should be done in such
a way that it does not destroy thesymmetry.
This means that you need three equalloads connected across the three pairsof wires.
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
20/53
20
Delta and Wye Connections
This looks like an equilateral triangle,
or delta, and is called a delta load.
Another symmetrical connection wouldresult if you connected one side of
each load together, and then the three
other ends to the three wires. Thislooks like a Y, and is called a wye
load.
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
21/53
21
Delta and WyeConnections cont
In a three-phase transformer, there is a three-
legged iron core.
Each leg has a respective primary and secondary
winding. As can be seen, the three-phase transformer
actually has 6 windings (or coils) 3 primary and 3
secondary. These 6 windings will be pre-connected at the
factory in one of two configurations: - Delta and WyeConnections/ Configurations.
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
22/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
23/53
23
Wye Connection
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
24/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
25/53
25
The Wyeor Y-connection
The Wyeor Y-connection, wherethe negative terminals of eachgenerator or load are connected to form the neutral terminal.
This results in a three-wire system, or if a neutral wire is provided, a
four-wire system.
Ip2Ip1
Ip3 IL3
IL2
IL1
IN
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
26/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
27/53
27
Phase & Line in Y-connection
In Y-connection, the phase and line
currents are obviously the same, but
the line voltages are greater than thephase voltages.
In the balanced case:
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
28/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
29/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
30/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
31/53
31
Phase & Line in -connection
As opposed to a Y-connection, in -
connection the phase and line voltages
are obviously the same, but the linecurrents are greater than the phase
currents.
In the balanced case:
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
32/53
32
versus Y
-connection Y-connection
VL= VP
IL
=IP
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
33/53
33
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
34/53
34
POWER IN THREE PHASE SYSTEM (Y AND )ARE THE SAME!!!
P 3 = 3 .VL . IL . cos
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
35/53
35
SUMMARY
Symbol Y
Voltage VL = VPH VL = 3 VPH
Current IL = 3 IPH IL = IPH
Steady state
(Keadaanseimbang)
V (closed loop) =VRY + VYB + VBR = 0 IN = IR + IY +IB = 0
Single phase powerfor each coil.
VPH . IPH . cos
Three phase power(phase element)
3 .VPH . IPH . cos
Three phase power(line element)
3 .VL . IL . cos
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
36/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
37/53
37
Example 2:
Di dalam satu sistem tiga fasa 4dawai, voltan talian ialah 415V dan
beban-beban resistif 10kW, 8kW dan5kW disambungkan di antara ketiga-tiga pengalir talian dan pengalir neutralseperti dalam rajah berikut. Kirakan:
Arus dalam setiap talian. Arus di dalam pengalir neutral
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
38/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
39/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
40/53
40
Kebaikan sistem tiga fasa berbanding sistemsatu fasa
Penggunaan bekalan kuasa AU untuk tujuan pemanasan filamen lampuelektrik adalah memadai dengan menggunakan sistem kuasa satu fasa.
Namun demikian, penggunaan sistem satu fasa untuk tujuan kendalian motorAU mempunyai kelemahannya. Salah satu kelemahan iaitu motor AU satufasa tidak dapat dimulakan putaran dengan sendiri (self-starting), sebaliknyabeza fasa antara gegelung tiga fasa membolehkan motor AU tiga fasamempunyai ciri kendalian permulaan kendiri.
Penjimatan bahan pengalir untuk kehilangan tembaga yang sama, apabilakuasa yang sama dipindahkan dalam sistem tiga fasa berbanding sistem satufasa.
Motor tiga fasa adalah kendalian permulaan kendiri tetapi tidak berlakudalam motor satu fasa.
Motor tiga fasa mempunyai faktor kuasa dan kecekapan yang lebih baik dan
saiz yang lebih kecil, bagi keluaran yang sama berbanding motor satu fasa. Daya kilas yang dihasilkan oleh motor tiga fasa adalah tetap, sementara daya
kilas motor aruhan satu fasa adalah berbentuk dedenyut.
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
41/53
41
Alatubah tiga fasa adalah lebih ringan, berkecekapan lebihbaik dan lebih murah berbanding alatubah satu fasa yangsama saiz.
Dalam sistem pengagihan tiga fasa, dua bentuk sambungan
biasanya dilakukan untuk menghasilkan nilai voltan yangberlainan daripada satu sumber bekalan yang sama, tanpapenambahan kos. Sambungan bintang menggunakanvoltan fasaantara fasa-fasa dan neutral yang lebih rendahbiasanya untuk kegunaan domestik;manakala sambungandelta menggunakan voltan yang lebih tinggiiaitu voltantalian(3 kali lebih besar) biasanya untuk kegunaan
perindustrian.
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
42/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
43/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
44/53
44
Copper loss is the term often given to heat produced by electrical currents in theconductors oftransformerwindings, or other electrical devices.
Copper losses are an undesirable transfer ofenergy, as are core losses, which resultfrom induced currents in adjacent components.
The term is applied regardless of whether the windings are made ofcopperor anotherconductor, such as aluminium. Hence the term winding loss is often preferred.
A related term, load loss closely related but not identical, since an unloaded transformerwill have some winding loss. Copper losses result from Joule heating and so are also referred to as "I squared R
losses", in deference to Joule's First Law. This states that the energy lost each second, orpower, increases as the square of the current through the windings and in proportion tothe electrical resistance of the conductors. Copper Loss = I2R
where I is the current flowing in the conductor and R the resistance of the conductor. WithI in amperes and R in ohms, the calculated power loss is given in watts.
With high-frequency currents, winding loss is affected by proximity effect and skin effect,and cannot be calculated as simply.
For low-frequency applications, the power lost can be minimized by employingconductors with a large cross-sectional area, made from low-resistivity metals.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heathttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_currenthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_conductorhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transformerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Induced_currenthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Core_losshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Induced_currenthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Copperhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aluminiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joule_heatinghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_(physics)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Square_(algebra)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joule%27s_first_lawhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proportionality_(mathematics)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proportionality_(mathematics)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secondhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_(physics)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Square_(algebra)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proportionality_(mathematics)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amperehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proximity_effect_(electromagnetism)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skin_effecthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resistivityhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resistivityhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skin_effecthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proximity_effect_(electromagnetism)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Watthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amperehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proportionality_(mathematics)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Square_(algebra)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_(physics)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secondhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joule%27s_first_lawhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joule_heatinghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aluminiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Copperhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Induced_currenthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Core_losshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transformerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_conductorhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrical_currenthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat -
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
45/53
45
Salah satu kelemahan iaitu motor AU
satu fasa tidak dapat dimulakan
putaran dengan sendiri (self-starting). Explain what is self-starting?
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
46/53
46
Large industrial synchronous motors
are self started by embedded squirrel
cage conductors in the armature,acting like an induction motor.
The electromagnetic armature is only
energized after the rotor is brought upto near synchronous speed.
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
47/53
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
48/53
48
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
49/53
49
Mini-quiz to check your
understanding
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
50/53
Wh t d l t i l
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
51/53
51
What does an electricaltransformer do?
a) It changes the direction of AC
electricity
b) It changes the voltage of DCelectricity
c) It changes the voltage of AC
electricity
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
52/53
52
QUIZ!!!
What is the difference between AC
and DC electricity?
Why do we use AC instead of DC? How do we create AC electricity?
-
7/30/2019 Unit1_3 Phase System
53/53
53