UNIT: 3 - file · Web viewUNIT: 3. NETWORK MEDIA & HARDWARE . TOPICS AND SUB-TOPICS. 3.1....
Transcript of UNIT: 3 - file · Web viewUNIT: 3. NETWORK MEDIA & HARDWARE . TOPICS AND SUB-TOPICS. 3.1....

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
UNIT: 3
NETWORK MEDIA & HARDWARE
TOPICS AND SUB-TOPICS
3.1 Transmission Media: Unguided and Guided media, Wired and Wireless, UTP, Coaxial and Fiber optical cable 3.2 Types of Connectors: RJ-45, RJ-11, BNC, BNC –T, BNC Terminator, Fiber optic connectors: Subscriber Channel (SC), Straight Tip (ST), Mechanical transfer – registered jack (MT-RJ) connectors 3.3 Network Interface Card (NIC), ARCNET, Ethernet. 3.4 Network connecting devices: Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateway, Access point, Wireless Access points 3.5 Servers introduction: File, Print, Mail, Proxy, Web
3.1 Transmission Media
The path through which data is transmitted from one place to another in called channel. It is also known as communication media or transmission media. These are different types of transmission media 1) Guided media 2) Unguided media
1) Guided Media: In guided media communication device are directly connected with each other by using some physical media like wires. It also called bounded media. Wire pair is one of the most commonly used communication media wire pair is usually made of copper.Examples: Twisted pair, Co-axial cables, fiber optical cables, etc.
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 1

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
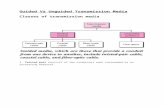
2) Unguided Media:In unguided media communication devices communication with each other through air or space using broadcast radio signals, microwave signals and infrared signals unguided media is used where it is impossible to install cable data can be transfer all over the world using media. It doesn't use any physical connectors between the two devices communicating. Usually the transmission is send through the atmosphere. Wireless media is used when a physical obstruction or distance blocks are used with normal cable media.Examples: Microwave, Communication satellite, Cellular radio, etc.
1) Wired Transmission: Wired transmission media is media used to transfer information over a network, such as a twisted pair cable.Various types: coaxial cables, telephone lines, and basically any information or data transmitted through a wire. Wired transmission media is more secure than wireless so that hackers have a much less oppurtunity to access your computer system. Wired transmission media would typically have a greater start-up cost because of the multiple wires, dependability, and probable installation fee.
2) Wireless Transmission: Wireless transmission media is transmitting information or data through microwave, infrared, or radio wave signals to satellites or radio towers. Walls in a building can present a problem with a wireless transmission medium signal because concrete and metal can interfere with the waves.
1) Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)This is the most popular form of cables in the network and the cheapest form that is used in industries. The UTP has four pairs of wires and all inside plastic sheathing.There are 6+ different types of UTP categories. UTP-CAT5e is the most popular UTP cable, it came to replace the well-known coaxial cable.
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 2

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
Types of UTP Cables (CAT 1 to CAT 6):
CAT1 is typically telephone wire. This type of wire is not capable of supporting computer network traffic and is not twisted
CAT2, CAT3, CAT4, CAT5 and CAT6 are network wire specifications. This type of wire can support computer network and telephone traffic.
CAT2 is used mostly for token ring networks, supporting speeds up to 4 Mbps.
CAT3, CAT4 and CAT5 cable are actually 4 pairs of twisted copper wires. For higher network speeds (100Mbps plus) you must use CAT5 wire, but for 10Mbps CAT3 will sufficient.
CAT6 wire was originally designed to support gigabit Ethernet. It is similar to CAT5 wire, but contains a physical separator between the 4 pairs to further reduce electromagnetic interference.
The biggest reason that we call it Twisted Pair is to protect the wires from interference from themselves. Each wire is only protected with a thin plastic sheath.
2) Co-axial Cable:Coaxial cable is a type of cable that has an inner conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a same geometric axis. The of coaxial design is that electric and magnetic fields are confined to the dielectric with little leakage outside the shield. Electric and magnetic fields outside the cable are largely kept from causing interference to signals inside the cable.
It is used for carrying weak signals that cannot tolerate interference from the environment or for stronger electrical signals that must not be allowed to radiate or couple into adjacent structures or circuits.
3) Optic Fibre Cable:
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 3

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
F.O cable is based on optical fibers, which are long, flexible, hair-width strands of ultra-pure glass. It is a technology that uses glass (or plastic) threads (fibers) to transmit data. A fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves.
Fiber optics has several advantages over traditional metal communications lines:1) Fiber optic cables have a much greater bandwidth than metal cables. This means that they can carry more data. 2) Fiber optic cables are less susceptible than metal cables to interference.3) Fiber optic cables are much thinner and lighter than metal wires.4) Data can be transmitted digitally (the natural form for computer data) rather than analogically.
3.2 Types of Connectors:
1) RJ-45: Short for Registered Jack-45. It is an eight-wire connector used commonly to connect computers onto a local-area networks (LAN) especially Ethernets.
This connector is most commonly connected to the end of Cat5 cable, which is connected between a computer network card and a network device such as a network router.
T-568A and T-568B are the two wiring standards for RJ-45 connector data cable specified by TIA/EIA-568-A wiring standards document.
The difference between the two is the position of the orange and green wire pairs. It is preferable to wire to T-568B standard.
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 4

