Unit Two: Chapter Four Sensation and Perception. Warm up 02/17 ●How do your senses (sight,...
-
Upload
kory-young -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Unit Two: Chapter Four Sensation and Perception. Warm up 02/17 ●How do your senses (sight,...

Unit Two: Chapter Four
Sensation and Perception

Warm up 02/17
● How do your senses (sight, hearing, smelling, etc.) influence your behavior and mental processes?

The Basics
● Absolute Threshold○ weakest amount of stimulus that can be
sensed○ dog’s absolute threshold for hearing is lower
than humans○ App that only young people can hear○ differs from person to person

The Basics
● Differences in Threshold○ minimum difference between 2 stimuli
● Signal Detection Theory○ distinguishing sensory info
■ setting■ your physical state■ your mood■ your attitudes
○ focus on what you consider important○ different people find different things
important

The Basics
● Sensory Adaptation○ sense change to adapt to an environment○ more sensitive to weak stimuli & less
sensitive to unchanging stimuli■ eyes adjusting to the dark■ People in cities adjusting to sound of traffic

Vision
● Light ○ wavelengths - not all visible to humans

Vision
● The Eye○ light enters the eye and then is projected onto
a surface○ pupil - determines the amount of light that is
let in■ sensitive to light and emotions
○ lens - adjusts to keep objects in focus○ retina - consists of neurons
■ photoceptors - sends visual input to the brain

Vision
● blind spot - places in the eye that lack photoceptors
● rods and cones - types of photoceptors○ rods- brightness of light○ cones - color vision
● Visual Acuity ○ sharpness of vision

Vision
● Color Vision○ color circle - complementary colors○ afterimages - you perceive the afterimage of
a color once you view it for a while■ complementary pair


Vision
● Color Blindness○ not normal color vision○ unable to distinguish colors○ missing or malfunctioning cones○ total color blindness is rare

Activity
● Create your own color wheel. There is also an example in the book. ○ complementary colors are across from one
another
● Create your own afterimage.○ Remember the afterimage includes the
complementary color.


Chapter 4 Vocabulary
● sensation● perception● absolute threshold● difference threshold● signal-detection theory● sensory adaptation● pupil● lens● retina● gate theory● vestibular sense● similarity● continuity● stroboscopic motion
● photoreceptors● blind spot● visual activity● afterimage● cochlea● auditory nerve● conductive deafness● sensorineural deafness● olfactory nerve● kinesthesis● closure● proximity● monocular cues● binocular cues● retinal disparity

Warm Up 10/10
● When was the last time you had a vision test?
● Do you require glasses or contacts?

READ! ~10 minutes

Warm Up 02/18
● Do you rely more on your hearing or your sight?
● Why?

Hearing
● Pitch○ how high or low a sound is○ depends on the # of cycles per second○ we can hear things between 20 and 20,000
cycles per second
● Loudness○ depends on the height (amplitude) of sound
waves

Hearing
● The Ear○ outer, middle, and inner ear○ eardrum separates outer and middle ear
■ vibration transmits sound to the hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup
○ cochlea - converts vibrations into neural impulses that are transmitted to the brain

Hearing
● Deafness○ conducive deafness
■ damage to middle ear■ prevents people from hearing quieter sounds■ hearing aids can help
○ senisorineural deafness■ unable to perceive sounds of certain
frequencies■ neurons in cochlea are destroyed■ disease or prolonged exposure to loud sounds
● ipod deafness is real!

Hearing
● Deafness○ deafness in the world today
■ American Sign Language taught in schools■ “closed captioning”■ research on repairing ear damage


Warm Up 02/19
● Have you ever had a food craving? ● What food?

Other Senses
● Smell○ closely connected to taste○ receptor neurons deep in each nostril○ sends info through the olfactory nerve○ adapt to scents quickly

Other Senses
● Taste○ primary - sweet, sour, salty, and bitter○ umami - “savory”○ receptor neurons on taste buds on tongue
■ you can have low sensitivity to certain tastes
○ taste cells can re grow in a week

Other Senses
● Skin Senses○ pressure
■ sensory receptors in root of hair cells■ different parts of body more sensitive to
pressure than others○ temperature
■ neurons just beneath the skin■ different receptors for warmth and cool

Other Senses
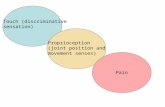
● Skin Senses○ pain
■ pain receptors send message to spinal cord and thalamus
■ pain chemical = prostaglandin■ Gate theory = brain can only process so
many messages at a time● if you rub a sore spot on the body it distracts brain
from pain
■ phantom limb pains in amputees● neural impulse in stump left by missing limb

Other Senses
● Body Senses○ Vestibular
■ tells you if you are standing upright without using eyes
■ keep balance○ Kinesthesis
■ position and motion of the body■ info comes from joints, tendons, and
muscles

Grab a partner
● First, one of you demonstrate a complex set of movements○ dance, sports, yoga
● Second, the other member of the pair repeat the movement back.○ write down what the movement was and if it
was easy or difficult
● Switch Roles and repeat

Sensation Walks
● You’ll need to create something to block out your vision for our sensation walks…
● I have paper in the front.

Activity
● Smell/Taste Log○ write down over the course of today
everything you smell or taste○ was there a pattern?

Warm up 02/20
● What is perception?● How could it be different from a
sensation?

Perception
● Perceptual Organization○ closure
■ Gestalt psychology■ perceive object with gaps as whole
○ figure-ground perception■ figures against a background
○ other■ proximity (nearness)■ similarity (similar objects belong together)■ continuity (continuous patterns)

Perception
● Movement○ is hard to discern with only your eyes
● Stroboscopic Motion○ rapid progression of images - looks like
motion

Perception
➔ Depth Perception◆ monocular cues
● only need one eye to perceive them● some objects seem more distant
◆ binocular cues● both eyes required to perceive● retinal disparity

monocular cues

Perception
➔ Perceptual Constancies◆ size constancy
● you maintain the ability to distinguish the size of something no matter what distance away it is
◆ color constancy● things keep their color even in different
lighting◆ shape constancy
● same shape no matter the angle you view it

Perception
➔ Visual Illusions◆ Muller-Lyer illusion◆ Ponzo illusion
● example

Other Visual Illusions

other Visual illusions

Create your own Visual Illusions
● It can be a recreation of one we’ve talked about...or you can create something completely original