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 5

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
2) RJ-11:More commonly known as a modem port, phone connector, phone jack or phone line, the Registered Jack-11 (RJ-11) is a 4 or 6 wire connection for telephone and Modem connectors.
3) BNC (Bayonet Neill–Concelman):The BNC connector is a miniature quick connect/disconnect radio frequency connector used for coaxial cable.
4) BNC-T Connector:This type of connector is extended version of BNT connector.
4) BNC Terminator:
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 6

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
For termination of coaxial cable BNC Terminator is used.
5) Fiber optic connectors:For termination of Fiber optic cable 3 types of terminators are used.
a) Subscriber Channel (SC):
The Subscriber Connector (SC) is a fiber optic connector with a push-pull latching mechanism that provides quick insertion and removal while ensuring a positive connection. Subscriber Connectors are inexpensive, trouble-free, and robust.
b) Straight Tip Connector (ST):Straight Tip connector is a fiber-optic cable connector that uses a bayonet plug and socket. It was the first de facto standard connector for most commercial wiring. For bi-directional transmission, two fiber cables and two ST connectors are used.
c) Mechanical Transfer – Registered Jack (MTRJ):
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 7

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
Two fibers are included in one connector that looks a lot like an RJ45. That’s where the last part of the name came from. Alignment pins are used to mate the connectors. MT-RJ’s come in two versions, with mating pins (male) and without (female).
3.3 Network Interface Card (NIC), ARCNET, Ethernet:
1) Network Interface Card (NIC):NICs are used to connect a PC to a network. The NIC provides a physical connection between the networking cable and the computer's internal bus. Different computers have different bus architectures. NICs come in three basic varieties: 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32- bit. The larger the number of bits that can be transferred to the NIC, the faster the NIC can transfer data to the network cable.
Many NIC adapters comply with Plug-n-Play specifications. On these systems, NICs are automatically configured without user intervention, while on non-Plug-n-Play systems,
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 8

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
configuration is done manually through a setup program and/or DIP switches.Cards are available to support almost all networking standards, including the latest Fast Ethernet environment.
Fast Ethernet NICs are often 10/100 capable, and will automatically set to the appropriate speed. Full duplex networking is another option, where a dedicated connection to a switch allows a NIC to operate at twice the speed.
2) ARCNET:ARCNET is a widely-installed local area network (LAN) technology that uses a token-bus scheme for managing line sharing among the workstations and other devices connected on the LAN. The LAN server continuously circulates empty message frames on a bus (a line in which every message goes through every device on the line and a device uses only those with its address). When a device wants to send a message, it inserts a "token" (this can be as simple as setting a token bit to 1) in an empty frame in which it also inserts the message. When the destination device or LAN server reads the message, it resets the token to 0 so that the frame can be reused by any other device.
The scheme is very efficient when traffic increases since all devices are afforded the same opportunity to use the shared network.ARCNET can use coaxial cable or optic lines. ARCNET is one of four major LAN technologies, which also include Ethernet, token ring and FDDI.
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 9

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
3) Ethernet:Ethernet is a local-area network (LAN) architecture developed by Xerox Corporation in cooperation with DEC and Intel in 1976. Ethernet uses a bus or star topology and supports data transfer rates of 10Mbps.
The Ethernet specification served as the basis for the IEEE 802.3 standard, which specifies the physical and lower software layers. It is one of the most widely implemented LAN standards. Ethernet is a link layer protocol in the TCP/IP stack, describing how networked devices can format data for transmission to other network devices on the same network segment, and how to put that data out on the network connection.The most commonly installed Ethernet systems are called 100 BASE-T (the "BASE-T" part means the systems use twisted-pair cabling) and provide transmission speeds up to 100 megabits per second (Mbps).
3.4 Network connecting devices: Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateway, Access point, Wireless Access points
1) Repeater:In telecommunications, a repeater is an electronic device that receives a signal and retransmits it at a higher level or higher power, or onto the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances.
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 10

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
The repeaters are used in places where amplification of input signal is necessary. It regenerates the input signal, and amplifies only the desirable signal. Hence, the noise component of the signal is eliminated.The repeaters are necessary since, during the transmission of the signals over long distances, the signal has attenuation, delay distortions and noise, which lead in loss of data. Hence, in order to prevent this, the regenerative repeaters are used.
2) Hub:A hub is a common connection point for devices in a network. Hubs are commonly used to connect segments of a LAN. A hub contains multiple ports.
.When a packet arrives at one port, it is copied to the other ports so that all segments of the LAN can see all packets.
3) Bridge:A bridge is a device which works in the Data Link Layer. Initial bridges were used to connect only 2 LAN’s, but the most recent ones perform similar operation as the switches. It also works on the principle of transfer of information using the MAC addresses of the ports.
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 11

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
4) Switch:A switch is an intelligent device that works in the data link layer. The term intelligent refers to the decision making capacity of the Switch. It establishes a link between the sender and the receiver based on the MAC addresses.
Simultaneous data transfer is possible in a switch. It is also to be noted that a switch is a secure device, because it sends information only to the desired destinations.
5) Router:Router does the job of connecting multiple devices in a LAN to the internet using the same IP address.Any computer can be connected to the internet via MODEM, which performs the modulation and the demodulation operations.
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 12

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
But, when there are more than one computer at home or in an organization, and you have a single internet connection, you need a Router. Router is a device which is used when multiple devices need to connect to the Internet using the same IP.
6) Gateway:A gateway is a device used to connect networks using different protocols. In order to communicate with a host on another network, an IP host must be configured with a route to the destination network. If a configuration route is not found, the host uses the gateway (default IP router) to transmit the traffic to the destination host. The default t gateway is where the IP sends packets that are destined for remote networks.
As an example we use a telephone network and internet networks, which works on different technologies. The telephone network follows the ISDN, and the Internet follows the IP. Here, 2 different technologies are being used. In this case, the router fails to work, since the router cannot understand the functionalities of both the networks. Hence, we require a Gateway, which acts as a translator in communicating between the 2 networks.
7) Wireless Access Points:A wireless network adapter card with a transceiver sometimes called an access point, broadcasts and receives signals to and from the surrounding computers and passes back and forth between the wireless computers and the cabled network.
Access points act as wireless hubs to link multiple wireless NICs into a single subnet. Access points also have at least one fixed Ethernet port to allow the wireless network to be bridged to a traditional wired Ethernet network.
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 13

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
3.5 Servers introduction: File, Print, Mail, Proxy, Web
A server is a computer program that provides services to other computer programs (and their users) in the same or other computers.
1) Web Server: Specific to the Web, a Web server is the computer program (housed in a computer) that serves requested HTML pages or files. Web servers are computers that deliver (serves up) Web pages. Every Web server has an IP address and possibly a domain name. Any computer can be turned into a Web server by installing server software and connecting the machine to the Internet. There are many Web server software applications, including public domain software and commercial packages.A Web client is the requesting program associated with the user. The Web browser in your computer is a client that requests HTML files from Web servers.Example: For example, if you enter the URL http://www.yahoo.com/index.html in your browser, this sends a request to the Web server whose domain name is yahoo.com. The server then fetches the page named index.html and sends it to your browser.
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 14

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
2) Proxy server:In computer networks, a proxy server is a server (a computer system or an application) that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resource available from a different server and the proxy server evaluates the request as a way to simplify and control its complexity. A proxy server may reside on the user's local computer, or at various points between the user's computer and destination servers on the Internet. Proxy servers have two main purposes 1) to improve performance and 2) to filter requests.
3) Mail Server:A mail server (sometimes also referred to an e-mail server) is a server that handles and delivers e-mail over a network, usually over the Internet. A mail server can receive e-mails from client computers and deliver them to other mail servers. A mail server can also deliver e-mails to client computers. E-mail server is a computer within your network that works as your virtual post office. A mail server usually consists of a storage area where e-mail is stored for local users, a set of user definable rules which determine how the mail server should react to the destination of a specific message.
4) Print Server:A print server, or printer server, is a device that connects printers to client computers over a network. It accepts print jobs from the computers and sends the jobs to the appropriate printers, queuing the jobs locally to accommodate the fact that work may arrive more quickly than the printer can actually handle. Ancillary functions include the ability to inspect the queue of jobs to be processed, the ability to reorder or delete waiting print jobs, or the ability to do various kinds of accounting (such as counting pages, which may involve reading data generated by the printer). A print server may be a networked computer with one or more shared printers.
5) File Server:A file server is a computer responsible for the central storage and management of data files so that other computers on the same network can access the files. A file server allows users to share information over a network without having to physically transfer files by Compact disk or some other external storage device. Any computer can be configured to be a host and act as a file server. In its simplest form, a file server may be an ordinary PC that handles requests for files and sends them over the network.
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 15

SUB NAME & CODE: IDC (3361704) UNIT:3 SEM:6
Questions based on Unit-3
1) Explain the characteristics of Guided and Unguided transmission media. (GTU Summer-2015)
2) What is advantage of Co-axial cable over conventional cable?
3) Explain Fiber Optic cable and its advantages.
4) List out different types of Connectors and explain RJ-45.
5) What is Gateway? Explain briefly.
6) Explain Print server and Mail server in brief.
7) Explain the concept of ARCnet. (GTU Summer-2015)
8) Explain Fiber optic connectors with neat sketch. (GTU Summer-2015).
9) Explain the features of different types of servers. (GTU Summer-2015).
G.P.GANDHINAGARIC DEPT Page 16